[The Innovators: How New Cryptocurrencies Are Shaping The Future Of Blockchain]
Executive Summary

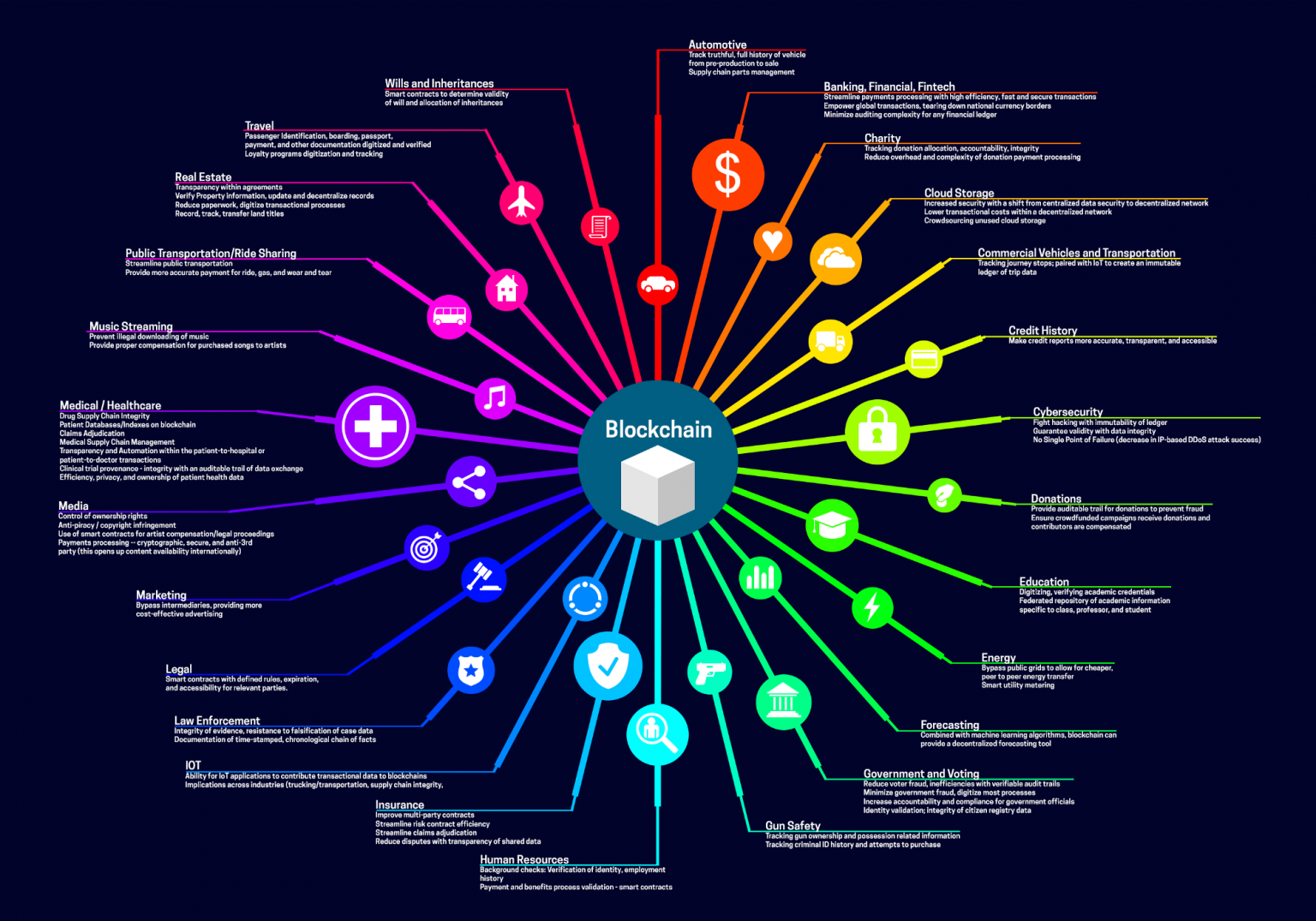
New cryptocurrencies are emerging, offering innovative solutions and advancements that are reshaping the blockchain landscape. These novel digital assets are pushing the boundaries of technology, offering unique features, and introducing new concepts that are poised to revolutionize the future of blockchain and its diverse applications.

Introduction
Cryptocurrencies have captured worldwide attention, particularly with the meteoric rise of Bitcoin. However, beyond the realm of Bitcoin lies a vast landscape of diverse cryptocurrencies, each boasting distinct characteristics and purpose. These novel digital assets are introducing revolutionary concepts and innovative solutions that are influencing the future of blockchain technology.
FAQs
- What are the key attributes of new cryptocurrencies?
- How do these cryptocurrencies contribute to the evolution of blockchain?
- What industries are most impacted by these advancements?
Advances in Consensus Mechanisms
The consensus mechanism is a fundamental aspect of blockchain technology, ensuring the integrity and security of the network. Emerging cryptocurrencies are introducing novel consensus algorithms that enhance efficiency, scalability, and resilience.
- Proof-of-Stake (PoS): Requires validators to stake their cryptocurrency holdings to verify transactions.
- Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS): Elects a limited number of delegates who are responsible for transaction validation.
- Proof-of-Elapsed-Time (PoET): Uses trusted execution environments to measure elapsed time, ensuring公平ness in block creation.
- Proof-of-Importance (PoI): Weights voting power based on factors such as account balance and transaction history.
- Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG): Replaces blockchain with a directed graph structure, enabling parallel transaction processing.
Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Smart contracts are programmable code stored on the blockchain, enabling the execution of complex agreements autonomously. New cryptocurrencies are pioneering advanced smart contract capabilities and facilitating the development of sophisticated dApps.
- Support for Multiple Programming Languages: Allows developers to create smart contracts using various programming languages, increasing flexibility and customization.
- Cross-Chain Interoperability: Enables smart contracts to interact with multiple blockchains, fostering interoperability and data sharing.
- Improved Security and Privacy: Incorporates advanced cryptographic algorithms and privacy-enhancing techniques to safeguard smart contract execution.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): Allows for the creation of self-governing organizations managed by smart contracts, reducing the need for intermediaries.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Empowers users to access financial services, such as lending, borrowing, and trading, without the involvement of traditional intermediaries.
Scalability and Performance
Scalability challenges have plagued blockchain networks, limiting their adoption. New cryptocurrencies are tackling these issues through innovative approaches to enhance transaction throughput and reduce latency.
- Sharding: Divides the blockchain network into smaller partitions called “shards,” enabling parallel processing of transactions.
- Layer-2 Solutions: Operates on top of existing blockchains, providing scalability improvements without modifying the base layer.
- Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs): Employs a graph structure instead of a blockchain, eliminating the need for block confirmation, resulting in faster transaction speeds.
- Compression and Optimization: Utilizes advanced techniques to compress data and optimize network protocols, reducing bandwidth requirements.
- Off-Chain Transactions: Moves transactions off the main blockchain onto separate channels or platforms, freeing up network resources for critical operations.
Security and Privacy
Security and privacy are paramount in the realm of digital assets. New cryptocurrencies are incorporating robust security measures and privacy-enhancing features to safeguard user funds and protect sensitive information.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Requires multiple forms of verification before authorizing transactions, enhancing account security.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Allows users to prove their identity or ownership without revealing any sensitive information, preserving privacy.
- Encrypted Transactions: Utilizes cryptography to protect the confidentiality and integrity of transaction data.
- Privacy Coins: Focuses on anonymity and untraceability of transactions, offering enhanced privacy for users.
- Hardware Security Modules (HSMs): Physical devices that store cryptographic keys and perform secure cryptographic operations, providing a tamper-proof layer of security.
Interoperability and Cross-Chain Solutions
Interoperability between different cryptocurrencies has been a challenge, but new projects are emerging to bridge these gaps and facilitate seamless communication across diverse blockchain networks.
- Cross-Chain Atomic Swaps: Enables direct peer-to-peer exchange of different cryptocurrencies without the need for intermediaries.
- Blockchain Bridges: Connects disparate blockchains, allowing for the transfer of assets, data, and smart contract execution across different networks.
- Interoperability Protocols: Define common standards and protocols that facilitate communication and interaction between different blockchain platforms.
- Sidechains: Separate blockchains that are linked to the main blockchain, providing a trusted environment for experimenting with new features and expanding functionality.
- Multi-Chain DApps: Applications that operate across multiple blockchain networks, leveraging the unique strengths of each platform to offer comprehensive solutions.
Conclusion
New cryptocurrencies are revolutionizing the blockchain landscape with their cutting-edge innovations. These digital assets are shaping the future of blockchain by introducing novel consensus mechanisms, advancing smart contracts and dApps, addressing scalability and performance challenges, enhancing security and privacy, and promoting interoperability across diverse blockchain platforms. As the cryptocurrency realm continues to evolve, these innovative projects will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in driving the future of blockchain technology and its wide-ranging applications.
Keyword Tags
- New Cryptocurrencies
- Blockchain Innovations
- Consensus Mechanisms
- Smart Contracts
- Cross-Chain Interoperability
