The Challenges of Reverse Engineering

Reverse engineering is the process of deconstructing a system or product to understand its design, functionality, and implementation. While it can be a valuable tool for learning, troubleshooting, and security analysis, it comes with its own set of challenges. Here are some of the most common difficulties faced during the reverse engineering process:

-
Lack of Documentation: Many systems and products are not accompanied by detailed technical documentation, making it difficult to gain a comprehensive understanding of their inner workings. This lack of information can hinder the reverse engineering process and lead to errors or misunderstandings.
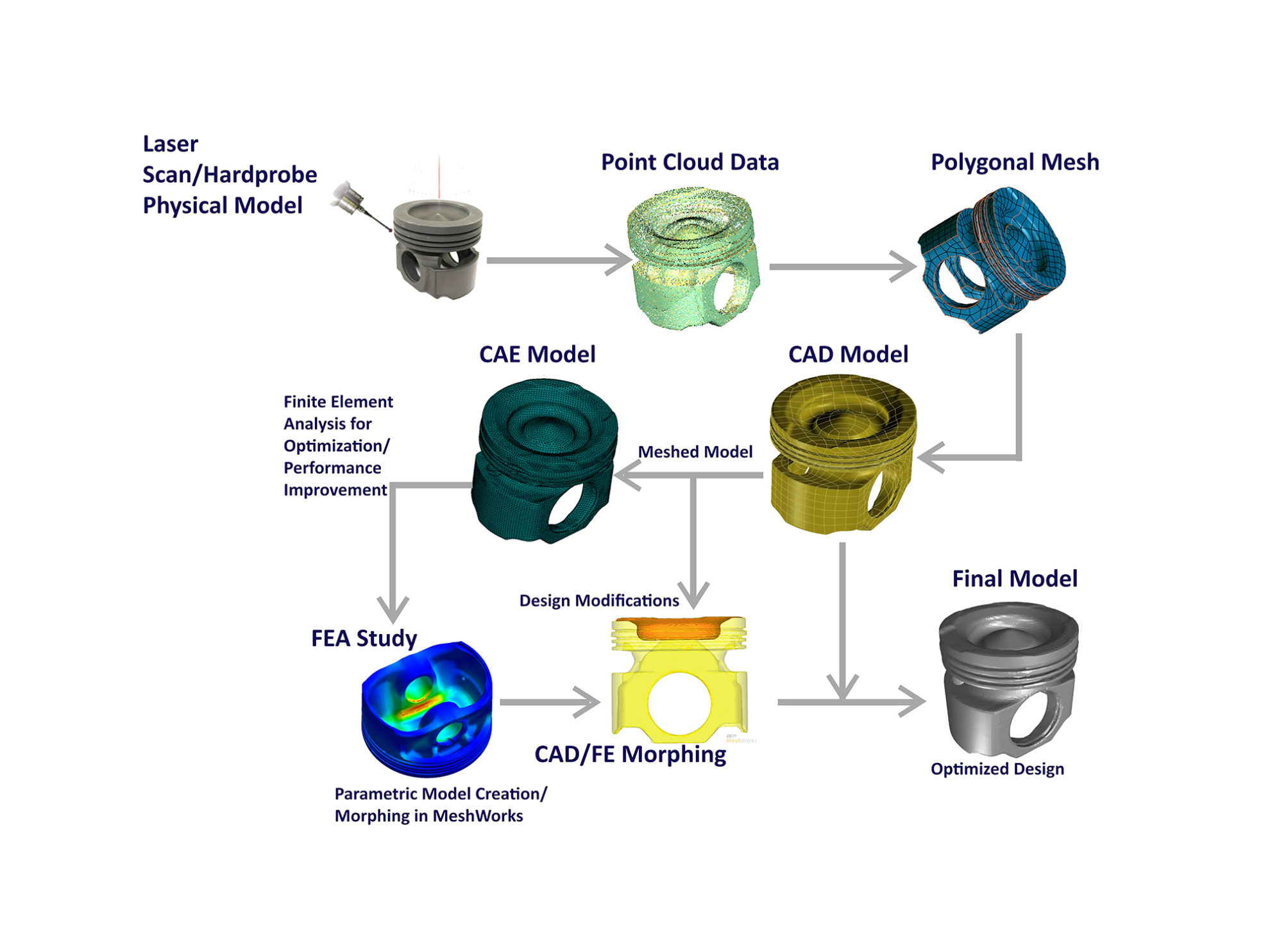
-
Complexity: Reverse engineering complex systems, such as software applications or electronic devices, can be an overwhelming task. The sheer number of components, their interconnections, and the underlying code or circuitry can make it difficult to identify and comprehend the functionality of the system as a whole.
-
Time Constraints: Reverse engineering can be a time-consuming process, especially for large or intricate systems. This can be a challenge when faced with deadlines or resource limitations, and it can be difficult to balance the need for thorough analysis with the need for timely results.
-
Proprietary Information: Reverse engineering proprietary or copyrighted systems can raise ethical and legal concerns.Unauthorized reverse engineering may be prohibited by law or by the terms of service of the software or product being reverse engineered. This can limit the scope of reverse engineering activities and can have implications for the use and dissemination of the resulting information.
-
Tool Limitations: Automated reverse engineering tools, such as disassemblers or decompilers, can simplify certain aspects of the process. However, they are not always able to handle all situations, and their output may require manual interpretation and analysis. This can introduce human error and can hinder the efficiency of the reverse engineering process.
-
Security Threats: Reverse engineering can involve the analysis of sensitive systems or data, which can pose security risks. By exposing the inner workings of a system, reverse engineering can potentially make it more vulnerable to attacks or unauthorized access. This requires careful consideration of security implications throughout the reverse engineering process.
-
Updating and Maintenance: Reverse engineered systems and products may need to be updated or maintained over time as their underlying components or functionality change. This can be a challenge, especially if the original documentation is unavailable or the system has been extensively modified. It requires ongoing effort to keep up with the evolving system and to ensure its continued accuracy and reliability.
