Early Days: Physical Network Infrastructure and Content Delivery
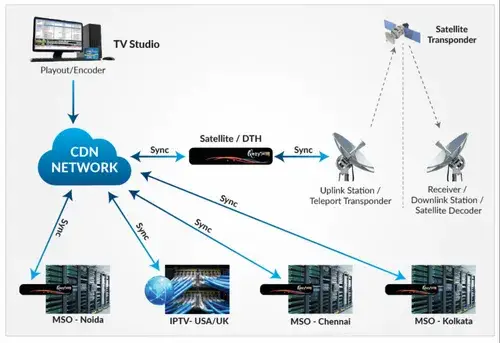
- Dedicated lines: High-bandwidth physical connections between media sources and distribution points.
- Caching nodes: Servers strategically placed in different locations to store and deliver popular content closer to users.
Emergence of Internet-Based CDN
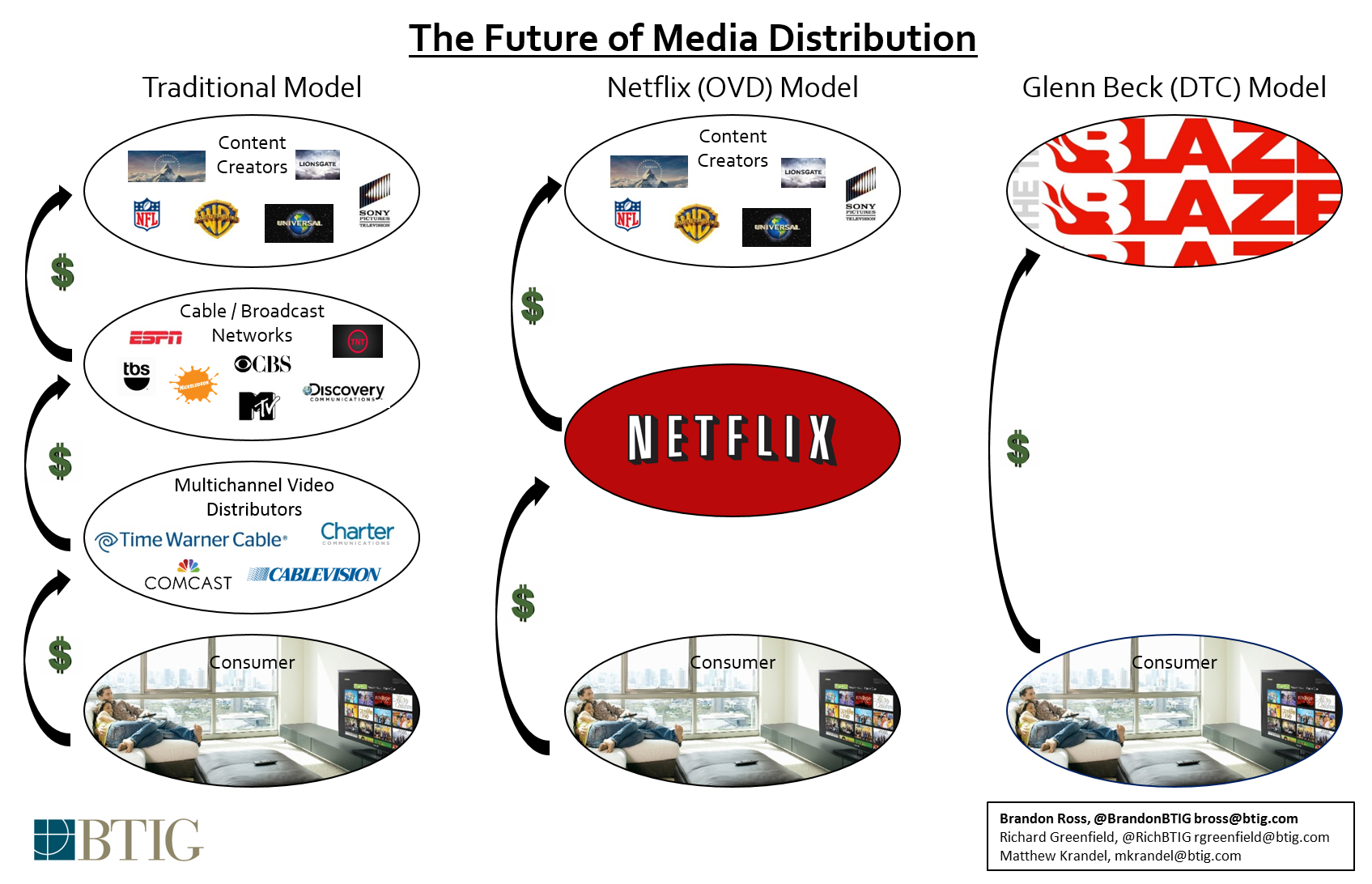
- HTTP caching: Web browsers’ ability to store content locally and reduce bandwidth consumption.
- Commercial CDNs: Specialized providers offering CDN services to businesses, including media companies.
Content-Aware Routing and Adaptive Streaming

- Content-aware routing: Directs user requests to the server with the best network performance.
- Adaptive streaming: Adjusts video quality based on available bandwidth, ensuring smooth playback even during network fluctuations.
Cloud-Based CDN
- Virtual machines: CDNs implemented on cloud platforms, providing scalability and cost-effectiveness.
- Global reach: Cloud-based CDNs enable content delivery to a wide geographic audience.
Edge Computing for Video Acceleration
- Edge servers: Small, powerful devices deployed at the network edge, closer to users.
- Video transcoding: On-the-fly video processing to optimize for different devices and bandwidths.
- Real-time video distribution: Low-latency delivery for live events and interactive applications.
Advanced Analytics and Optimization
- Video analytics: Detailed insights into audience behavior, content performance, and network usage.
- Machine learning: Algorithms optimize content delivery and reduce latency based on real-time data.
Emerging Trends
- 5G and Mobile CDN: 5G networks promise ultra-fast and reliable connections, enabling high-quality mobile video delivery.
- Blockchain and Smart Networks: Decentralized technologies for secure and efficient content distribution.
- Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality: Immersive experiences require high-bandwidth and low-latency CDN solutions.
Benefits of CDN Technologies for Media Distribution
- Reduced bandwidth costs
- Improved content delivery performance
- Enhanced user experience
- Scalability and flexibility
- Global reach and high availability
- Increased security and reliability## The Evolution Of CDN Technologies For Media Distribution
Executive Summary
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) have revolutionized the way media is distributed online. By caching content on servers located around the world, CDNs reduce latency, improve video quality, and enhance the overall user experience. This article explores the evolution of CDN technologies, examining the key factors that have driven their development and the impact they have had on the media industry.
Introduction
In the early days of the internet, media content was typically delivered directly from the origin server to the user’s device. However, as the internet grew in popularity and the demand for online video increased, the limitations of this approach became apparent. Latency, caused by the distance between the origin server and the user’s device, resulted in slow loading times and poor video quality.
FAQs
Q: What is a CDN?
A: A CDN is a global network of servers that stores and delivers content to users based on their location.
Q: How does a CDN improve performance?
A: By caching content on servers closer to the user, CDNs reduce latency and improve video quality.
Q: What are the benefits of using a CDN?
A: CDNs offer numerous benefits, including reduced latency, improved video quality, enhanced scalability, increased reliability, and reduced bandwidth costs.
CDN Technologies
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
Adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR) is a technique used to deliver video content at different quality levels based on the user’s internet connection speed. ABR players automatically adjust the bitrate of the video stream to ensure a smooth and uninterrupted viewing experience.
- Supports multiple video qualities
- Adapts to varying internet speeds
- Maintains a consistent viewing experience
HTTP Live Streaming
HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) is a streaming protocol developed by Apple that allows media content to be delivered over HTTP. HLS divides video into small segments that are downloaded and played sequentially.
- Delivers content over HTTP
- Compatible with a wide range of devices
- Supports adaptive bitrate streaming
WebRTC
WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication) is a technology that enables real-time communication between browsers. WebRTC can be used to deliver live video and audio streams to users.
- Supports live streaming over the web
- Reduces latency and improves video quality
- Encrypted for secure communication
Peer-to-Peer Delivery
Peer-to-peer (P2P) delivery is a technique that leverages users’ devices to distribute content. P2P networks reduce the load on CDN servers and improve performance.
- Distributes content through user devices
- Reduces CDN server load
- Improves scalability
Content Acceleration
Content acceleration techniques, such as TCP optimization and CDN caching, reduce latency and improve the overall performance of CDN delivery.
- Optimizes TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
- Caches content on CDN servers
- Reduces latency and improves performance
Conclusion
Content Delivery Networks have played a crucial role in the evolution of media distribution. By adopting innovative technologies, CDNs have overcome the challenges of latency, unreliable connectivity, and scalability. As the demand for online video continues to grow, CDNs will continue to evolve, providing the infrastructure and services necessary to deliver a seamless and high-quality viewing experience to users worldwide.
Keyword Tags
- Content Delivery Networks (CDN)
- Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
- HTTP Live Streaming
- WebRTC
- Peer-to-Peer Delivery
