Role of CDN in Streaming Media
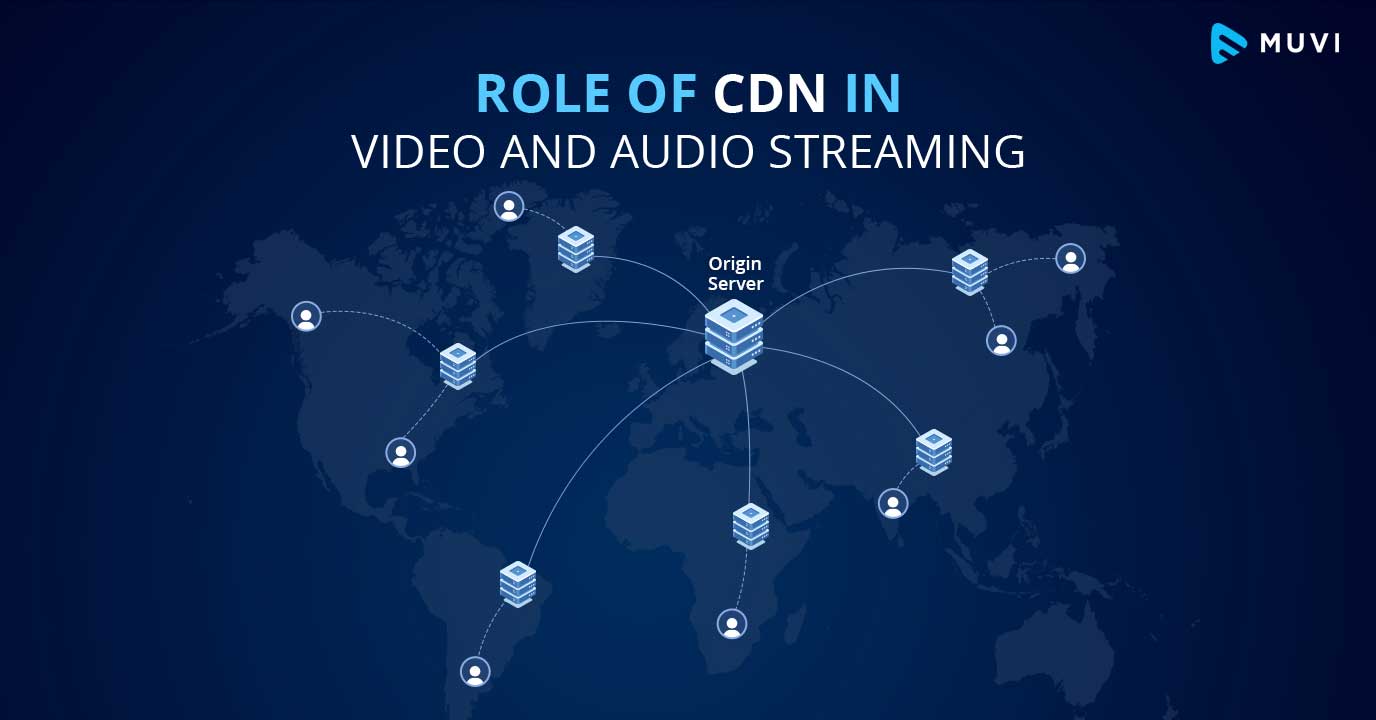
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) plays a vital role in streaming media by:

- Distributing content closer to users: CDNs have multiple edge servers located globally, reducing latency and improving content delivery speed.
- Caching popular content: CDNs cache frequently requested content on their edge servers, further reducing latency and improving performance.
- Load balancing: CDNs distribute traffic across multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed.
- Security: CDNs provide security features such as DDoS protection and DRM (Digital Rights Management) to protect content from unauthorized access.
Challenges

- High bandwidth requirements: Streaming media can consume significant bandwidth, making it challenging for CDNs to deliver content efficiently.
- Dynamic content: Streaming media is often dynamic and changes frequently, requiring CDNs to update their caches regularly.
- Geoblocking and licensing restrictions: CDNs must adhere to geographical restrictions and licensing agreements, which can limit the availability of content in certain regions.
- Contention and congestion: During peak traffic periods, CDNs can experience congestion and contention, leading to performance degradation.
Solutions
1. Adaptive Bitrate Streaming:
- CDNs use adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR) to deliver content at different resolutions and bitrates.
- This allows CDNs to optimize bandwidth usage and provide smooth playback experience even on low-bandwidth connections.
2. Caching Strategies:
- CDNs employ various caching strategies, such as tiered caching and dynamic caching, to improve content delivery speed and reduce latency.
- They also use pre-caching and proactive caching techniques to anticipate user demand and cache content before it is requested.
3. Network Optimization:
- CDNs leverage network optimization techniques such as route optimization, traffic shaping, and peering to improve network performance and reduce congestion.
- They also use intelligent routing algorithms to determine the optimal path for content delivery.
4. Security Enhancements:
- CDNs implement advanced security measures, such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, and intrusion detection systems, to protect content from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- They also comply with industry standards and best practices to ensure data privacy and security.
5. Cloud-Based Solutions:
- Cloud-based CDNs provide scalable and cost-effective solutions for streaming media delivery.
- They leverage the elastic infrastructure of cloud providers to handle dynamic traffic patterns and ensure consistent performance.
Conclusion
CDNs are essential for efficient and reliable streaming media delivery. By leveraging adaptive bitrate streaming, caching strategies, network optimization, security enhancements, and cloud-based solutions, CDNs overcome challenges and provide optimal content delivery experiences for users.## The Role Of CDN In Streaming Media: Challenges And Solutions
Executive Summary
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) play a crucial role in the efficient delivery of streaming media, ensuring seamless playback and minimizing interruptions for end-users. However, CDNs face unique challenges in handling the high bandwidth and low latency requirements of streaming media. This article explores the key challenges associated with CDN usage in streaming media, identifies potential solutions, and highlights the benefits of utilizing CDNs for optimal media delivery. By leveraging the capabilities of CDNs, organizations can overcome streaming bottlenecks, enhance user experience, and drive business growth.
Introduction
The rise of streaming media has revolutionized content consumption, providing users with on-demand access to videos, music, and live events. However, delivering high-quality streaming media requires a robust and efficient infrastructure to handle the massive data transfer and ensure seamless playback. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) have emerged as a vital component of the streaming media landscape, providing the necessary infrastructure and capabilities to deliver content effectively to end-users. However, CDNs face unique challenges in managing the high bandwidth and low latency demands of streaming media. This article delves into these challenges, explores potential solutions, and outlines the benefits of utilizing CDNs for optimal streaming media delivery.
FAQs
1. What is the role of a CDN in streaming media?
A CDN plays a critical role in streaming media delivery by distributing content across a network of geographically dispersed servers, known as edge servers. This decentralized approach reduces the distance between content and end-users, resulting in faster delivery speeds, improved buffering times, and enhanced video quality.
2. What are the key challenges faced by CDNs in streaming media?
CDNs face several challenges in streaming media, including:
- High bandwidth requirements: Streaming media requires high bandwidth to deliver high-quality video and audio streams. CDNs must ensure sufficient bandwidth capacity to handle the data-intensive nature of streaming media.
- Low latency requirements: Latency, or the delay between the moment a user requests content and the moment it starts playing, is critical in streaming media. CDNs must have low-latency networks to minimize buffering and ensure a smooth playback experience.
- Geographical dispersion of users: Streaming media users are spread across vast geographical regions. CDNs require a globally distributed network to ensure that content is delivered efficiently to users in different locations.
3. What are the benefits of using a CDN for streaming media?
CDNs provide numerous benefits for streaming media delivery, including:
- Improved content delivery speeds: By caching content on edge servers closer to end-users, CDNs reduce latency and improve delivery speeds, resulting in faster buffering and smoother playback.
- Enhanced video quality: CDNs utilize advanced caching and optimization techniques to enhance video quality and reduce rebuffering, ensuring a high-quality viewing experience for users.
- Reduced infrastructure costs: Using a CDN eliminates the need for organizations to invest in and maintain their own content delivery infrastructure, reducing operational costs and freeing up resources for core business activities.
Subtopics
1. Content Caching
Content caching is a fundamental aspect of CDN operation, enabling the storage of frequently requested content on edge servers closer to end-users. This reduces the distance that data must travel, resulting in faster delivery speeds and lower latency. Key considerations for content caching include:
- Caching algorithms: CDNs employ various algorithms to determine which content to cache and for how long, based on factors such as content popularity, user location, and network conditions.
- Cache capacity: The amount of storage space available on edge servers for caching content is critical to ensure efficient delivery.
- Cache coherency: CDNs must ensure that cached content remains consistent with the original source, even when the source content changes.
2. Network Optimization
Network optimization techniques are essential for reducing latency and improving the overall performance of CDN networks. Key network optimization strategies include:
- Traffic routing: CDNs utilize intelligent traffic routing algorithms to direct user requests to the most optimal edge servers based on factors such as network congestion, server load, and user location.
- Load balancing: CDNs distribute traffic load evenly across multiple edge servers to prevent overloading and ensure consistent performance.
- Congestion control: CDNs implement congestion control mechanisms to prevent network congestion and maintain optimal data transfer rates.
3. Security and Reliability
Security and reliability are paramount for CDNs, as they handle large volumes of sensitive user data and must ensure uninterrupted content delivery. Key security and reliability considerations include:
- Data encryption: CDNs employ encryption techniques to protect user data during transmission and storage, safeguarding it from unauthorized access.
- Redundancy and failover: CDNs establish redundant network connections and backup servers to ensure high availability and prevent service disruptions in the event of outages.
- DDoS protection: CDNs implement DDoS mitigation strategies to protect their networks from distributed denial-of-service attacks, ensuring uninterrupted service during malicious traffic surges.
4. Analytics and Reporting
Analytics and reporting capabilities are crucial for CDNs to monitor their performance, identify areas for improvement, and adapt to changing user demands. Key analytics and reporting features include:
- Performance monitoring: CDNs provide real-time monitoring of network performance metrics such as latency, throughput, and packet loss, enabling proactive identification and resolution of issues.
- Usage reporting: CDNs offer detailed reports on content usage patterns, including information on popular content, user demographics, and geographic distribution.
- Customer insights: CDNs provide insights into user behavior and preferences, helping organizations tailor their streaming strategies and optimize content delivery for specific audiences.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability and flexibility are essential for CDNs to handle fluctuating traffic demands and support growing user bases. Key scalability and flexibility considerations include:
- Automatic scaling: CDNs automatically adjust their capacity based on traffic demand, ensuring optimal performance during peak usage periods without compromising user experience.
- Geographic expansion: CDNs can expand their network reach to new regions or locations to meet growing demand and improve content delivery for users in underserved areas.
- API integration: CDNs provide APIs that allow organizations to integrate their streaming solutions with other systems and applications, enabling customization and automation.
Conclusion
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) play a vital role in the seamless delivery of streaming media, providing high bandwidth, low latency, and geographically distributed content distribution. However, CDNs face unique challenges in managing the demanding requirements of streaming media. By implementing effective content caching strategies, optimizing network performance, ensuring security and reliability, leveraging analytics and reporting capabilities, and embracing scalability and flexibility, organizations can harness the power of CDNs to overcome these challenges and deliver high-quality streaming media experiences to their users. Utilizing CDNs enables organizations to expand their reach, enhance user engagement, and drive business growth in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Keyword Tags
- CDN for streaming media
- Challenges in CDN streaming
- Solutions for CDN streaming
- Benefits of CDN streaming
- Subtopics in CDN streaming
