Reverse Engineering in the Art World: Replicating Lost Works

Reverse engineering is a process of taking something apart and analyzing its construction in order to create a replica. This process has been used for centuries in many fields, including the art world. Artists have long used reverse engineering to replicate lost or damaged works of art.
History of Reverse Engineering in Art
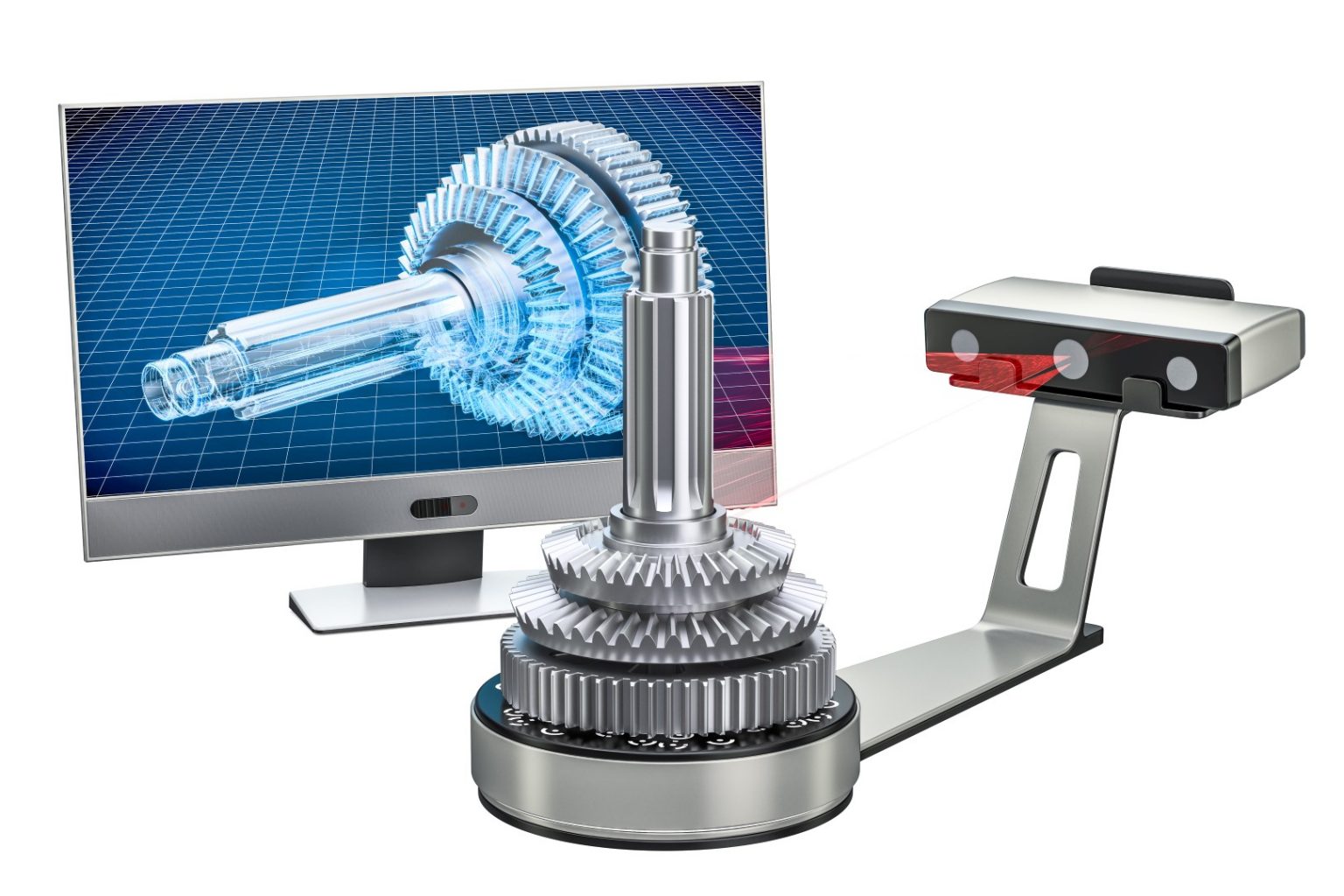

The practice of reverse engineering in the art world dates back to ancient times. One of the earliest examples of this practice is the Egyptian artist Thutmose, who lived during the 18th dynasty (1550-1292 BC). Thutmose was known for his ability to replicate ancient Egyptian statues and paintings.
In the Renaissance, artists such as Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo used reverse engineering to study the works of classical artists. They would often make drawings or models of ancient sculptures and paintings, which they would then use to create their own works of art.
In the 19th and 20th centuries, reverse engineering was used by artists to replicate lost or damaged works of art. For example, the French artist Jean-Louis David used reverse engineering to create a replica of the ancient Greek statue of Apollo Belvedere. The American artist John Singer Sargent used reverse engineering to create a replica of the painting “The Ghent Altarpiece” by Jan van Eyck.
How Reverse Engineering Works
The process of reverse engineering in the art world typically involves the following steps:
- The artist first examines the original work of art and takes detailed notes about its construction.
- The artist then makes drawings or models of the original work of art.
- The artist uses the drawings or models to create a replica of the original work of art.
The replica is not always an exact copy of the original work of art. The artist may make changes to the replica, such as using different materials or changing the size or color of the work of art.
Advantages of Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering can be a valuable tool for artists who want to replicate lost or damaged works of art. There are several advantages to using reverse engineering, including:
- It allows artists to study the construction of the original work of art in great detail.
- It helps artists to understand the techniques and materials that were used to create the original work of art.
- It provides artists with a starting point for creating their own works of art.
Disadvantages of Reverse Engineering
There are also some disadvantages to using reverse engineering, including:
- It can be a time-consuming and expensive process.
- The replica is not always an exact copy of the original work of art.
- The artist may not have the same level of skill as the artist who created the original work of art.
Overall, reverse engineering can be a valuable tool for artists who want to replicate lost or damaged works of art. However, it is important to be aware of the advantages and disadvantages of using this process before embarking on a reverse engineering project.# Reverse Engineering In The Art World: Replicating Lost Works
Executive Summary
The art world has a long history of innovation, with artists constantly pushing the boundaries of creativity and expression. In recent years, there has been a growing trend of reverse engineering in the art world. This involves using new scientific techniques and technologies to recreate or replicate lost works of art. This trend has been met with both excitement and skepticism, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about and appreciate art.
Introduction
For centuries, people have been fascinated by lost works of art. Whether it’s the legendary treasures of ancient civilizations or the masterpieces that were destroyed in fires or wars, these works have captured our imagination and left us wondering what they might have looked like. Today, thanks to advances in technology, it is becoming possible to replicate lost works of art with astonishing accuracy.
Subtopics:
1. The Importance of Replicating Lost Works
Lost works of art can provide valuable insights into the past. They can offer clues about historical events, artistic techniques, and cultural values. However, as these works continue to disappear, it becomes increasingly evident that without replicas, a crucial link to our collective history and identity will be severed forever.
- Cultural Significance: Replicating lost works helps preserve and appreciate cultural heritage.
- Educational Value: Replicas serve as educational tools, immersing people in past artistic styles and techniques.
- Emotional Connection: Replicas foster emotional connections between viewers and lost masterpieces, bridging the gap between past and present.
2. Reverse Engineering Techniques
Like detectives piecing together a puzzle, art restorers and conservators employ advanced techniques to reconstruct lost masterpieces. The process involves a blend of science, technology, and meticulous craftsmanship.
- Materials Analysis: Analyzing the pigments, binders, and other materials used in existing artworks provides insights into the original techniques and materials.
- Digital Modeling: 3D scanning and computer modeling techniques digitally recreate lost works, allowing for detailed examination and study.
- Replica Creation: Using a combination of traditional and modern methods, skilled artisans create physical replicas that strive to faithfully reproduce the original.
3. Ethical Considerations
The replication of lost works of art is not without its ethical challenges. Questions arise regarding authenticity, copyright, and the potential for fraud. Balancing these concerns with the desire to preserve and appreciate lost works is essential for responsible reverse engineering practices.
- Authenticity: Replicas lack the historical context and emotional resonance of originals, but they can still hold artistic and cultural value.
- Copyright: The replication of copyrighted works may require permission from the copyright holder, potentially limiting the accessibility of replicas.
- Fraud: To maintain integrity, accurate labeling and clear differentiation between replicas and originals are crucial.
4. Impact on the Art Market
The availability of high-quality replicas can impact the art market. While replicas may not carry the same value as originals, they can provide an alternative for those unable to acquire or exhibit original works.
- Market Value: The availability of replicas can influence the demand and prices of original works.
- Accessibility: Replicas make art more accessible to a broader audience, potentially fostering greater appreciation for art.
- Educational Role: Replicas can serve as educational tools in museums, exhibitions, and educational institutions, enhancing understanding of artistic techniques and styles.
5. The Future of Reverse Engineering
The ongoing advancement of scientific and technological capabilities promises even more sophisticated reverse engineering techniques. This holds the potential to unlock new insights into lost works of art and make them accessible to a wider audience.
- New Materials and Techniques: Future research may lead to the development of new materials and techniques for more accurate and authentic replicas.
- Artificial Intelligence: Integrating AI into reverse engineering processes can enhance the analysis of materials and the recreation of lost works.
- Expanded Application: The application of reverse engineering techniques could be extended to other fields, such as architecture and archaeology.
Conclusion
Replicating lost works of art through reverse engineering has the potential to bridge the gap between the past and the present, allowing us to appreciate and learn from works that would otherwise be lost forever. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more impressive and accurate replicas of lost masterpieces. However, the ethical and practical implications of reverse engineering must be carefully considered to ensure responsible and meaningful replication practices.
Keyword Phrase Tags:
- Reverse engineering in art
- Replication of lost works of art
- Techniques for reverse engineering art
- The ethics of reverse engineering art
- Impact of reverse engineering on the art market

It is an interesting dilemma. Thanks for sharing your thoughts.
I don’t think copying art is ever right. I think that’s cheating.!!!!
I wonder if this could be used to recreate other lost works of art. Also what are the implications for copyright?
I’m not sure if I agree with this. I think there’s a difference between copying a work of art and replicating a lost work. This seems like a slippery slope to me.
So, what you’re saying is that we can now use technology to copy lost works of art. I wonder what the original artists would think about that.
Oh, great. So now we can just copy all the lost works of art. This is a perfect example of how technology is ruining everything.
I wonder if we could use this technology to create a replica of the Mona Lisa with a mustache.
This is a fascinating application of technology. I wonder if there are any ethical concerns that need to be considered.
I’m sure the insurance companies can’t wait to get their hands on this. This was written very well. Thank you.
I think it will be interesting to see how this technology develops in the future. I wonder if it will eventually be possible to create perfect replicas of lost works of art.