Impact of Next-Generation Networks on CDN Strategies
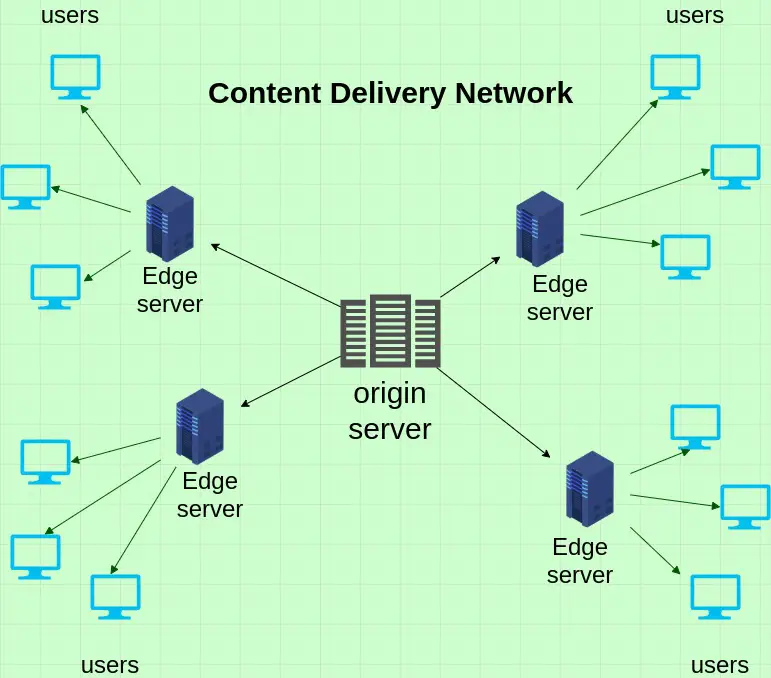
Key Points:

- Next-generation networks with faster speeds and lower latency enable new CDN use cases and optimize existing ones.
- Enhanced capabilities of 5G, fiber broadband, and edge computing impact CDN infrastructure, capacity, and delivery efficiency.
- CDNs can leverage these networks to reduce latency, improve content availability, and enhance personalized experiences.
Infrastructure and Capacity Enhancements:

- 5G and fiber broadband: Offer significantly higher bandwidth and lower latency, enabling CDNs to deliver large volumes of high-quality content simultaneously.
- Edge computing: Brings computing capabilities closer to end users, reducing content retrieval time and offloading traffic from centralized CDN nodes.
Improved Content Availability and Latency:
- Reduced latency: Next-generation networks minimize latency, making real-time streaming, gaming, and interactive applications more accessible.
- Global reach: CDNs can expand their reach by utilizing 5G networks with extended coverage and capacity to penetrate underserved areas.
Personalized and Contextualized Experiences:
- Device awareness: CDNs can detect user devices and adapt content delivery based on factors such as screen size, connection speed, and location.
- Content optimization: Edge computing enables CDNs to perform content optimization in real-time, adjusting formats and transcoding videos to match users’ preferences.
CDN Strategy Considerations:
- Infrastructure investments: CDNs need to upgrade their infrastructure to leverage next-generation networks effectively.
- Partnerships: Collaboration with telecom providers and cloud partners is crucial to access and optimize network capabilities.
- Content caching: CDNs can optimize content caching strategies based on predicted user demand and network conditions.
- Security and privacy: Enhanced network speeds require robust security measures and data protection.
Specific Use Cases:
- Immersive gaming: Next-generation networks support low-latency multiplayer gaming and virtual reality experiences requiring large bandwidth.
- Live streaming: Improved availability and low latency enable seamless live video streaming with high-quality resolution.
- Augmented and virtual reality: Next-generation networks provide the necessary infrastructure for delivering immersive AR/VR experiences with reduced latency.
- Enterprise applications: Cloud-based enterprise applications can benefit from reduced latency and increased bandwidth, improving productivity and collaboration.
Conclusion:
Next-generation networks are a game-changer for CDN strategies. CDNs can leverage these capabilities to reduce latency, improve content availability, and enhance personalized experiences. By adapting to the evolving network landscape, CDNs can optimize their infrastructure, capacity, and content delivery strategies to meet the evolving demands of users and applications in the future.# The Impact of Next-generation Networks on CDN Strategies
Executive Summary
The rollout of next-generation networks (NGNs) such as 5G and fiber optics is transforming the way Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) operate. These networks offer significantly higher bandwidth, lower latency, and increased reliability, enabling CDNs to deliver content more efficiently and effectively. As a result, CDNs are adapting their strategies to take advantage of NGNs, improving content delivery performance and user experience.
Introduction
CDNs have traditionally relied on a combination of fixed and mobile networks to deliver content to end users. However, the limitations of these networks, such as limited bandwidth and high latency, have constrained CDN performance. NGNs address these limitations, providing CDNs with the necessary infrastructure to deliver content at unprecedented speeds and quality.
FAQs
Q: What are the key benefits of NGNs for CDNs?
- Increased bandwidth: NGNs provide significantly higher bandwidth, enabling CDNs to deliver more content at faster speeds.
- Lower latency: Reduced latency allows CDNs to deliver content with less delay, improving user experience.
- Improved reliability: NGNs offer increased reliability, minimizing content delivery failures and ensuring consistent performance.
Q: How are CDNs adapting their strategies to take advantage of NGNs?
- Edge Computing: CDNs are deploying edge computing capabilities to bring content closer to end users, reducing latency and improving performance.
- Network Optimization: CDNs are optimizing their networks to take advantage of NGN features, such as network slicing and traffic steering.
- Content Caching: CDNs are enhancing their content caching strategies to take advantage of NGNs’ increased bandwidth and reliability.
Q: What are the expected impacts of NGNs on the future of CDN delivery?
- Enhanced User Experience: NGNs will enable CDNs to deliver content with improved quality and reduced buffering, leading to a better user experience.
- New Applications: NGNs will facilitate the development and deployment of new content-heavy applications, such as virtual reality and augmented reality.
- Increased Competition: The availability of NGNs will increase competition among CDNs, driving innovation and improved services.
Key Subtopics
Edge Computing
Edge computing involves deploying computing resources closer to end users, reducing latency and improving content delivery performance.
- Benefits: Reduced latency, improved content caching, enhanced user experience.
- Considerations: Deployment costs, security concerns, resource management.
Network Optimization
Network optimization involves adjusting network parameters and configurations to improve CDN performance and efficiency.
- Benefits: Increased bandwidth utilization, reduced latency, improved reliability.
- Considerations: Network complexity, configuration expertise, traffic analysis.
Content Caching
Content caching involves storing content closer to end users, enabling faster content delivery and reducing latency.
- Benefits: Reduced bandwidth consumption, improved content availability, enhanced user experience.
- Considerations: Cache size, content freshness, cache allocation.
Virtualization and Containerization
Virtualization and containerization technologies enable CDNs to deploy and manage multiple content delivery services on a single physical infrastructure.
- Benefits: Resource optimization, increased flexibility, improved scalability.
- Considerations: Performance overhead, security risks, management complexity.
Analytics and Monitoring
Analytics and monitoring tools provide insights into CDN performance, allowing CDNs to optimize their strategies and ensure consistent delivery.
- Benefits: Performance monitoring, traffic analysis, user experience analytics.
- Considerations: Data collection methods, analysis techniques, security concerns.
Conclusion
The rollout of NGNs is a significant development that will have a profound impact on CDN strategies. By leveraging the capabilities of these networks, CDNs can improve content delivery performance, enhance user experience, and enable new content-heavy applications. As NGNs become more widely adopted, CDNs will continue to adapt their strategies and invest in technologies that optimize content delivery over these networks.
Keyword Tags
- Next-Generation Networks
- Content Delivery Networks
- Edge Computing
- Network Optimization
- CDN Strategies

