[Reverse Engineering Security]
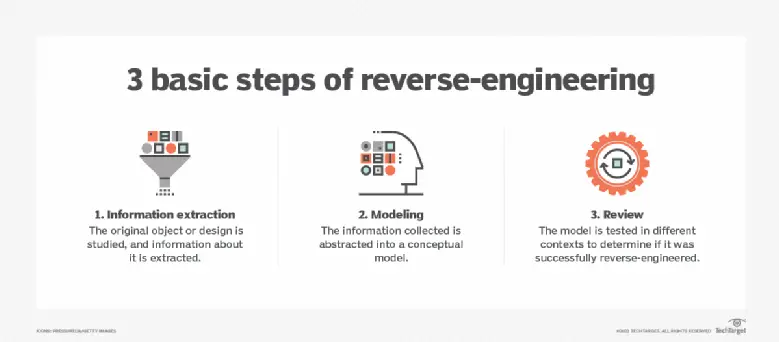
Executive Summary
Reverse engineering security involves scrutinizing software, hardware, or communication protocols to discern their inner workings. This practice aids in detecting vulnerabilities, bolstering security mechanisms, and safeguarding against cyberthreats. By delving into the intricate details of systems, security professionals can unearth potential weaknesses, enabling the development of robust defenses.

Introduction
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, the significance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. With the advent of sophisticated cyberattacks, organizations and individuals alike face an ongoing battle to protect their sensitive data and systems. Reverse engineering security emerges as a critical weapon in this cybersecurity arsenal, empowering experts to dissect and analyze systems, unraveling their innermost secrets.
Subtopics and Descriptions
Vulnerability Assessment
Vulnerability assessment entails identifying potential weaknesses within a system that could be exploited by malicious actors.
- Vulnerability Identification: Scanning and analyzing systems to detect known and previously undiscovered vulnerabilities.
- Impact Analysis: Assessing the severity and impact of vulnerabilities to prioritize remediation efforts.
- Exploitation Techniques: Determining methods that attackers could use to leverage vulnerabilities.
Security Mechanism Evaluation
Security mechanisms are employed to protect systems from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats. Evaluating these mechanisms is crucial for ensuring their effectiveness.
- Cipher Analysis: Deciphering and assessing cryptographic algorithms and protocols to identify vulnerabilities.
- Access Control Review: Examining authorization and authentication mechanisms to detect potential bypasses.
- Network Traffic Inspection: Analyzing network traffic patterns to identify suspicious activities and anomalies.
Protocol Analysis
Communication protocols govern how data is transmitted and exchanged between systems. Reverse engineering security involves analyzing these protocols to identify potential weaknesses and improve security.
- Protocol Specification Review: Studying protocol specifications to understand their functionality and limitations.
- Implementation Verification: Verifying that protocol implementations adhere to specifications and are free from vulnerabilities.
- Traffic Monitoring: Monitoring protocol traffic to detect malicious or unauthorized activities.
Hardware Analysis
Hardware devices can harbor vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers. Reverse engineering security enables the analysis of hardware to uncover potential threats and bolster defenses.
- Circuit Design Examination: Inspecting hardware circuit designs to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Firmware Analysis: Analyzing firmware code to uncover hidden functionality or exploitable bugs.
- Side-Channel Attacks Assessment: Evaluating the susceptibility of hardware to side-channel attacks, such as power analysis or electromagnetic emanations.
Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence encompasses the collection and analysis of information about cyber threats. Reverse engineering security plays a vital role in understanding the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) of attackers.
- Malware Analysis: Dissecting malware samples to uncover their capabilities, infection vectors, and potential impact.
- Botnet Investigation: Identifying and analyzing botnets, networks of compromised devices, to understand their command-and-control mechanisms.
- Attacker Techniques Examination: Studying the methods and techniques used by attackers to gain unauthorized access and exploit vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering security is an indispensable practice in the realm of cybersecurity. By methodically examining systems and protocols, security professionals can uncover vulnerabilities, evaluate security mechanisms, and gain a comprehensive understanding of potential threats. This knowledge empowers organizations and individuals to proactively mitigate risks, strengthen defenses, and safeguard their sensitive data from the ever-evolving threat landscape.
Keyword Tags
- Reverse Engineering Security
- Vulnerability Assessment
- Security Mechanism Evaluation
- Protocol Analysis
- Threat Intelligence
FAQ
Q: What are the main benefits of reverse engineering security?
A: Reverse engineering security provides insights into system vulnerabilities, strengthens security mechanisms, and enhances threat intelligence.
Q: What tools are commonly used for reverse engineering security?
A: Tools include disassemblers, debuggers, protocol analyzers, and hardware emulation platforms.
Q: How can reverse engineering security help prevent cyberattacks?
A: By identifying vulnerabilities and improving security measures, reverse engineering security can reduce the likelihood and impact of cyberattacks.
Q: What are common challenges in reverse engineering security?
A: Challenges include dealing with obfuscated code, encrypted data, and complex hardware architectures.
Q: How can organizations effectively implement reverse engineering security?
A: Establishing a structured process, employing skilled security professionals, and leveraging automation tools are key to effective implementation.

