The Challenges of Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering is the process of taking apart an existing product and analyzing its components to understand how it works. This can be a challenging and time-consuming process, especially for complex products. Some of the challenges involved in reverse engineering include:
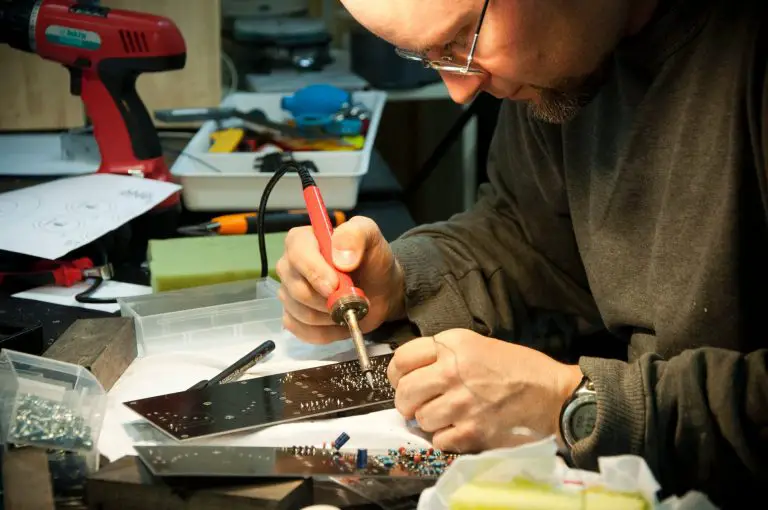

- Access to the product: In some cases, it may be difficult or impossible to obtain access to the product that you want to reverse engineer. This could be due to legal restrictions, proprietary information, or simply because the product is no longer available.
- Lack of documentation: Even if you have access to the product, you may not have access to the documentation that explains how it works. This can make it difficult to understand the product’s design and functionality.
- Complex design: Some products are very complex and may contain thousands of components. This can make it difficult to understand how the product works and how the components interact with each other.
- Time and resources: Reverse engineering can be a time-consuming and resource-intensive process. It may require a team of engineers with specialized skills and equipment.
Despite the challenges, reverse engineering can be a valuable tool for product development, troubleshooting, and innovation. By understanding how a product works, you can learn from its design and improve upon it. Reverse engineering can also be used to identify potential security vulnerabilities and to create new products that are compatible with existing ones.## [The Challenges Of Reverse Engineering]

Executive Summary
Reverse engineering is a complex and demanding process, involving its fair share of challenges. Understanding these challenges is crucial for establishing realistic expectations, implementing appropriate methodologies, and mitigating potential risks throughout the reverse engineering process.
Introduction
Reverse engineering, the process of deconstructing a system or product to understand its design, functionality, and principles, presents a unique set of challenges that require careful consideration. This intricate process involves analyzing and interpreting existing artifacts, often without access to complete documentation or design specifications, making it both an intellectually stimulating and technically demanding endeavor.
FAQ
1. What are some common obstacles encountered in reverse engineering?
2. How can the absence of documentation and design specifications hinder the reverse engineering process?
3. What strategies can be employed to mitigate the challenges posed by legacy or obsolete systems?
Challenges in Reverse Engineering
1. Incomplete or Lack of Documentation
– Absence of design schematics: Reverse engineering often relies on existing documentation, including blueprints, schematics, and technical specifications, to guide the process. However, in many cases, such documentation may be incomplete, outdated, or non-existent.
– Limited access to source code: For software systems, obtaining the original source code can be essential for understanding the system’s design and implementation. However, access to source code may be restricted or unavailable, posing a significant challenge to the reverse engineering process.
– Incomplete or missing requirement specifications: Requirements specifications outline the intended purpose, functionality, and constraints of a system. Without these specifications, reverse engineers may struggle to understand the system’s objectives and make informed decisions during the analysis process.
2. Legacy or Obsolete Systems
– Limited availability of expertise: Legacy systems may have been developed using technologies that are no longer widely used, making it difficult to find skilled engineers with the necessary knowledge and experience to assist in the reverse engineering process.
– Lack of compatibility with modern tools: Reverse engineering tools and techniques may not be compatible with older or obsolete systems, necessitating the use of specialized or custom-developed solutions.
– Difficulty in obtaining hardware and software components: For physical systems, obtaining replacement or spare parts for legacy components can be challenging, especially if the original manufacturers are no longer in operation or if the components are no longer produced.
3. Intellectual Property Rights
– Copyright and patent infringement: Reverse engineering may involve analyzing and reproducing aspects of a system that are protected by copyright or patents. This can raise legal concerns and ethical considerations, requiring careful attention to intellectual property rights.
– Trade secret protection: Reverse engineering can potentially reveal sensitive or confidential information, such as trade secrets or proprietary algorithms. Unauthorized disclosure of such information can lead to legal and financial consequences.
– Balancing IP protection with innovation: Striking a balance between protecting intellectual property rights and fostering innovation is crucial. Reverse engineering can contribute to technological advancements, but it is essential to respect the rights of creators and innovators.
4. Security and Safety Considerations
– Vulnerabilities and exploits: Reverse engineering can uncover security vulnerabilities and potential exploits in a system, exposing it to malicious attacks. It is crucial to address these vulnerabilities promptly to mitigate security risks.
– Safety concerns: Reverse engineering physical systems can involve working with potentially hazardous materials or components. Proper safety precautions must be taken to minimize risks to personnel and the environment.
– Ethical implications: Reverse engineering techniques can be used for both legitimate and illegitimate purposes. It is important to consider the ethical implications of the reverse engineering process and ensure its responsible use.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering presents a complex and challenging landscape, requiring a combination of technical expertise, analytical thinking, and a deep understanding of the system under analysis. Overcoming the challenges discussed above is essential for successful reverse engineering outcomes. By carefully considering these challenges and implementing appropriate strategies, organizations and individuals can effectively harness the power of reverse engineering to gain valuable insights into existing systems and drive innovation.
Keyword Tags
- Reverse Engineering
- Challenges in Reverse Engineering
- Incomplete Documentation
- Legacy Systems
- Intellectual Property Rights
- Security and Safety Considerations
