Setting Up A Basic FTP Server with Vsftpd
Introduction

Vsftpd (Very Secure FTP Daemon) is a popular open-source FTP server for Linux systems. It is known for its security features and ease of use. In this guide, we will explain how to set up a basic FTP server with Vsftpd on a Linux system.

Prerequisites
To follow this guide, you will need:
- A Linux system with root access
- A text editor such as nano or vim
Step 1: Install Vsftpd
First, you need to install the Vsftpd package. The instructions will vary depending on your Linux distribution. Here are the commands for some common distributions:
- Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo apt install vsftpd - CentOS/Red Hat Enterprise Linux:
sudo yum install vsftpd
Step 2: Configure Vsftpd
After installation, you need to configure Vsftpd. Edit the configuration file /etc/vsftpd.conf using a text editor. Here are some essential settings to consider:
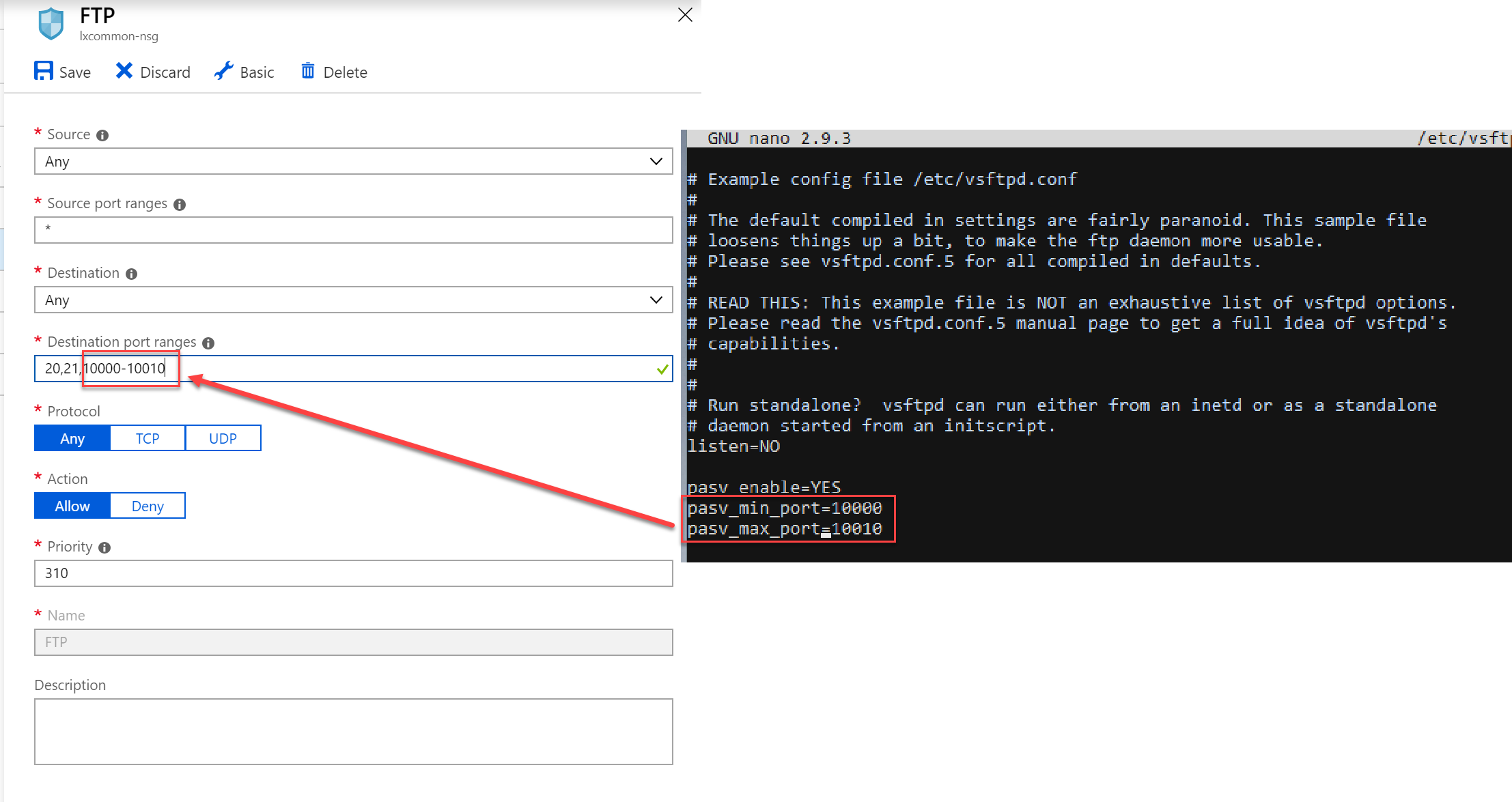
- listen_port: Set the port on which the FTP server will listen. The default is 21.
- anonymous_enable: Enable or disable anonymous FTP access.
- local_enable: Enable or disable local FTP access.
- write_enable: Enable or disable write access to the FTP server.
- chroot_local_user: Enable or disable chrooting local users to their home directories.
Step 3: Create FTP Users
You can create FTP users using the adduser command. For example, to create a user named ftpuser, run the following command:
sudo adduser ftpuserSet a password for the user. You can also add additional users as needed.
Step 4: Enable FTP Service
Now you need to enable the FTP service. The commands to do this depend on your system:
- Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo systemctl enable vsftpd - CentOS/Red Hat Enterprise Linux:
sudo systemctl enable vsftpd.service
Step 5: Start FTP Service
Start the FTP service:
- Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo systemctl start vsftpd - CentOS/Red Hat Enterprise Linux:
sudo systemctl start vsftpd.service
Step 6: Test FTP Service
You can test the FTP service using an FTP client. Here’s an example using the FTP command:
ftp ftp://ftpuser:password@your_server_ipIf you can connect and access the FTP server, then the setup is successful.
Conclusion
You have now installed and configured a basic FTP server with Vsftpd. This guide provides a solid foundation for setting up an FTP server on your Linux system.## Setting Up A Basic FTP Server With Vsftpd
Executive Summary
This article provides a comprehensive guide to setting up a basic FTP server using Vsftpd. It covers the essential steps, configurations, and troubleshooting tips to establish a secure and functional FTP server. By following these instructions, readers can effectively share and transfer files over a network.
Introduction
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) remains a widely used method for transferring files between computers over a network. Vsftpd is a popular FTP server software that is both secure and easy to configure, making it suitable for various applications. This article will guide readers through the process of setting up a basic FTP server using Vsftpd on a Linux system.
Installing and Configuring Vsftpd
-
Installation: Begin by installing Vsftpd using your system’s package manager, such as “apt-get” for Debian-based systems or “yum” for Red Hat-based systems.
-
Configuration File: The main configuration file for Vsftpd is “/etc/vsftpd.conf”. Open this file with a text editor and make the necessary changes.
-
Anonymous Access: By default, Vsftpd allows anonymous access. To disable this, set “anonymous_enable” to “NO”.
-
User Permissions: Create user accounts with appropriate permissions to access the FTP server. Configure the “local_root” directive to define the home directory for each user.
-
Security Settings: Enable SSL/TLS encryption by setting “ssl_enable” to “YES”. Adjust firewall settings to allow FTP traffic on the designated port (default: 21).
Setting Virtual Users and Groups
-
Virtual Users: Virtual users are created outside of the system’s user database specifically for FTP access. Configure Vsftpd to use a dedicated user database file using the “guest_username” and “guest_passwd” directives.
-
Virtual Groups: Virtual groups allow you to assign multiple users to a single group for access control. Create a group in the user database file and add users to it using the “guest_group” directive.
File Permissions and Access Control
-
File Permissions: Set appropriate file permissions to control who can access and modify files on the FTP server. Use the “write_enable” directive to allow users to upload files.
-
Access Control Lists (ACLs): Implement ACLs to define fine-grained access permissions for specific users or groups. Configure ACLs using the “chgrp” and “chmod” commands.
-
Chroot Jail: Restrict users to their home directories to prevent them from accessing other parts of the system. Enable chroot jail by setting “chroot_local_user” to “YES”.
Troubleshooting FTP Issues
-
Connection Issues: Ensure that the FTP server is running and that firewall settings allow connections on the designated port.
-
Authentication Errors: Verify that user credentials are correct and that virtual users and groups are configured properly.
-
File Transfer Errors: Check file permissions and ensure that users have write permissions if they are experiencing issues uploading files.
-
Slow Transfer Speeds: Optimize network settings and consider using a different port for FTP traffic to improve performance.
Conclusion
Setting up a basic FTP server with Vsftpd is a straightforward process that allows for secure and efficient file sharing and transfer. By following the steps outlined in this article and customizing configurations based on specific requirements, you can establish a reliable FTP server that meets your needs.
Keyword Phrase Tags
- FTP Server Setup
- Vsftpd Configuration
- File Transfer Protocol
- Virtual Users and Groups
- File Permissions and Access Control

Nice post! I was able to easily setup a FTP server using your guide. No problem encountered at all.
This guide is terrible! I followed the instructions exactly and my server gives me 403 forbidden error. I give up on this article.
You can also add a welcome message to your FTP server by adding
“`
ftp_greeting=Welcome to my FTP server!
“`
to your config file (/etc/vsftpd.conf).
I think you should use ProFTPD instead of vsftpd. It’s more secure and has more features.
Wow, such a great guide. It’s a pity that I already know how to set up a FTP server.
Yeah, this is the best FTP server guide ever. I mean, who needs to read the official documentation when we have this masterpiece?
I tried to follow this guide but my cat ate the keyboard. Now I have a FTP server with a bunch of random characters as the password.
This guide is ok. It would be better if it had more screenshots.