Understanding the AI algorithm: How Machines Learn

In the era of digital revolution, AI algorithms have advanced leaps and bounds reshaping industries and transforming our daily lives. To understand how these technologies operate, it’s essential to unveil the inner workings of machine learning algorithms, exploring the underlying concepts and approaches responsible for their impressive abilities.

Key Concepts:
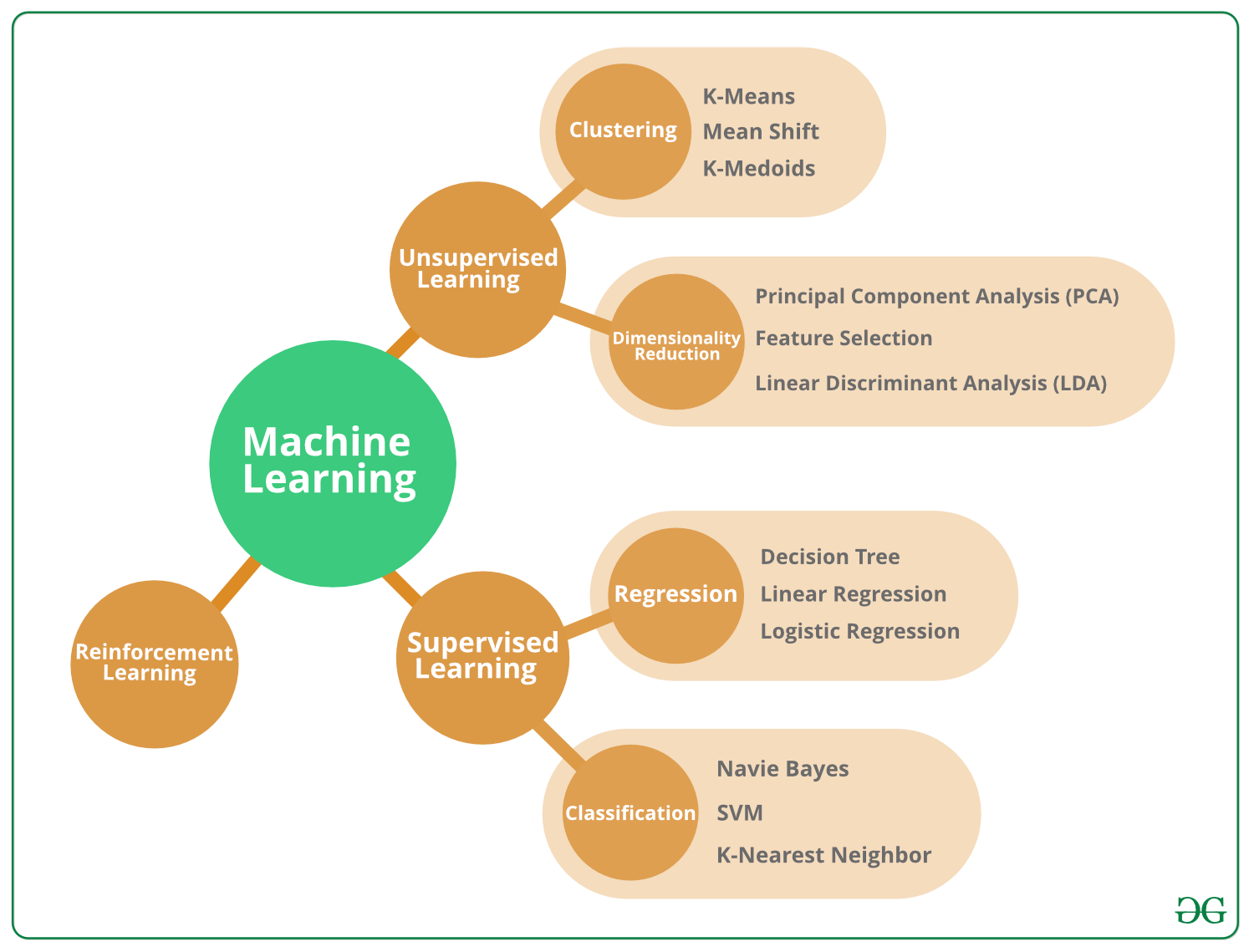
- Algorithms: AI algorithms are a set of instructions or rules that enable computers to perform specific tasks.
- Data: These algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to uncover patterns, trends, and decision-making knowledge.
- Parameters: Algorithms are characterized by adjustable parameters, comparable to adjustable settings on a radio that tailors functionality based on specific requirements.
- Learning: As algorithms analyze more data, they improve their accuracy and proficiency, a process known as machine learning.
Approaches:
1. Feature Engineering:
- Identifying Relevant Features: Feature engineering is a crucial preliminary step of any machine learning project.
- Data Points: Features represent distinct data attributes valuable for analysis, such as age, gender, and previous purchases.
- Transforming Raw Data: Features are derived from raw data by applying transformations, feature selection, and feature extraction methodologies.
2. Data Preparation:
- Formatting Datasets: Input data is cleansed, sorted, and formatted making it compatible with the algorithms.
- Cleaning and Transforming: Data undergoes processing through various tools and techniques resulting in homogeneous and consistent dataset structure.
3. Hyperparameter Optimization:
- Optimization: Hyperparameters are high-level controls of an algorithm, akin to engine settings in a car.
- Algorithms Efficacy: Optimizing hyperparameters enhances the algorithms overall performance and efficiency.
4. Training the Model:
- Learning Patterns: The model learns patterns, correlations, and relationships between different features within the training data using various algorithms, such as linear regression, support vector machines, and decision trees.
- Iterations: Algorithms progressively refine their ability to detect patterns with each training cycle.
5. Evaluating and Selecting the Models:
- Validation: Models are validated with a different unseen dataset called the test set.
- Selection: The optimal model is selected based on pre-determined evaluation criteria, such as accuracy or precision.
In Essence:
These AI algorithms, empowered by vast data sets, continuous learning, and computational power, are unlocking new realms of possibilities, revolutionizing diverse fields such as healthcare, finance, and transportation. Their ability to analyze vast troves of data and discern intricate patterns has propelled advancements once deemed unimaginable. While understanding the AI algorithm is essential, their boundless potential leaves us pondering the consequences of entrusting these technologies with evermore significant responsibilities.

The post was amazing
Very beautiful
I hate this
I don’t understand
This is incorrect. Machines use magic
What a great invention
Wow
Ha ha