The Evolution of AI: From Basic Algorithms to Advanced Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has come a long way since its inception in the mid-20th century. From basic algorithms to advanced machine learning, the evolution of AI has been marked by significant milestones.
Basic Algorithms (1950s-1970s)
The early days of AI were characterized by the development of basic algorithms such as rule-based systems and decision trees. These algorithms used predefined rules to solve specific problems. While simple, these algorithms laid the foundation for more complex AI techniques.
Expert Systems (1970s-1990s)
Expert systems were a type of AI that used knowledge bases, which were collections of facts and rules, to solve problems. They were designed to emulate the expertise of human professionals and were often used in fields such as medicine and finance.
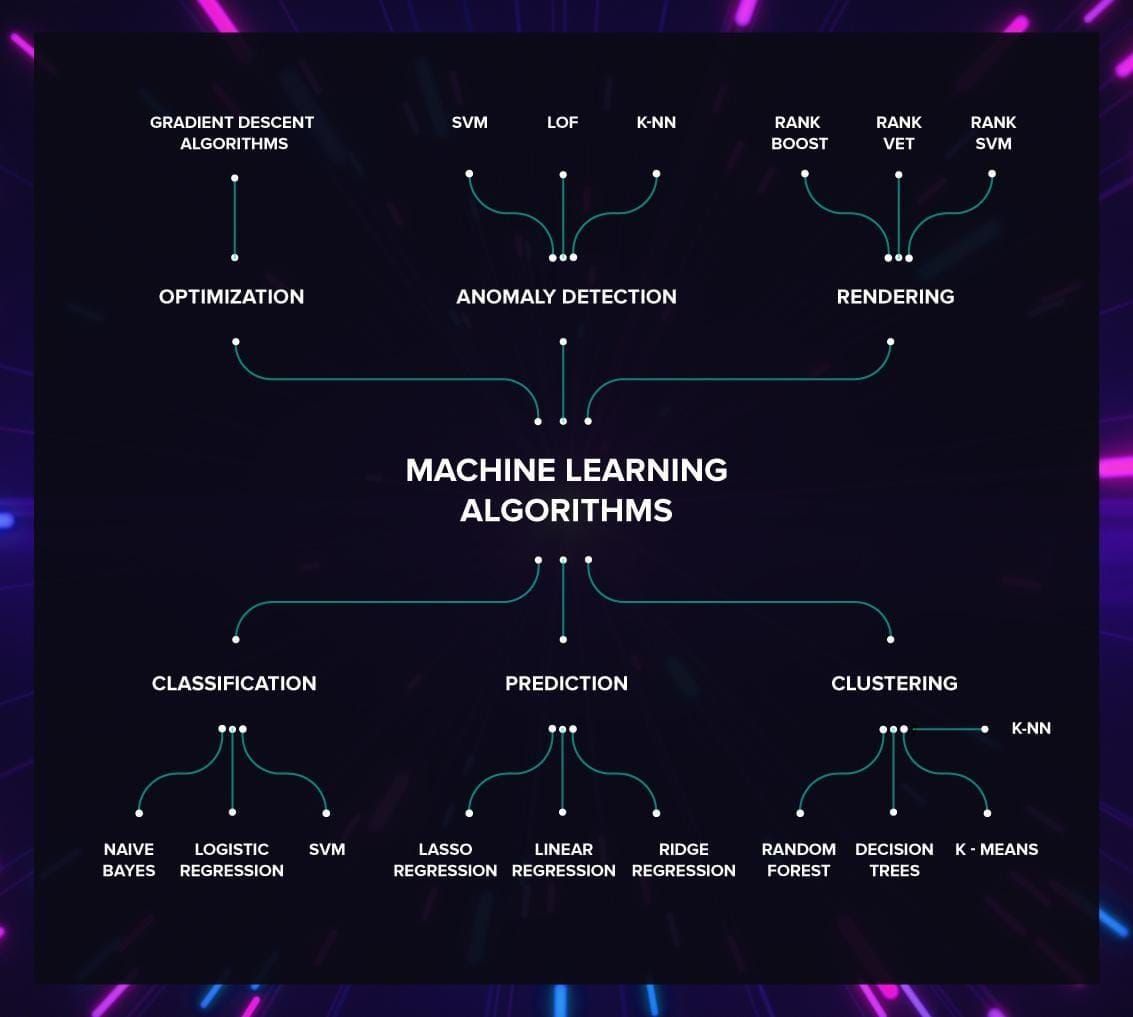
Machine Learning (1990s-Present)
The advent of machine learning marked a significant shift in the development of AI. Machine learning algorithms allow computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time. This approach has led to numerous breakthroughs, including:
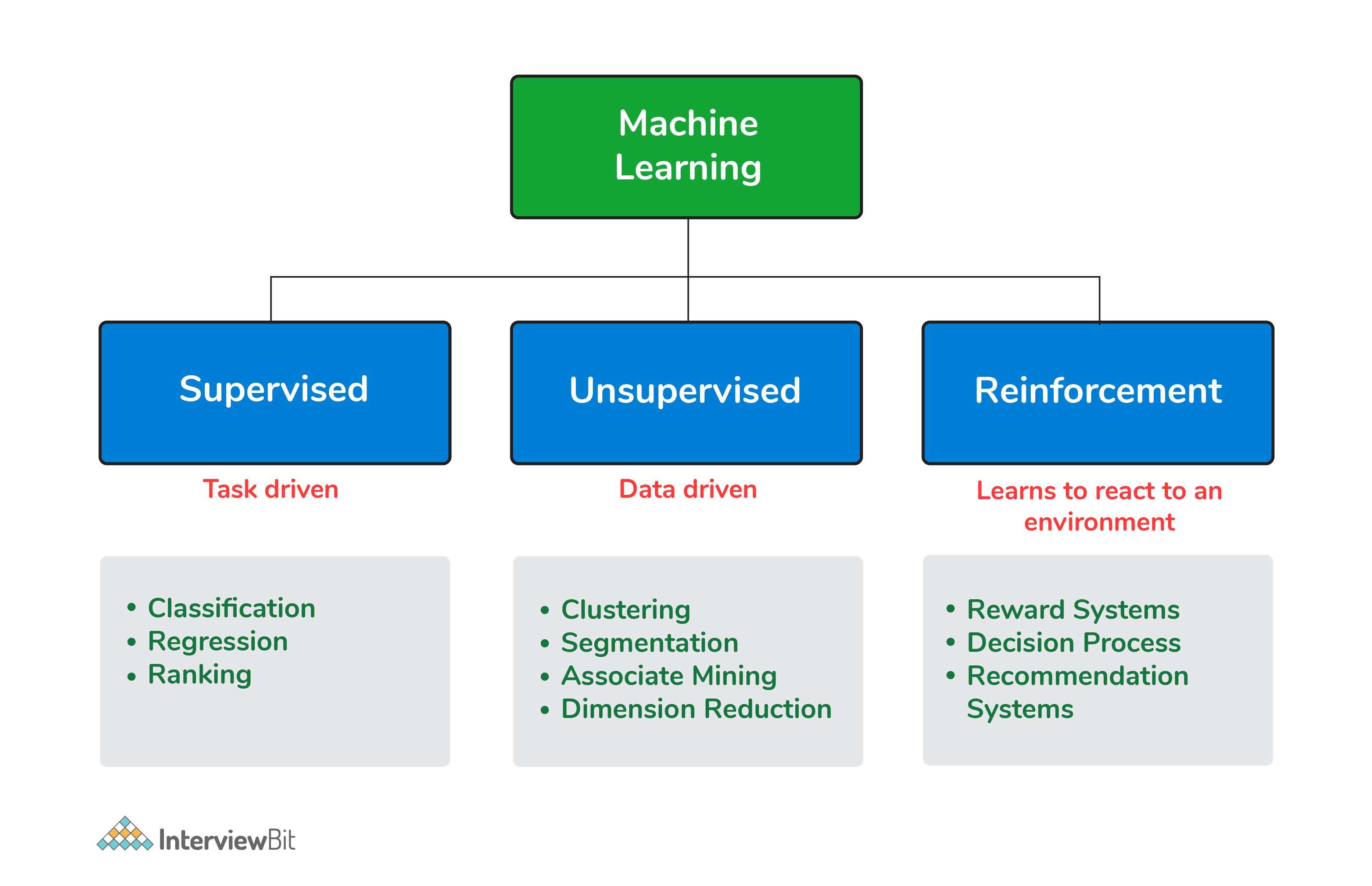
- Supervised Learning: Algorithms that learn from labeled data, where each example is associated with a correct answer.
- Unsupervised Learning: Algorithms that learn from unlabeled data, where there is no pre-defined correct answer.
- Deep Learning: A type of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks with multiple hidden layers.
Advanced Machine Learning (2024s-Present)
In recent years, AI research has focused on developing more advanced machine learning techniques. These include:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Algorithms that enable computers to understand and generate human language.
- Computer Vision: Algorithms that allow computers to “see” and interpret images.
- Reinforcement Learning: Algorithms that allow computers to learn through trial and error by interacting with their environment.
Impact of AI
The evolution of AI has had a profound impact on various industries, including healthcare, finance, and transportation. AI-powered systems are used for tasks such as medical diagnosis, fraud detection, and self-driving cars. As AI continues to advance, it is expected to play an increasingly important role in our lives, transforming the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us.[The Evolution of AI: From Basic Algorithms to Advanced Machine Learning]
Executive Summary
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized diverse sectors, transforming how we live, work, and interact with the world. From its inception as rudimentary algorithms to its current sophistication in machine learning, AI has evolved tremendously. This article delves into the fascinating journey of AI, exploring its transformative stages and highlighting significant milestones that have shaped its evolution.
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a dominant force in modern society. In its relentless evolution, AI encompasses a vast spectrum of technologies, from rudimentary algorithms to sophisticated machine learning models. This article traces the fascinating journey of AI, examining its transformative stages, key milestones, and the profound impact it has had on various aspects of human endeavor.
FAQs
- What is AI?
- AI refers to the capability of machines to exhibit behavior typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, and problem-solving.
- How does AI work?
- AI leverages algorithms and statistical models to analyze data, identify patterns, and make predictions or decisions.
- What are the different types of AI?
- AI encompasses a range of types, including narrow AI (performing specific tasks), general AI (performing multiple tasks), and artificial superintelligence (exceeding human cognitive abilities).
Milestones in the Evolution of AI
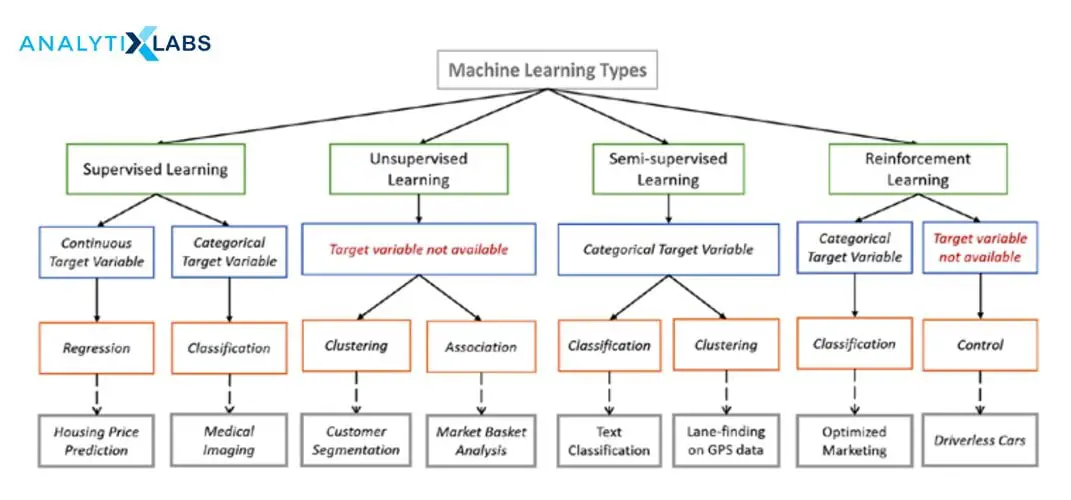
Machine Learning
Description: Machine learning empowers computers to learn from data without explicit instructions, allowing them to identify patterns and make predictions.
- Supervised learning: Training models on labeled data to map inputs to outputs.
- Unsupervised learning: Finding hidden structures and patterns in unlabeled data.
- Reinforcement learning: Learning through trial and error, receiving rewards or penalties for actions.
- Generative adversarial networks (GANs): Two neural networks compete to generate realistic data and accurately discriminate between real and generated samples.
Deep Learning
Description: Deep learning utilizes artificial neural networks with multiple layers to analyze and learn from complex data.
- Convolutional neural networks (CNNs): Specialized for image and video recognition, identifying patterns and features in visual data.
- Recurrent neural networks (RNNs): Handling sequential data, such as text and time series, preserving contextual information.
- Transformer neural networks: Introduced in 2024, allowing for efficient and accurate processing of sequential data, outperforming RNNs in many applications.
- Attention mechanisms: Enhancing model performance by selectively focusing on specific parts of input data, improving learning and comprehension.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Description: NLP enables computers to understand and process human language, facilitating communication and information extraction from text data.
- Text classification: Categorizing text documents into predefined classes based on their content.
- Sentiment analysis: Identifying the emotions and opinions expressed in text.
- Machine translation: Automatically translating text from one language to another.
- Named entity recognition: Extracting specific entities (e.g., names, locations, organizations) from text.
Computer Vision
Description: Computer vision empowers computers to “see” and interpret visual data, enabling object recognition, facial detection, and more.
- Image classification: Identifying and categorizing objects or scenes in images.
- Object detection: Locating and recognizing specific objects within an image.
- Semantic segmentation: Assigning labels to each pixel in an image, providing a detailed understanding of the scene.
- Facial recognition: Identifying and matching human faces, often used for security and surveillance.
Robotics
Description: Robotics combines AI, mechanics, and sensors to create machines capable of performing physical tasks autonomously.
- Mobile robots: Navigating and interacting with the physical world, often used for exploration, delivery, or manufacturing.
- Collaborative robots: Working alongside humans in shared workspaces, assisting with tasks or enhancing safety.
- Industrial robots: Performing repetitive or dangerous tasks in manufacturing and production environments.
- Humanoid robots: Resembling human form and capabilities, often used for research or entertainment.
Conclusion
The evolution of AI has been marked by constant innovation and rapid advancement, transforming our world in countless ways. As AI continues to evolve, we can expect even more profound changes in the years to come. From enhancing healthcare to revolutionizing transportation, AI holds the promise of a future where human ingenuity and technological capabilities converge to create a world of limitless possibilities.
Relevant Keyword Tags
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Machine Learning
- Deep Learning
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Computer Vision
- Robotics
