Reverse Engineering in the Manufacturing Industry

Reverse engineering is a process of analyzing an existing product to understand its design, function, and manufacturing process. In the manufacturing industry, reverse engineering is used for a variety of purposes, including:
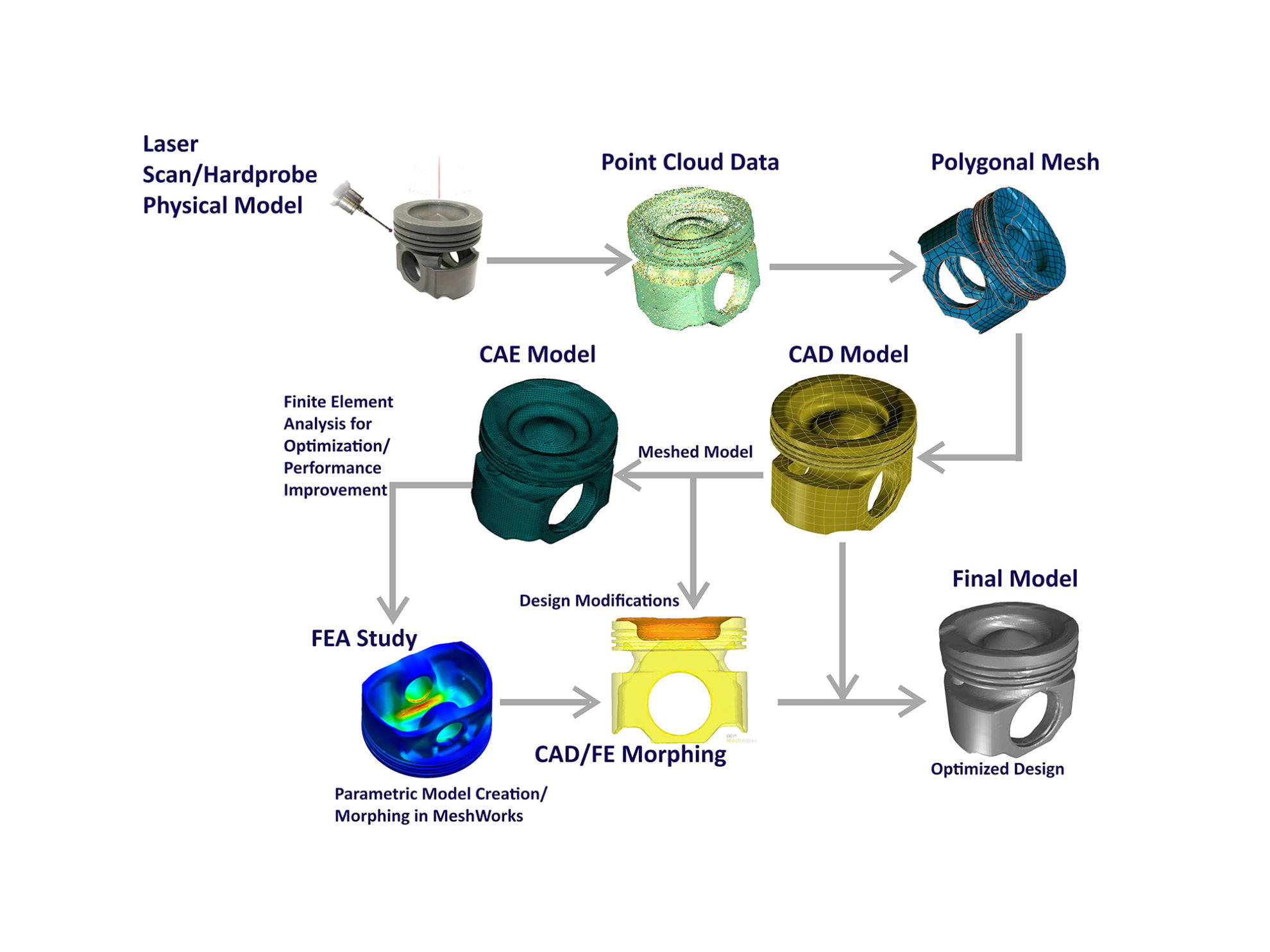
- Product improvement: By understanding the design and manufacturing process of a competing product, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement in their own products.
- Process optimization: Reverse engineering can help manufacturers to identify inefficiencies in their own manufacturing processes and develop ways to improve them.
- Cost reduction: By understanding the manufacturing process of a cheaper product, manufacturers can identify ways to reduce their own costs.
- New product development: Reverse engineering can help manufacturers to develop new products by providing them with insights into the design and manufacturing processes of similar products.
The process of reverse engineering typically involves the following steps:

- Disassembly: The product is disassembled into its individual components.
- Inspection: The components are inspected to determine their design, function, and materials.
- Analysis: The components are analyzed to understand how they fit together and how they work.
- Documentation: The results of the analysis are documented in a report.
Reverse engineering can be a valuable tool for manufacturers who are looking to improve their products, processes, or costs.
Here are some of the commonly used reverse engineering tools:
- coordinate measuring machines (CMMs)
- laser scanners
- X-ray CT scanners
- computer-aided design (CAD) software
The use of reverse engineering is increasing in the manufacturing industry as manufacturers look for ways to improve their products and processes. By understanding the design and manufacturing processes of competing products, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement in their own products and processes.## Reverse Engineering In The Manufacturing Industry
Executive Summary
Reverse engineering is a critical process in the manufacturing industry for a variety of reasons, from enhancing product design to boosting productivity and innovation. Its systematic approach fosters innovation by allowing manufacturers to analyze competing products and determine their inner workings, enabling them to improve upon existing designs, optimize processes, and identify potential areas for improvement. This ultimately leads to more efficient and cost-effective manufacturing practices.
Introduction:
Reverse engineering is a valuable tool that empowers manufacturers to break down and analyze existing products in order to understand their design, construction, and functionality. This information is then utilized to create new products or enhance existing ones, incorporating superior features and improvements.
FAQs:
- What are the benefits of reverse engineering?
- Enhanced product design
- Maximized productivity
- Increased innovation
- Optimized product performance
- Reduced manufacturing costs
- How does reverse engineering work?
- Disassembling the product
- Analyzing its components
- Determining the product’s design and functionality
- Creating a new or improved product based on the analyzed information
- What are the applications of reverse engineering in manufacturing?
- Product improvement
- Process optimization
- Innovation
- Quality control
- Cost reduction
Top 5 Subtopics:
1. Product Design and Development
- Identifying Opportunities: Reverse engineering enables manufacturers to gain insights into innovative design concepts, enhancing their product development capabilities.
- Benchmarking: Benchmarking competitors’ products aids in understanding industry trends, identifying competitive advantages, and establishing design benchmarks.
- Troubleshooting: Analyzing existing products provides valuable information for troubleshooting potential design flaws, ensuring reliability and performance optimization.
- Customization: Reverse engineering allows for the creation of customized products tailored to specific customer requirements, increasing customer satisfaction and enhancing product value.
2. Process Optimization
- Productivity Improvement: Reverse engineering helps identify areas for process improvement, reducing production time, optimizing resource allocation, and increasing overall efficiency.
- Waste Reduction: By studying efficient designs, manufacturers can identify ways to minimize material usage, reduce waste, and enhance environmental sustainability.
- Quality Control: Robust quality control measures can be implemented by examining the design and construction of competitor’s products, ensuring the highest quality standards.
- Innovation: Reverse engineering fosters a culture of continuous improvement in manufacturing processes and practices, promoting innovation and adaptability.
3. Quality Control
- Product Inspection: Reverse engineering is an effective tool for inspecting incoming components and finished goods, verifying their conformance to specifications and standards.
- Failure Analysis: Identifying the root causes of product failures through reverse engineering helps prevent future failures and enhance product reliability.
- Material Analysis: Analyzing competitor’s products enables manufacturers to gain insights into material selection, composition, and properties, guiding their own material choices.
- Quality Management: Reverse engineering provides a framework for establishing comprehensive quality management systems, ensuring the production of high-quality products that meet customer expectations.
4. Innovation
- New Product Ideas: Reverse engineering inspires the generation of novel products, helping manufacturers stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
- Technology Adaptation: Integrating new technologies into existing designs through reverse engineering accelerates innovation and fosters technological advancements.
- Patent Protection: Understanding competitive designs through reverse engineering aids in identifying potential patent infringements, safeguarding intellectual property.
- Research and Development: Reverse engineering provides a solid foundation for research and development, facilitating the creation of innovative concepts and advanced manufacturing techniques.
5. Cost Reduction
- Material Cost Optimization: Reverse engineering assists manufacturers in optimizing material selection and usage, reducing costs without compromising on product quality.
- Process Efficiency: Enhanced efficiency through process optimization leads to reduced production costs, increasing profit margins and competitiveness.
- Design Optimization: Identifying inefficiencies in competitor’s products through reverse engineering allows for improved designs, resulting in reduced manufacturing costs.
- Waste Reduction: Minimizing waste by analyzing efficient designs not only benefits the environment but also the manufacturer’s bottom line.
Conclusion:
Reverse engineering has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, empowering companies to achieve higher levels of efficiency, innovation, and profitability. By systematically dismantling and analyzing existing products, manufacturers can uncover valuable insights into design, construction, and functionality. This information is then strategically utilized to enhance product development, optimize processes, boost quality control, cultivate innovation, and ultimately reduce manufacturing costs. As the industry continues to evolve amidst rapid technological advancements, reverse engineering will remain an indispensable tool for manufacturers striving to stay competitive and drive future success.
Keyword Tags:
- Reverse engineering
- Manufacturing
- Product development
- Process optimization
- Innovation
- Quality control
- Cost reduction
