Ubuntu LTS vs. CentOS Stream: The Battle For Long-term Stability
Executive Summary

CentOS Stream and Ubuntu Long-Term Support (LTS) are both popular Linux distributions that offer long-term stability and support. However, there are some key differences between the two distributions that make them better suited for different use cases. In this article, we will compare and contrast Ubuntu LTS and CentOS Stream, focusing on their release cycles, software repositories, support options, and use cases. By the end of this article, readers will have a clear understanding of the strengths and weaknesses of each distribution and will be able to make an informed decision about which one is right for them.
Introduction
When choosing a Linux distribution for a long-term project, stability and support are two of the most important factors to consider. Ubuntu LTS and CentOS Stream are both known for their long-term stability and support, but there are some key differences between the two distributions that make them better suited for different use cases. In this article, we will explore the differences between Ubuntu LTS and CentOS Stream, helping you to choose the right distribution for your next project.
Release Cycles
Ubuntu LTS
- Regular Release Cycle: Ubuntu LTS releases a new version every two years, with each version being supported for five years.
- Long-Term Support: Ubuntu LTS provides long-term support for its releases, meaning that security patches and bug fixes are available for the entire five-year support period.
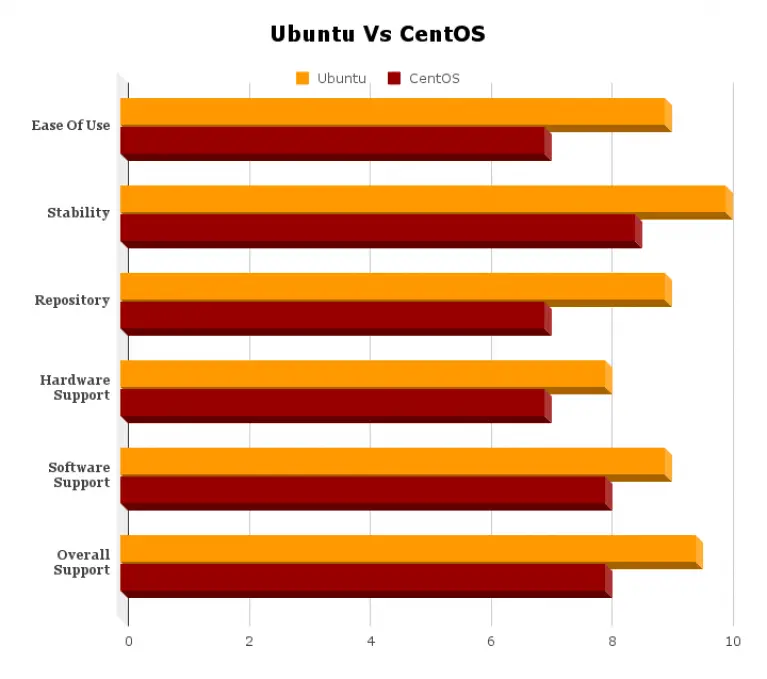
- Stability: Ubuntu LTS is known for its stability, making it a good choice for production environments.
CentOS Stream
- Rolling Release: CentOS Stream follows a rolling release model, meaning that new versions are released on a continuous basis.
- Continuous Updates: CentOS Stream provides continuous updates, which means that users always have access to the latest software and security patches.
- Stability: CentOS Stream is generally considered to be less stable than Ubuntu LTS, as it is more prone to breaking changes.
Software Repositories
Ubuntu LTS
- Official Repositories: Ubuntu LTS has a large selection of official repositories, which contain a wide range of software packages.
- Third-Party Repositories: Ubuntu LTS also has a large number of third-party repositories, which provide access to even more software packages.
- Package Management: Ubuntu LTS uses the APT package manager, which is a powerful and easy-to-use tool for installing, updating, and removing software packages.
CentOS Stream
- Official Repositories: CentOS Stream has a smaller selection of official repositories than Ubuntu LTS.
- Third-Party Repositories: CentOS Stream also has a smaller number of third-party repositories than Ubuntu LTS.
- Package Management: CentOS Stream uses the YUM package manager, which is similar to APT but has some different features.
Support Options
Ubuntu LTS
- Commercial Support: Ubuntu LTS offers commercial support from Canonical, the company behind Ubuntu.
- Community Support: Ubuntu LTS also has a large community of users and contributors who provide support on forums and mailing lists.
- Documentation: Ubuntu LTS has extensive documentation available online, which can be helpful for users who need assistance with installation, configuration, or troubleshooting.
CentOS Stream
- Community Support: CentOS Stream is supported by a community of users and contributors who provide support on forums and mailing lists.
- Documentation: CentOS Stream has some documentation available online, but it is not as extensive as the documentation available for Ubuntu LTS.
Use Cases
Ubuntu LTS
- Production Environments: Ubuntu LTS is a good choice for production environments where stability is critical.
- Long-Term Projects: Ubuntu LTS is also a good choice for long-term projects, as it provides five years of support.
- Desktop Use: Ubuntu LTS is a popular choice for desktop use, as it is easy to use and has a wide range of software available.
CentOS Stream
- Development and Testing: CentOS Stream is a good choice for development and testing, as it provides access to the latest software and security patches.
- Short-Term Projects: CentOS Stream is also a good choice for short-term projects, as it does not require a long-term commitment.
- Servers: CentOS Stream is a popular choice for servers, as it is stable and secure.
Conclusion
In this article, we have explored the differences between Ubuntu LTS and CentOS Stream, two popular Linux distributions that offer long-term stability and support. We have examined their release cycles, software repositories, support options, and use cases. By now, readers should have a clear understanding of the strengths and weaknesses of each distribution and should be able to make an informed decision about which one is right for them.
Keyword Phrase Tags
- ubuntu lts vs centos stream
- centos stream vs ubuntu lts
- ubuntu lts vs centos stream stability
- ubuntu lts vs centos stream software repositories
- ubuntu lts vs centos stream use cases

Very nice and applicable to my daily work. Great article.
It’s very bad and not well written
This explains that very clearly, especially compared to other blogs.
There is no need for the comparison between these two packages
Yes, I agree with that, that is exactly what I think
Very persuasive, I’ll follow your tips
What about the new version of Centos, not the stream? What is the difference between the different versions?
There could be a small dictionary of the acronyms used
Great, thanks for sharing this, keep going!
You should edit this, the repository was renamed but is still linked with the old name