Improved Data Protection and Security:

- Encryption and Data Integrity: CDNs encrypt data in transit and at rest, ensuring data privacy and integrity during transmission.
- SSL/TLS Support: CDNs provide SSL/TLS support to protect data from eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Web Application Firewall (WAF): A WAF can be integrated into a CDN to filter malicious traffic and protect against attacks like SQL injection and DDoS.
Enhanced DDoS Mitigation:
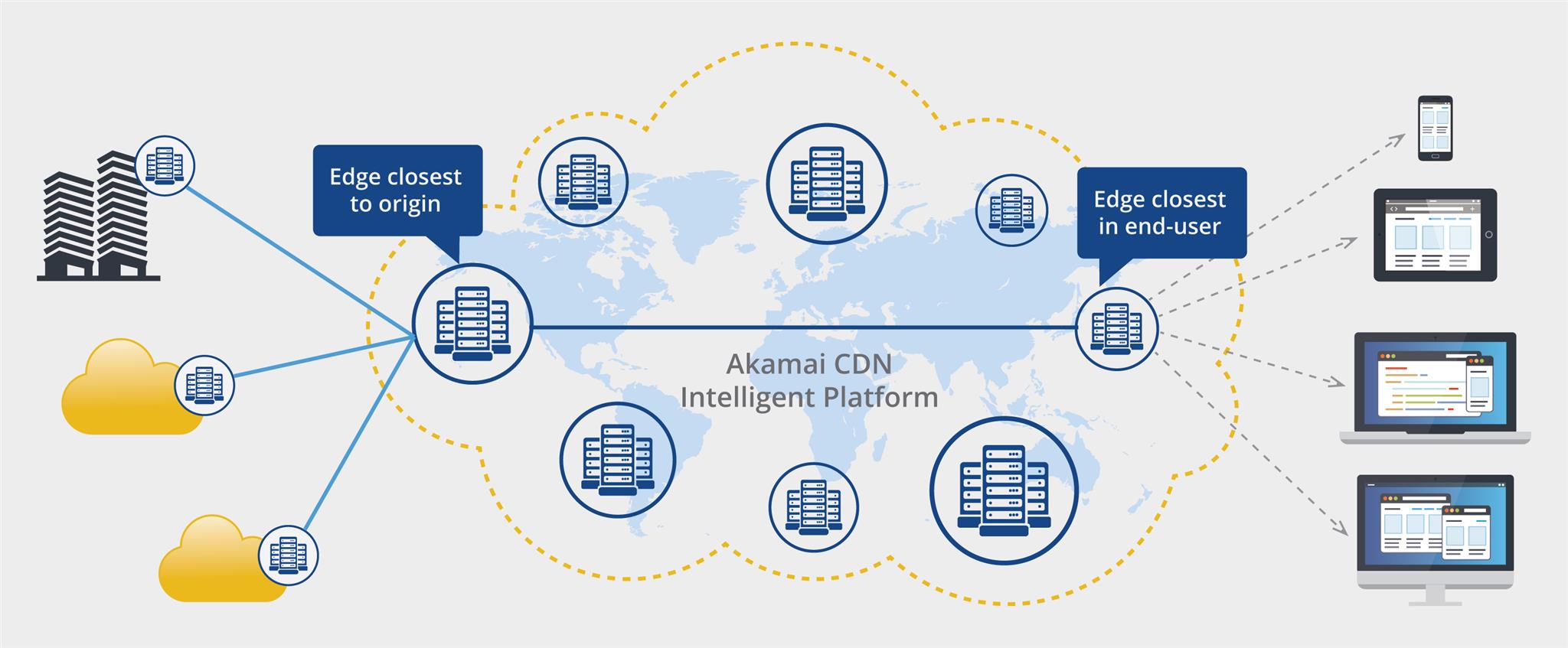
- Distributed Points of Presence (PoPs): CDNs have multiple PoPs around the globe, which distribute web traffic and prevent a single point of failure.
- Content Replication and Caching: Content is cached at multiple PoPs, reducing the likelihood of DDoS attacks overwhelming a single server.
- IP Blocklists: CDNs maintain IP blocklists to ban malicious actors and prevent them from accessing protected resources.
Protection Against Vulnerabilities:
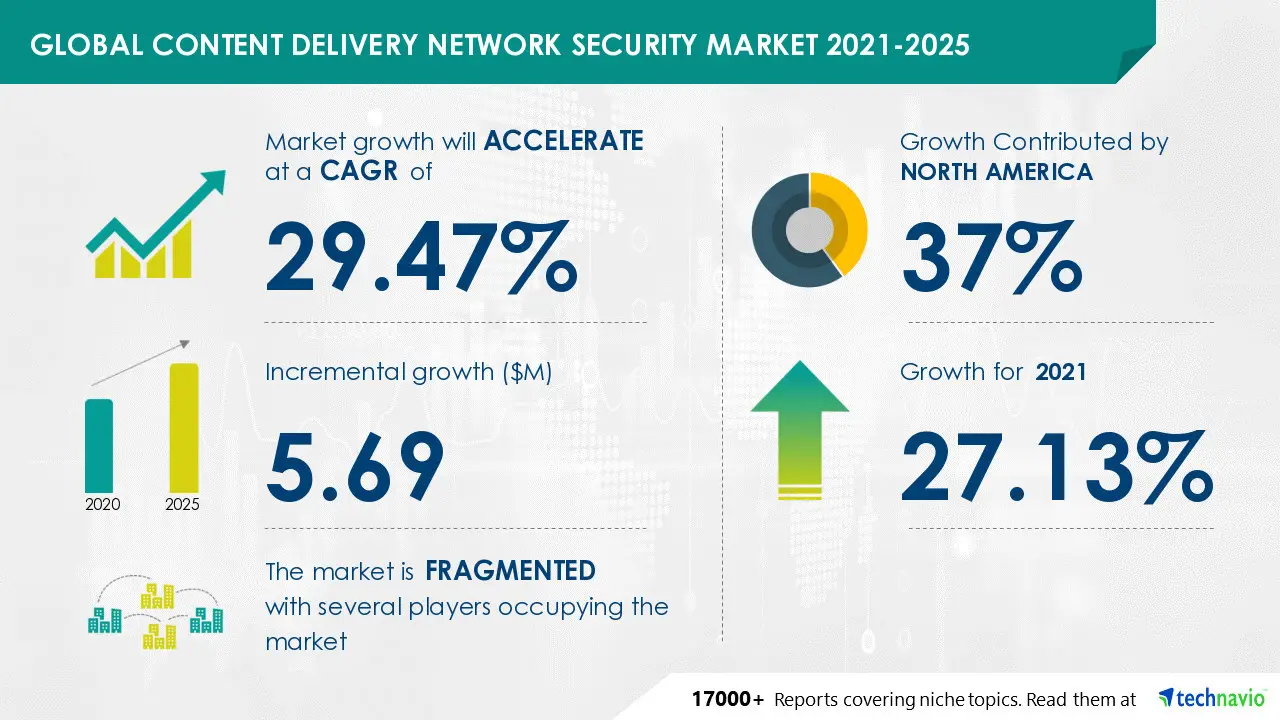
- Regular Security Patches: CDNs regularly apply security patches to address software vulnerabilities and mitigate known exploits.
- Security Monitoring and Alerts: CDNs continuously monitor for security threats and provide alerts to administrators.
- Compliance with Security Standards: CDNs often adhere to security standards such as ISO 27001 and PCI DSS, ensuring compliance with industry best practices.
Other Security Benefits:
- Reduced Latency and Load Balancing: CDNs distribute content closer to users, which reduces latency and improves security by reducing the risk of data interception.
- Centralized Access Control: CDNs provide centralized access control, allowing administrators to manage user access and enforce security policies from a single point.
- Enhanced Reputation: Using a reputable and secure CDN can enhance the security reputation of a website or application.## Security Benefits Of Using A Content Delivery Network
Executive Summary
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) offer numerous security benefits for businesses. They protect websites and applications from various cyber threats, enhance data privacy, and improve compliance with industry regulations. By leveraging CDNs, organizations can safeguard their digital assets, maintain customer trust, and ensure the continuity of their online operations.
Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, protecting websites and applications from cyber threats is of paramount importance. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) play a crucial role in enhancing website security by distributing content across multiple servers located worldwide. This distributed architecture offers numerous security advantages, including:
FAQs
-
What is a Content Delivery Network (CDN)?
A CDN is a globally distributed network of servers that delivers content, such as websites, videos, and images, to users based on their geographic location. It improves website performance, reduces latency, and enhances the user experience. -
How does a CDN improve website security?
CDNs provide various security features, such as DDoS mitigation, WAF, and SSL encryption, which help protect websites from cyber threats, malicious traffic, and data breaches. -
What types of security threats can a CDN mitigate?
CDNs can mitigate various cyber threats, including DDoS attacks, malware injections, phishing attempts, and data breaches. They also help prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information and protect websites from spam and other malicious activities.
DDoS Mitigation
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks are designed to overwhelm a website or server with excessive traffic, causing the website to become inaccessible. CDNs can mitigate DDoS attacks by absorbing and filtering malicious traffic, ensuring that legitimate users can continue to access the website.
- Geo-blocking: Restricts access to malicious traffic based on geographic location.
- Rate Limiting: Limits the number of requests from a single source, preventing DDoS attacks.
- Blacklisting: Blocks known malicious IP addresses to prevent further attacks.
- Load Balancing: Distributes traffic across multiple servers, reducing the impact of DDoS attacks.
Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A WAF is a security measure that filters incoming traffic and blocks malicious requests based on a set of predefined rules. CDNs can integrate WAFs into their network, providing enhanced protection against web application vulnerabilities and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- SQL Injection Prevention: Blocks SQL injection attacks that attempt to manipulate database queries.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Prevention: Protects against XSS attacks that inject malicious code into web pages.
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) Prevention: Prevents unauthorized actions on behalf of legitimate users by blocking CSRF attacks.
- Malware Scanning: Scans web traffic for malware and blocks access to infected content.
SSL Encryption
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) encryption ensures that data transmitted between a website and a user’s browser is encrypted, protecting it from eavesdropping and data breaches. CDNs can encrypt traffic using SSL certificates, enhancing data privacy and compliance with industry regulations.
- Data Protection: Encrypts sensitive data, such as customer information and financial transactions, to prevent unauthorized access.
- Compliance: Meets industry regulations, such as PCI DSS and HIPAA, which require the protection of sensitive data.
- Improved Customer Trust: Demonstrates commitment to data security, building customer trust and credibility.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Benefits: Encrypted websites receive a slight ranking boost in search engine results.
Data Redundancy and Disaster Recovery
CDNs store content on multiple servers across various locations, ensuring data redundancy and minimizing the risk of data loss. In case of a server outage or disaster, content can be seamlessly served from other servers, maintaining website availability and protecting against data corruption.
- Data Replication: Replicates data across multiple servers, ensuring the continuity of content delivery.
- Geographic Distribution: Stores content on servers in different geographic regions, improving availability and performance.
- Disaster Recovery: Provides a backup plan in case of natural disasters or hardware failures, ensuring business continuity.
Improved Compliance
CDNs assist organizations in meeting industry regulations and compliance requirements by providing security features, such as data encryption, access control, and auditing tools. By leveraging CDNs, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to data protection and compliance, avoiding potential legal liabilities and fines.
- Privacy Regulations: Complying with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, by protecting personal data and providing transparency to users.
- PCI DSS Compliance: Facilitating compliance with PCI DSS standards for protecting payment card data.
- HIPAA Compliance: Supporting healthcare organizations in meeting HIPAA regulations for data security and patient privacy.
Conclusion
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) offer a comprehensive suite of security benefits for businesses, protecting websites and applications from cyber threats, enhancing data privacy, and improving compliance with industry regulations. By leveraging CDNs, organizations can safeguard their digital assets, maintain customer trust, and ensure the continuity of their online operations. In the face of evolving cyber threats and stringent data protection laws, CDNs have become indispensable tools for businesses seeking to protect their websites and applications.
Relevant Keyword Tags
- Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Website Security
- DDoS Mitigation
- Web Application Firewall (WAF)
- Data Security
