Smart Contracts: Automating Trust with Blockchain Technology
Executive Summary
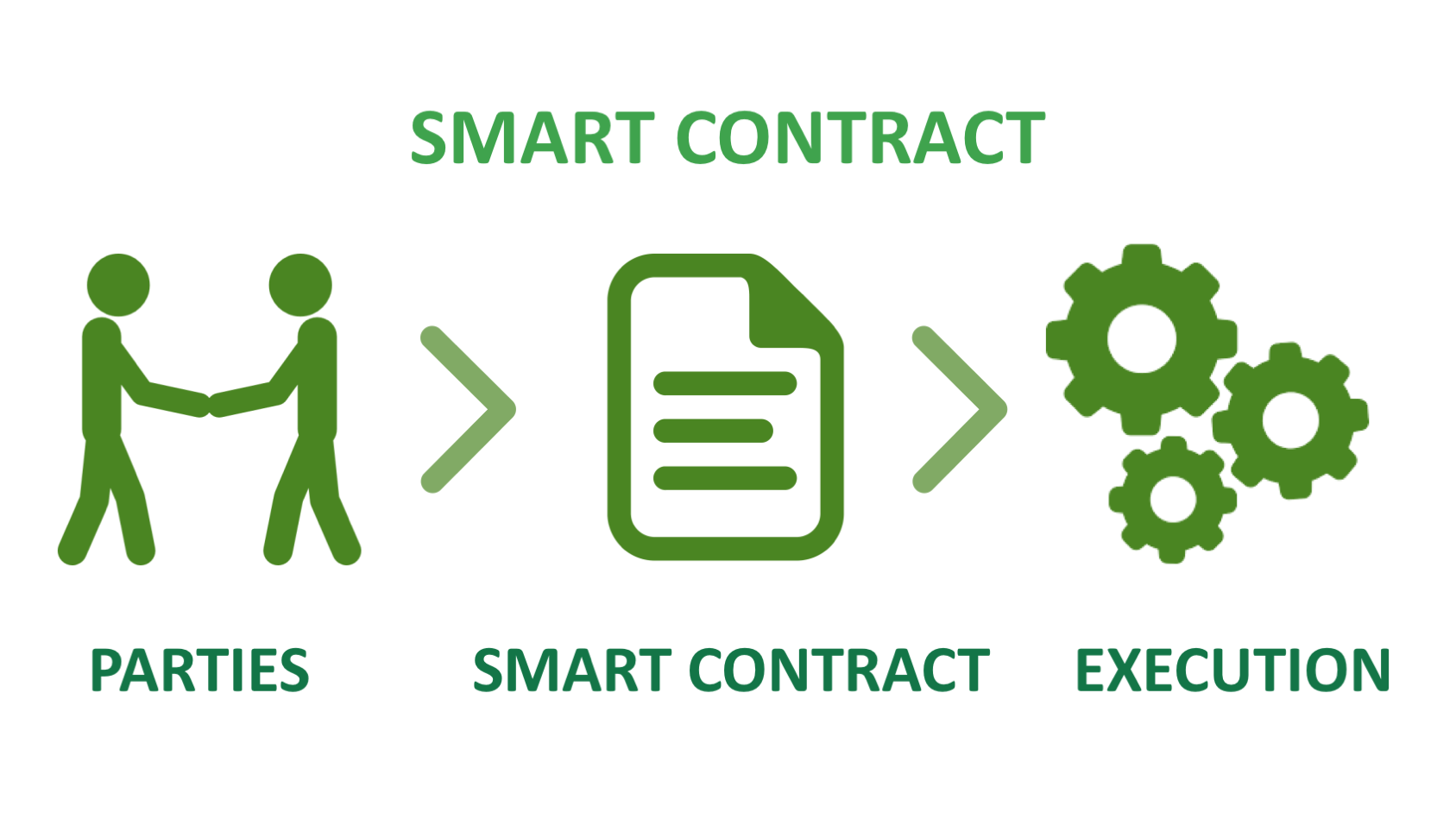
Smart contracts, driven by blockchain technology, are revolutionizing transactions by introducing automated trust and enforcing agreements without the need for intermediaries. This innovative technology enables the secure and verifiable execution of agreements, automating processes, reducing costs, and enhancing transparency.

Introduction
Traditionally, contracts have relied on paper-based or digital signatures to establish trust and accountability. However, these methods are often time-consuming, prone to fraud, and subject to interpretation. Smart contracts address these limitations by leveraging blockchain technology to create tamper-proof, self-executing contracts that ensure trust and automation.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts offer a wide range of benefits that have the potential to transform various industries:
- Automated Execution: Smart contracts eliminate the need for manual processes or third-party intermediaries, automating the execution of pre-defined terms and conditions.
- Enhanced Trust: Blockchain technology provides immutable records of all transactions, fostering trust between parties and reducing the risk of disputes.
- Reduced Costs: By eliminating the need for lawyers, notaries, and mediators, smart contracts can significantly reduce transaction costs.
- Transparency and Traceability: Smart contracts create transparent audit trails, allowing all parties to track the progress and status of an agreement.
- Improved Security: Smart contracts leverage the decentralized nature of blockchain, ensuring that contracts cannot be altered or tampered with.
Key Subtopics
1. Implementation
Smart contracts are implemented using high-level programming languages such as Solidity and Vyper. They consist of code that explicitly defines the conditions and actions to be executed when certain parameters are met. Developers create and deploy smart contracts onto blockchain networks, ensuring security and immutability.
2. Use Cases
Smart contracts have diverse applications across industries, including:
- Supply chain management: Tracking and verifying the movement of goods and assets.
- Financial services: Facilitating automated payments, loan approvals, and insurance claims.
- Healthcare: Managing patient records, prescription fulfillment, and insurance reimbursement.
- Voting systems: Enabling secure and transparent voting processes.
- Real estate: Automating property transactions, title transfers, and rental agreements.
3. Security Considerations
Smart contracts are inherently secure due to the immutability of blockchain technology. However, vulnerabilities can emerge from coding errors, hacks, and malicious actors. Developers must prioritize security best practices, such as thorough testing, code auditing, and regular updates.
4. Legal Framework
The legal implications of smart contracts are still evolving. Jurisdictions are grappling with establishing regulations that govern their enforceability, liability, and dispute resolution mechanisms. It is crucial for policymakers and legal professionals to address these issues to provide clarity and foster the adoption of smart contracts.
5. Future Prospects
Smart contracts are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of business and governance. Their potential applications include:
- Automating complex financial agreements
- Streamlining government processes
- Enhancing voting systems
- Creating decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs)
- Facilitating cross-border transactions
Conclusion
Smart contracts are empowering individuals and organizations by enabling them to create automated, secure, and transparent agreements. By leveraging blockchain technology, they have the potential to revolutionize industries, reduce costs, and foster trust in the digital era. While the technology continues to evolve and legal frameworks are being established, smart contracts hold immense promise for transforming the way we conduct business and interact with one another.
Keyword Tags
- Smart Contracts
- Blockchain
- Automation
- Trust
- Digital Transformation
