Reverse Engineering in Medical Devices: Enhancing Healthcare

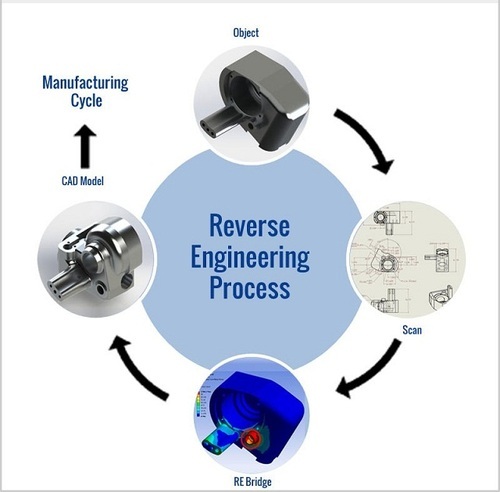
Reverse engineering has become an integral part of the medical device industry, playing a crucial role in enhancing healthcare. This process involves deconstructing existing medical devices to gain insights into their design, functionality, and manufacturing processes. It allows manufacturers to improve upon existing devices, identify potential risks, and even create new and innovative solutions.
Benefits of Reverse Engineering in Medical Devices
-
Product Improvement: Reverse engineering enables manufacturers to analyze the strengths and weaknesses of existing medical devices. By understanding the design principles and materials used, they can identify areas for improvement. This leads to the development of next-generation medical devices with enhanced features, better performance, and increased reliability.
-
Risk Mitigation: Reverse engineering helps uncover hidden defects or potential risks associated with existing medical devices. By thoroughly examining the design and manufacturing processes, manufacturers can identify potential failure points and take steps to mitigate these risks. This results in safer and more reliable medical devices, reducing the likelihood of device malfunctions or adverse events.
-
Cost Reduction: Reverse engineering can help manufacturers identify cost-saving opportunities. By analyzing the materials and manufacturing processes used in existing devices, they can find ways to reduce production costs without compromising quality. This can lead to more affordable medical devices, making them more accessible to patients and healthcare providers.
-
Innovation: Reverse engineering fosters innovation by inspiring manufacturers to develop new and improved medical devices. By studying successful designs and understanding the underlying principles, engineers can come up with innovative solutions that address unmet medical needs. This leads to a continuous cycle of innovation, driving the progress of medical technology.
Applications of Reverse Engineering in Medical Devices
-
Implantable Devices: Reverse engineering is commonly used to analyze implantable devices such as pacemakers and artificial joints. By studying the design and materials used in existing devices, manufacturers can improve their functionality, reliability, and longevity.
-
Surgical Instruments: Reverse engineering is employed to create better surgical instruments with improved ergonomics, precision, and safety. By analyzing the design and performance of existing instruments, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement and develop innovative new designs.
-
Drug Delivery Systems: Reverse engineering helps develop more effective and targeted drug delivery systems. By studying the design and mechanisms of existing systems, manufacturers can create improved systems that deliver drugs more precisely and efficiently, reducing side effects and improving patient outcomes.
-
Medical Imaging Systems: Reverse engineering is used to analyze medical imaging systems such as MRI machines and ultrasound scanners. By understanding the design principles and underlying technologies, manufacturers can develop more advanced systems with improved image quality, speed, and accuracy.
Ethical Considerations in Reverse Engineering
While reverse engineering ofrece significant benefits, it raises ethical concerns related to intellectual property rights, patents, and patient safety. It is imperative for manufacturers to adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations to ensure that reverse engineering is conducted responsibly and does not infringe upon the intellectual property rights of others.
Conclusion:
Reverse engineering plays a vital role in enhancing healthcare by enabling manufacturers to improve existing medical devices, identify potential risks, reduce costs, and drive innovation. It has become an indispensable tool in the medical device industry, contributing to the development of safer, more reliable, and more effective medical technologies. However, it is essential to address ethical considerations and ensure that reverse engineering is conducted responsibly, respecting intellectual property rights and prioritizing patient safety.# Reverse Engineering In Medical Devices: Enhancing Healthcare
Executive Summary
Reverse engineering in medical devices involves deconstructing existing products to analyze their design, functionality, and materials. This process empowers manufacturers with valuable insights, enabling them to innovate, improve safety, and optimize performance in their medical device development. This article delves into the significance of reverse engineering in medical devices, exploring key subtopics such as intellectual property considerations, regulatory compliance, and quality assurance. The discussion also encompasses the benefits of this practice in terms of cost reduction, risk mitigation, and fostering innovation. By adopting reverse engineering, healthcare organizations can gain a competitive advantage, enhance patient outcomes, and drive advancements in medical technology.
Introduction
Reverse engineering in the medical device industry is a meticulous process that involves meticulously dissecting and analyzing existing medical devices to gain firsthand insights into their design, engineering principles, and manufacturing processes. This valuable knowledge helps manufacturers identify areas for potential improvements, which can pave the way for groundbreaking advancements in the medical device industry.
Intellectual Property Considerations
When embarking on reverse engineering, manufacturers must carefully navigate the ever-evolving landscape of intellectual property (IP) rights. It is crucial to understand and respect patent protections, trademarks, and copyrights associated with existing medical devices. Conducting thorough IP research, evaluating the scope of protection, and collaborating with legal experts are essential steps to ensure compliance and avoid infringement.
-
IP Research: Conduct extensive research to identify valid patents, trademarks, and copyrights related to the medical device in question.
-
Legal Consultation: Collaborate with IP attorneys to assess the enforceability, validity, and scope of IP protections, ensuring compliance.
-
Clearance and Licensing: Seek necessary clearances or licenses from the IP rights holders when appropriate to avoid potential IP infringement.
Regulatory Compliance
Manufacturers engaged in reverse engineering must adhere to stringent regulatory requirements to ensure the safety and efficacy of their products. These regulations encompass various aspects, including design controls, quality management systems, and clinical trials. Compliance with regulatory standards is non-negotiable and plays a pivotal role in ensuring the integrity and effectiveness of medical devices.
-
Design Controls: Implement a robust design control system that encompasses all stages of the product development lifecycle.
-
Quality Management: Establish a comprehensive quality management system aligned with ISO 13485 or other applicable standards.
-
Clinical Trials: Conduct rigorous clinical trials to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of the medical device before market authorization.
Quality Assurance
A meticulous quality assurance program is paramount in reverse engineering to ensure that the resulting products meet or exceed industry standards. Implementing stringent quality control processes and validation procedures is essential to guarantee the accuracy, reliability, and performance of the medical devices. Systematic monitoring and continuous improvement efforts are key to maintaining quality throughout the product lifecycle.
-
Quality Control: Establish rigorous quality control procedures to meticulously inspect and test medical devices, ensuring conformance to specifications.
-
Validation: Perform comprehensive validation studies to demonstrate that the medical device meets its intended use and complies with regulatory requirements.
-
Continuous Improvement: Foster a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging feedback, implementing corrective and preventive actions, and optimizing processes.
Benefits of Reverse Engineering in Medical Devices
Reverse engineering offers a multitude of benefits to manufacturers in the medical device industry. These advantages range from economic gains to improved product quality and innovation. By leveraging reverse engineering, manufacturers can streamline processes, reduce costs, mitigate risks, and accelerate innovation, ultimately propelling the industry forward.
-
Cost Reduction: By analyzing existing designs, manufacturers can identify areas for optimization, leading to reduced material and production costs.
-
Risk Mitigation: Thoroughly understanding the design and functionality of existing devices helps manufacturers identify potential risks early on, enabling proactive mitigation strategies.
-
Innovation and Differentiation: Reverse engineering sparks creativity and fosters innovation, encouraging manufacturers to develop unique and differentiated medical devices that address unmet clinical needs.
-
Knowledge Transfer: By dissecting existing devices, engineers and designers gain valuable insights into the latest technologies and trends, facilitating knowledge transfer and professional development.
-
Streamlined Development: Reverse engineering allows manufacturers to leverage existing designs as a starting point, accelerating the product development process and reducing time-to-market.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering has emerged as a transformative force in the medical device industry, enabling manufacturers to glean valuable insights from existing products and translate them into groundbreaking innovations. By carefully navigating intellectual property considerations, adhering to regulatory compliance, and implementing stringent quality assurance measures, manufacturers can harness the power of reverse engineering to develop safer, more effective, and cost-efficient medical devices. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, reverse engineering will undoubtedly play an increasingly pivotal role in driving advancements, improving patient outcomes, and enhancing the overall quality of healthcare.
Keyword Phrase Tags
- Reverse Engineering in Medical Devices
- Intellectual Property Considerations in Reverse Engineering
- Regulatory Compliance in Reverse Engineering
- Quality Assurance in Reverse Engineering
- Benefits of Reverse Engineering in Medical Devices

Thnak you for this insightful article very good !
I dont agree reverse engineering is always beneficial . Sometimes , companies just copy others work without improving it
Reverse engineering played a keyrole in the development of open-source medical devices, which have the potential to revolutionise healthcare in developing countries
While i appreciate the benefits of reverse engineering , i wonder if it sometimes discourages companies to invest in research when they know their products could be easily copied.
So, reverse engineering is basically like medical device archeology, unearthing the secrets of the past to build a better future. Except instead of Indiana Jones, we have engineers with stethoscopes.
Oh yes, reverse engineering is fantastic, especially when companies use it to create cheap knock-offs that put patients at risk. Way to go!
Reverse engineering in medical devices is like a game of Operation, but instead of tweezers, you’re using microscopes and instead of a metal tray, you’re operating on a beating heart. Talk about high stakes!
Reverse engineering has it’s place in the medical field. It can help reduce costs, foster innovation, and improve patient care. But let’s not kid ourselves, it can also lead to unscrupulous practices and safety concerns
I wonder if reverse engineering could be used to develop personalized medical devices tailored to individual patient’s needs? That would be a game-changer!
Reverse engineering can be a powerful tool, but it must be used responsibly. We need clear ethical guidelines to prevent companies from exploiting others’ innovations and to ensure patient safety.
At the end of the day, the goal of reverse engineering in medical devices should be to improve healthcare. If it leads to better, more affordable, and safer devices, then it’s a win-win.
The legal and ethical implications of reverse engineering in medical devices are complex. We need to strike a balance between encouraging innovation and protecting intellectual property rights.
As a patient, I’m grateful for the potential of reverse engineering to make medical devices more affordable and accessible. But I urge companies to prioritize patient safety and ethical practices.