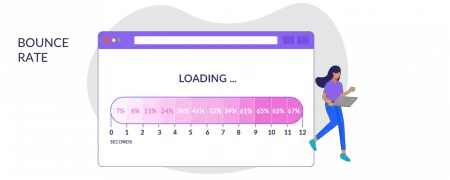
Impact of CDN on Load Times
A content delivery network (CDN) is a geographically distributed network of servers that stores cached content to improve the speed and efficiency of content delivery to end-users. By distributing content closer to the user, a CDN can significantly reduce load times:
- Increased Latency: CDNs reduce latency by caching content at edge servers in close proximity to users. This means that users can access content from the closest server, reducing the time it takes for content to load.
- Reduced Data Transfer: CDNs optimize data transfer by caching popular content and delivering it from the nearest server. This reduces the distance data has to travel, further improving load times.
- Multi-Pathing: CDNs often use multi-pathing techniques to distribute traffic across multiple paths, ensuring that content is delivered even in case of network congestion or outages.
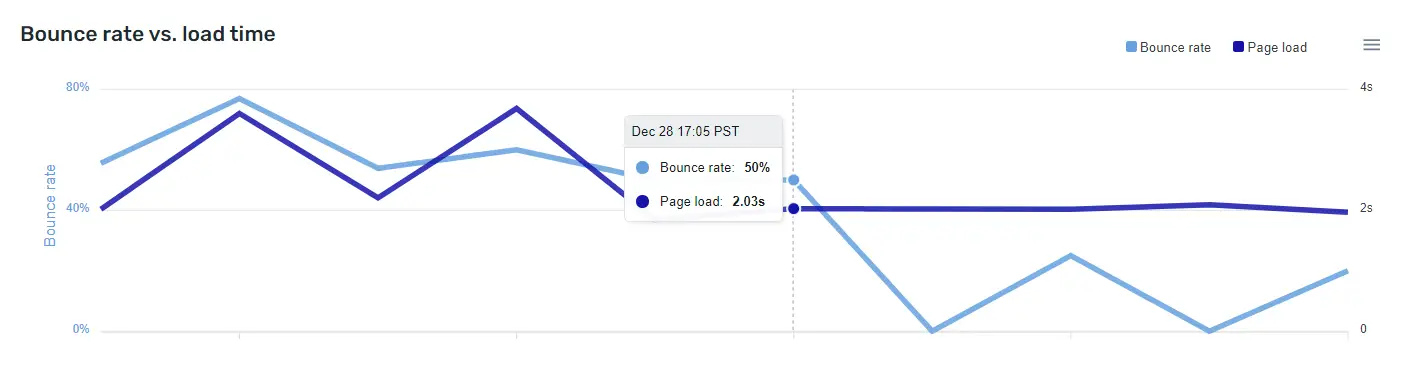
Impact of CDN on Bounce Rates
Load times have a direct impact on bounce rates:
- Reduced Bounce Rates: Faster load times lead to reduced bounce rates as users are less likely to abandon a website that loads quickly. Users who experience slow load times are more likely to become frustrated and leave the site.
- Improved Engagement: Faster load times improve user engagement as users are more likely to interact with content that loads quickly. This leads to increased time on site and lower bounce rates.
- Better User Experience: A CDN improves overall user experience by making websites load faster and more reliably. This results in higher user satisfaction and reduced bounce rates.
Additional Benefits of CDN
- Increased Website Capacity: CDNs can handle large amounts of traffic, ensuring that your website remains accessible during peak traffic periods.
- Enhanced Security: CDNs can provide additional security measures to protect your website from DDoS attacks and other threats.
- Cost Savings: CDNs can reduce bandwidth costs by caching popular content and reducing the load on your web server.
Conclusion
Implementing a CDN is essential for optimizing website performance and reducing bounce rates. By distributing content closer to users, CDNs significantly decrease load times and improve user engagement. As a result, websites with CDN experience lower bounce rates and higher user satisfaction.## The Impact of CDN on Load Times and Bounce Rates
Executive Summary
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) have become an essential part of the modern web, providing significant benefits in terms of website performance, user experience, and search engine ranking. This comprehensive guide explores the impact of CDN on load times and bounce rates, highlighting key factors and best practices.
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, website speed has become paramount. Users expect websites to load quickly and seamlessly, and any delay can result in frustration and abandonment. CDNs play a crucial role in optimizing website performance by delivering content from strategically located servers closer to end users, resulting in improved load times and reduced bounce rates.
FAQs
Q: What is a CDN?
A: A CDN is a network of geographically distributed servers that cache and deliver web content, such as images, videos, and scripts, to users.
Q: How does a CDN improve load times?
A: By caching content closer to end users, CDNs reduce the distance that data has to travel, resulting in faster content delivery and improved load times.
Q: Does CDN affect bounce rates?
A: Yes, CDNs can significantly impact bounce rates. Faster load times lead to a better user experience, reducing the likelihood of users bouncing from a website.
Subtopics
1. Reduced Latency
- Caching: CDNs store copies of frequently accessed content on servers closer to end users, eliminating the need for users to download it from the origin server.
- Reduced Distance: By delivering content from nearby servers, CDNs reduce the physical distance that data has to travel, resulting in lower latency and faster load times.
- Parallel Downloads: CDNs often allow for parallel downloads of content, which means multiple files can be downloaded simultaneously, further reducing load times.
2. Improved Cache Utilization
- Content Caching: CDNs cache static content, such as images, videos, and scripts, reducing the load on the origin server and providing faster access to users.
- Cache Control Headers: CDNs utilize cache control headers to determine how and when content should be cached, ensuring optimal performance.
- Personalized Caching: CDNs can implement personalization strategies to cache content based on user location or device type, delivering the most relevant content faster.
3. Load Balancing and Redundancy
- Distribution: CDNs distribute content across multiple servers, ensuring that requests are processed quickly and efficiently.
- Failover and High Availability: CDNs provide redundancy by replicating content on multiple servers, minimizing the impact of server failures or network issues.
- Optimized Routing: CDNs use intelligent routing algorithms to determine the best server to deliver content to end users, based on factors such as server load and user location.
4. Improved Security
- DDoS Mitigation: CDNs can mitigate Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks by filtering out malicious traffic and distributing content from multiple servers.
- SSL Offloading: CDNs can offload SSL encryption and decryption from the origin server, reducing server load and improving performance.
- Content Filtering: CDNs can implement content filtering mechanisms to prevent malware or malicious content from reaching end users.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
- Elastic Scaling: CDNs can automatically scale up or down based on traffic demand, ensuring optimal performance during peak loads.
- Flexible Deployment: CDNs offer various deployment options, including public, private, and hybrid, to meet specific website and business needs.
- Integration with Cloud Platforms: CDNs easily integrate with cloud platforms such as AWS and Azure, providing seamless content delivery and management.
Conclusion
CDNs have a significant impact on website performance, user experience, and search engine ranking. By reducing load times, improving cache utilization, providing load balancing and redundancy, enhancing security, and offering scalability and flexibility, CDNs enable websites to deliver content faster, engage users more effectively, and achieve better search engine visibility. Embracing CDNs is crucial for any modern website aiming to optimize its performance and ensure success in the competitive digital landscape.
Keyword Tags
- Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Website Performance
- Load Times
- Bounce Rates
- User Experience
