Evolution of CDN Technologies for Dynamic Content

Early CDN Technologies

- Content-centric CDNs: Focused on delivering static content like images, videos, and documents.
- Origin offloading: Reduced load on origin servers by caching content at edge locations.
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) distribution: Leveraged user devices to distribute content, improving availability.
Second-Generation CDNs
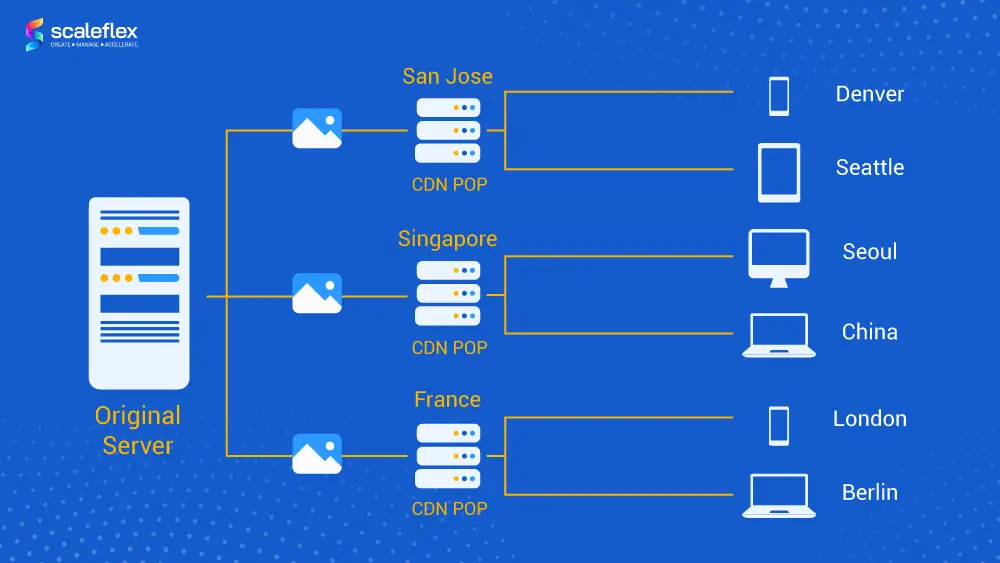
- Dynamic content support: Introduced support for real-time content, such as live streaming and personalized content.
- Adaptive bitrate streaming: Optimized content delivery based on device characteristics and network conditions.
- Content caching enhancements: Employed techniques like content hash tagging and universal hash tables for efficient caching.
Third-Generation CDNs
- Edge computing capabilities: Integrated edge compute nodes to process content near users, reducing latency.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML): Used to optimize content delivery, personalize user experiences, and identify malicious traffic.
- Network virtualization: Enabled flexible and scalable CDN architectures using software-defined networking (SDN).
Fourth-Generation CDNs
- Edge-as-a-Platform (EaaS): Provides a platform for developers to build and deploy applications at the edge, reducing time-to-market.
- Cloud-native CDNs: Built on cloud platforms, offering elasticity, scalability, and cost efficiency.
- Security enhancements: Implemented zero-trust models, intrusion detection systems, and threat intelligence to protect content and user data.
Emerging Trends
- 5G and Beyond: Utilizing faster networks to support higher-quality and more responsive dynamic content.
- Web3 and Metaverse: Enabling efficient delivery of immersive and interactive content for virtual worlds.
- Cognitive caching: Leveraging AI to predict user demand and pre-cache content for optimal performance.
- Edge Analytics: Analyzing data collected at the edge for real-time insights and content delivery optimization.
Benefits of CDN Technologies for Dynamic Content
- Reduced latency: Content is served from nearby edge locations, minimizing delays and improving user experience.
- Increased availability: Replicated content ensures high availability even in the event of localized outages.
- Personalized delivery: Dynamic content can be tailored to individual users based on preferences, location, and device.
- Improved security: CDNs implement security measures to protect content and user data from unauthorized access.
- Cost optimization: Shared infrastructure and efficient caching techniques reduce bandwidth costs and improve ROI.## [The Evolution Of CDN Technologies In Supporting Dynamic Content]
Executive Summary
The proliferation of dynamic content on the web has posed significant challenges for content delivery networks (CDNs). Traditional CDN architectures, designed for static content, struggle to efficiently deliver dynamic content, which is often personalized, interactive, and user-generated. This has led to the evolution of CDN technologies to cater to the unique requirements of dynamic content delivery. This article explores the advancements in CDN technologies, examining their capabilities and how they support the delivery of dynamic content.
Introduction
The rise of web applications, social media, and user-generated content has transformed the web into a vibrant and interactive ecosystem. This shift has brought about a surge in dynamic content, which poses unique challenges for CDN providers. Dynamic content is highly personalized, requiring real-time adaptation to user preferences and behavior. It is also often interactive, allowing users to engage with the content in various ways. To effectively deliver dynamic content, CDNs have evolved their technologies, embracing modern architectures and techniques tailored to the specific demands of this content type.
FAQ
1. What are the key challenges for CDNs in delivering dynamic content?
Dynamic content is characterized by its personalized, interactive, and user-generated nature. These attributes pose challenges for CDNs, including the need for real-time adaptation, support for interactive features, and handling of user-generated content with varying quality and formats.
2. How have CDN technologies evolved to meet these challenges?
CDNs have adopted various technological advancements to address the challenges of dynamic content delivery. These include intelligent caching mechanisms, edge computing capabilities, and the use of specialized content delivery protocols.
3. What are the benefits of using CDNs for dynamic content delivery?
Leveraging CDNs for dynamic content delivery offers numerous benefits, including improved performance and user experience, reduced latency, increased scalability, and enhanced security measures.
Key CDN Technologies for Dynamic Content Delivery
Intelligent Caching
One of the key advancements in CDN technology for dynamic content is the incorporation of intelligent caching mechanisms. Traditional caching approaches, based on static rules, are often ineffective for dynamic content, which can be frequently updated and highly personalized. Intelligent caching leverages machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms to dynamically adapt caching strategies based on factors such as user behavior, content popularity, and network conditions.
- Personalized Caching: Tailored caching based on individual user preferences and browsing history, optimizing content delivery for each user.
- Dynamic Content Identification: Intelligent algorithms identify dynamic content in real-time, enabling targeted caching strategies.
- Edge Caching: Caching dynamic content at the network edge, closer to users, reducing latency and improving performance.
Edge Computing
The integration of edge computing capabilities into CDNs has significantly enhanced their ability to deliver dynamic content effectively. Edge computing brings computation and storage resources closer to the end-users, reducing the distance that data must travel. This enables faster content delivery, reduced latency, and improved overall user experience.
- Low-Latency Delivery: By processing and delivering content at the edge, latency is minimized, resulting in a more responsive and immersive user experience.
- Localized Content Delivery: Edge computing allows CDNs to deliver content from the edge location closest to the user, optimizing delivery performance and reducing bandwidth costs.
- Personalized Content Optimization: Edge-based processing enables real-time customization and optimization of content based on user preferences and location.
Specialized Content Delivery Protocols
Traditional content delivery protocols, such as HTTP, are not optimized for the delivery of dynamic content. To address this, CDNs have developed specialized protocols that are tailored to the unique characteristics of dynamic content. These protocols provide efficient delivery, reduced latency, and improved security.
- HTTP/2 and HTTP/3: These protocols optimize the delivery of dynamic content by introducing features such as header compression, stream prioritization, and multiplexing.
- QUIC: A transport protocol designed for low-latency and secure delivery of dynamic content, offering reduced overhead and improved performance.
- WebSockets: A bidirectional communication protocol that enables real-time data exchange and interactive content delivery, supporting dynamic content with user interaction.
Conclusion
The evolution of CDN technologies has been driven by the increasing demand for dynamic content delivery. By embracing innovative architectures and techniques, CDNs have transformed their capabilities to effectively support the unique requirements of dynamic content. Intelligent caching, edge computing, and specialized content delivery protocols have become essential components of modern CDN architectures, enabling the delivery of dynamic content with improved performance, reduced latency, and enhanced user experience. As the demand for dynamic content continues to grow, CDNs will continue to evolve, further refining their technologies to meet the evolving needs of the web.
Relevant Keyword Tags
- CDN Technologies
- Dynamic Content Delivery
- Intelligent Caching
- Edge Computing
- Content Delivery Protocols
