The Blockchain Trilemma: Achieving Scalability, Security, and Decentralization
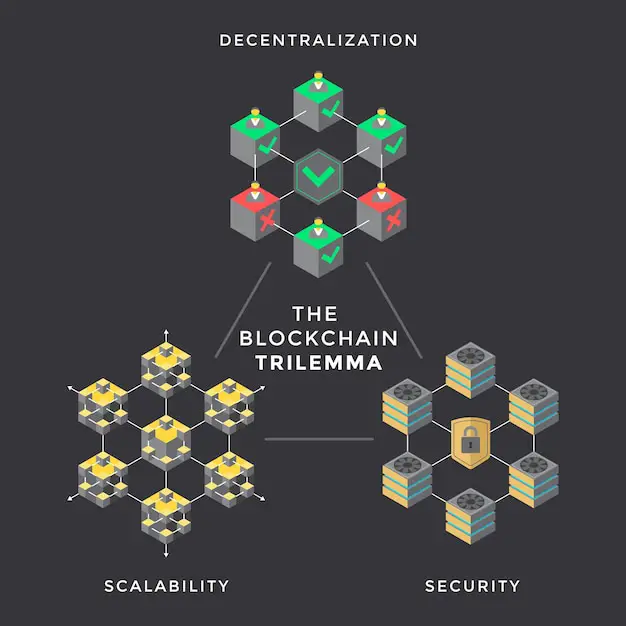
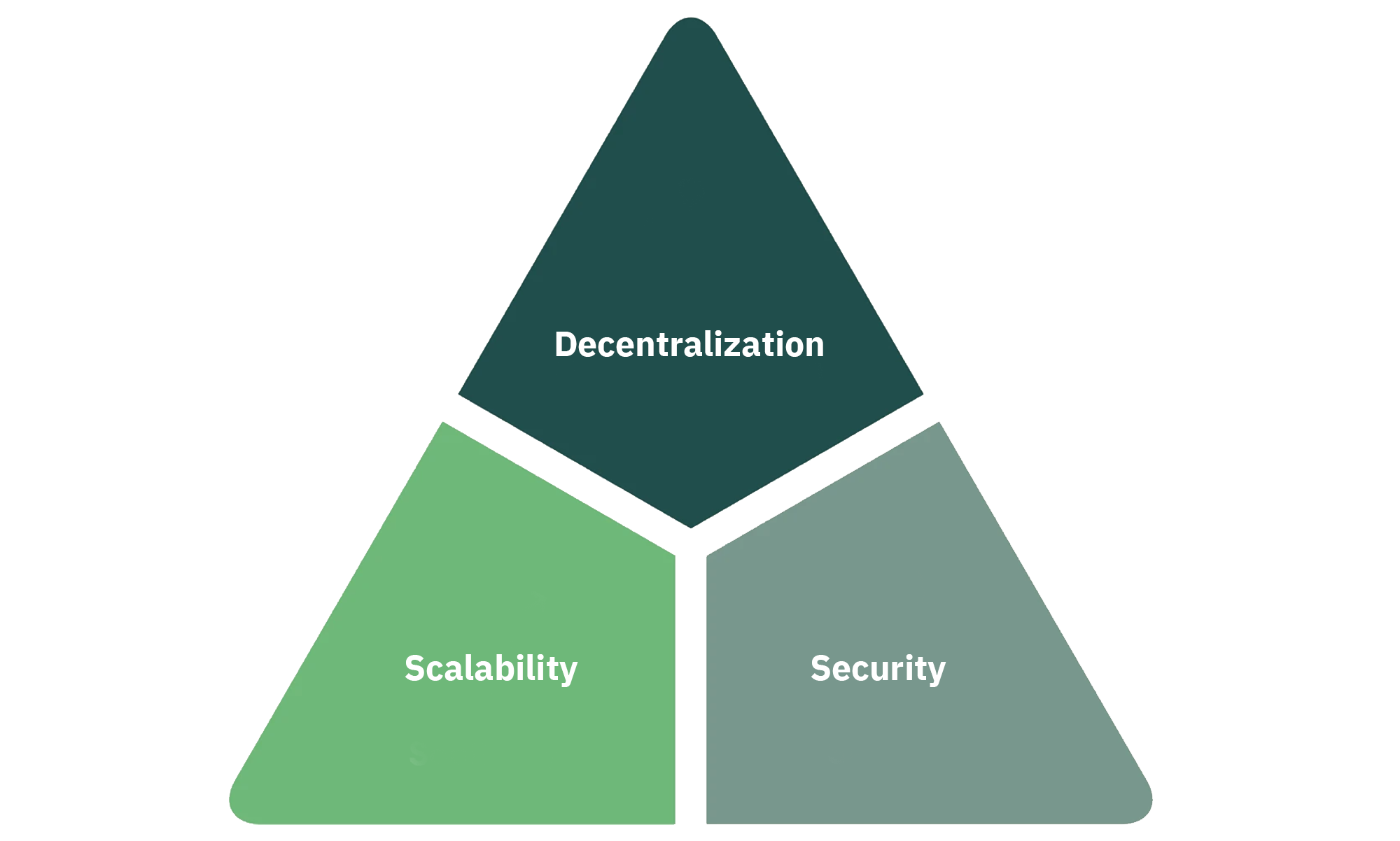
The blockchain trilemma poses a fundamental challenge in blockchain development, referring to the apparent trade-offs among three desirable qualities: scalability, security, and decentralization.
Scalability: Refers to the ability of a blockchain to process a high volume of transactions without compromising latency or transaction fees. High scalability allows for faster and cheaper transactions, making the blockchain more useful for everyday applications.
Security: Blockchains rely on robust security mechanisms to protect user funds and data from unauthorized access. Strong security measures help maintain the integrity and trustworthiness of the blockchain.
Decentralization: Decentralization implies that the blockchain is not controlled by any single entity or group of individuals. It is maintained by a distributed network of nodes, ensuring that no single party can manipulate or corrupt the system.
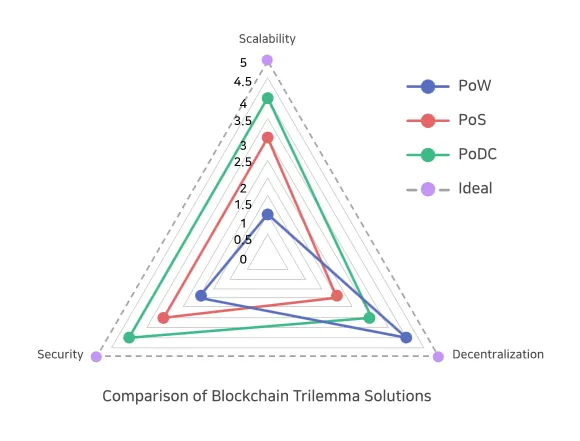
Resolving the blockchain trilemma is a complex undertaking. Traditionally, focusing on one aspect often comes at the expense of the others. For instance, increasing scalability by using centralized solutions may compromise decentralization. Conversely, prioritizing decentralization and security may result in slower transaction processing times.
However, recent advancements in blockchain technology have emerged to address the blockchain trilemma with innovative solutions. These approaches aim to improve scalability without sacrificing security or decentralization.
One approach involves off-chain transactions that process high-volume transactions outside the main blockchain. This reduces the load on the main network while maintaining security and decentralization. Another technique, sharding, divides the blockchain into smaller, parallel chains that process transactions simultaneously. This significantly increases scalability without compromising security.
Emerging consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Stake (PoS), consume less energy and offer faster validation times compared to legacy mechanisms like Proof-of-Work (PoW). Additionally, smart contract platforms like Ethereum are exploring novel architectures, such as rollups and layer-2 solutions, to enhance scalability while preserving security and decentralization.
These technological innovations demonstrate ongoing efforts to resolve the blockchain trilemma. As these solutions mature and gain adoption, we can expect blockchains to become more efficient, secure, and decentralized, enabling wider adoption and unlocking the transformative potential of decentralized technologies.## The Blockchain Trilemma: How New Cryptocurrencies Address Scalability, Security, And Decentralization
Executive Summary
The ‘Blockchain Trilemma’ refers to the inherent challenge of simultaneously achieving scalability, security, and decentralization in a blockchain system. Traditional blockchain architectures have struggled to optimize all three aspects simultaneously. Hence, innovative solutions emerge in new cryptocurrencies, attempting to overcome these limitations and enhance blockchain technology’s functionality.
Introduction
The emergence of blockchain technology has revolutionized various industries. However, it faces the ‘Blockchain Trilemma,’ where blockchains often excel in two out of three key attributes: scalability, security, and decentralization. This article explores how new cryptocurrencies address the trilemma, presenting innovative approaches to overcome these constraints.
Subtopics
1. Sharding
- Partitions the blockchain into smaller shards or sub-networks.
- Transactions are processed in parallel within each shard, improving transaction throughput.
- Maintains decentralization as each shard operates independently.
2. Off-Chain Transactions
- Processes transactions outside the main blockchain on a secondary network or layer.
- Reduces on-chain congestion and improves scalability.
- Relies on a trusted third party or consensus mechanism to ensure security.
3. Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)
- Replaces the traditional blockchain structure with a DAG, where transactions are arranged in a directed graph.
- Enables parallel processing and eliminates the need for mining, enhancing scalability.
- Requires novel consensus mechanisms to maintain security and decentralization.
4. Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
- Replaces energy-intensive proof-of-work mining with a stake-based consensus mechanism.
- Users validate transactions based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold.
- Improves scalability while maintaining a high level of security.
5. Cross-Chain Interoperability
- Enables different blockchains to communicate and transfer assets.
- Bridges gaps between isolated blockchain ecosystems.
- Facilitates a more interconnected and scalable blockchain landscape.
Conclusion
The ‘Blockchain Trilemma’ has long been a challenge for blockchain development. However, innovative solutions introduced in new cryptocurrencies demonstrate significant progress. Sharding, off-chain transactions, DAGs, PoS, and cross-chain interoperability offer promising approaches to enhance scalability, security, and decentralization. As these innovations continue to evolve and mature, the blockchain landscape will likely expand, enabling wider adoption and unlocking the full potential of blockchain technology.
Keyword Tags
- Blockchain Trilemma
- Scalability
- Security
- Decentralization
- New Cryptocurrencies
FAQs
-
Can all cryptocurrencies solve the Blockchain Trilemma?
- No, different cryptocurrencies adopt specific approaches that optimize certain aspects of the trilemma.
-
Is it possible to have a blockchain that is both secure and scalable?
- Yes, new cryptocurrencies are exploring innovative consensus mechanisms and architectural designs that aim to achieve this balance.
-
What are the trade-offs involved in optimizing one aspect of the trilemma?
- Optimizing one aspect may compromise another. For example, increasing scalability through sharding may introduce additional complexity and security challenges.
-
How do new cryptocurrencies ensure decentralization while improving scalability?
- Some cryptocurrencies implement off-chain transactions or DAGs to enhance scalability without compromising decentralization, as these approaches do not require a central authority.
-
What is the role of cross-chain interoperability in addressing the trilemma?
- Cross-chain interoperability promotes a more interconnected blockchain ecosystem, facilitating the exchange of assets and information, and enhancing overall scalability and utility.
