Reverse Engineering for Large Enterprises: A Strategic Imperative for Innovation

In the highly competitive and rapidly evolving business landscape, large enterprises are increasingly embracing reverse engineering as a strategic imperative for driving innovation and gaining competitive advantage. Reverse engineering involves the deconstruction of existing products or technologies to understand their design, functionality, and underlying principles. This systematic process provides valuable insights that can inform the development of new products, improve existing offerings, and identify potential risks and opportunities.
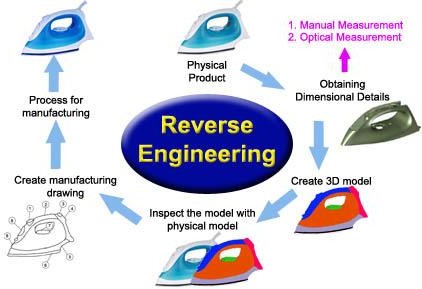
For large enterprises, reverse engineering offers significant benefits:
1. Competitive Intelligence: Reverse engineering allows companies to analyze the strengths and weaknesses of their competitors’ products. This information can be invaluable for identifying industry trends, market gaps, and potential areas for differentiation. By studying the design and technology employed by competitors, enterprises can gain a deeper understanding of industry best practices and potential disruptors.
2. New Product Development: Reverse engineering can accelerate the development of new products by providing a starting point for design and innovation. By examining successful products in the market, enterprises can leverage proven concepts and technologies to create unique and competitive offerings. This process can reduce the time and cost associated with R&D, enabling faster time-to-market and a response to evolving customer needs.
3. Quality Assurance: Reverse engineering can help enterprises improve the quality of their products by identifying potential design flaws and manufacturing defects. By analyzing existing products, engineers can identify weaknesses, conduct root cause analysis, and implement preventive measures to enhance the resilience and reliability of their own designs. This proactive approach reduces the risk of product failures and costly recalls.
4. Intellectual Property Protection: Reverse engineering can assist companies in protecting their intellectual property (IP) by detecting potential infringement and providing evidence in IP disputes. By examining the underlying design of competing products, enterprises can determine if their IP has been infringed upon and take appropriate legal action to protect their innovation.
5. Risk Management: Reverse engineering can help enterprises identify and mitigate potential risks associated with the design, manufacturing, and use of products. By studying the behavior of existing products, engineers can anticipate potential failure modes and design solutions to address them. This proactive approach enhances product safety, reduces legal liability, and safeguards the reputation of the enterprise.
Implementing Reverse Engineering in Large Enterprises:
To effectively implement reverse engineering in large enterprises, several key considerations should be addressed:
- Scalability: Large enterprises require a scalable reverse engineering process that can handle the analysis of multiple products simultaneously.
- Collaboration: Reverse engineering often involves cross-functional collaboration, requiring effective communication and coordination among engineers, product managers, and quality assurance teams.
- Data Management: The analysis of large volumes of data is essential for comprehensive reverse engineering. Enterprises need robust data management systems to store, organize, and analyze the collected information.
- Expertise: Reverse engineering requires specialized expertise in engineering, materials science, and manufacturing processes. Enterprises should invest in developing internal capabilities or partner with external experts to ensure successful execution.
- Ethics and Compliance: Reverse engineering must be conducted ethically and in compliance with intellectual property laws and regulations. Enterprises should establish clear guidelines to ensure proper conduct and avoid IP infringement.
By addressing these considerations and adopting a strategic approach to reverse engineering, large enterprises can unlock the full potential of this powerful technique to drive innovation, enhance competitiveness, and mitigate risk.## Reverse Engineering for Large Enterprises
Executive Summary
Reverse engineering is a powerful tool that can help large enterprises gain a competitive edge by understanding the inner workings of their competitors’ products and processes. By systematically deconstructing and analyzing these products and processes, enterprises can identify areas for improvement and innovation, enhance their own offerings, and ultimately increase market share. However, successful reverse engineering requires a strategic approach and a deep understanding of the specific industry and competitive landscape.
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving business environment, large enterprises face intense competition from both established rivals and emerging disruptors. To stay ahead in this competitive arena, enterprises must continuously seek ways to improve their products and services and gain a deeper understanding of their competitors’ strategies. Reverse engineering is a proven approach that enables enterprises to extract valuable knowledge from their competitors’ products and processes, empowering them to make informed decisions and gain a strategic advantage.
FAQs
-
What is reverse engineering?
- Reverse engineering involves systematically deconstructing and analyzing a product or process to understand its design, functionality, and underlying principles.
-
Why is reverse engineering important for large enterprises?
- It provides valuable insights into competitors’ products and processes, helps identify areas for improvement, and enables the development of innovative solutions.
-
What are the benefits of reverse engineering?
- It enhances product development, reduces time-to-market, and offers opportunities for cost optimization and competitive benchmarking.
Top 5 Subtopics in Reverse Engineering for Large Enterprises
1. Product Design Analysis
- Identify the materials, components, and manufacturing processes used in competitor products.
- Analyze product features, functionality, and user experience to identify areas for improvement.
- Deconstruct the product’s structure, architecture, and design principles.
- Reverse engineer the product’s software and firmware to understand its codebase and algorithms.
- Evaluate the product’s strengths and weaknesses compared to the enterprise’s own offerings.
2. Process Optimization
- Map out the competitor’s manufacturing and supply chain processes.
- Identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for cost reduction.
- Analyze the competitor’s quality control and testing procedures.
- Study the competitor’s best practices and areas where their processes can be improved.
- Develop recommendations for process enhancements and operational improvements.
3. Competitive Intelligence
- Gather insights into the competitor’s product strategy, market positioning, and customer base.
- Analyze the competitor’s patents, trademarks, and other intellectual property.
- Monitor the competitor’s financial performance, industry news, and analyst reports.
- Identify the competitor’s strengths, weaknesses, and potential threats.
- Develop strategies to neutralize the competitor’s advantages and capitalize on their weaknesses.
4. Innovation and R&D
- Use insights gained from reverse engineering to generate new product ideas and concepts.
- Identify potential technology breakthroughs and disruptive technologies.
- Explore new materials, components, and manufacturing techniques.
- Foster a culture of innovation and encourage cross-functional collaboration.
- Develop a roadmap for future product development and technology initiatives.
5. Cost Reduction and Value Engineering
- Analyze the competitor’s production costs and identify areas for cost savings.
- Identify opportunities for material substitution, design optimization, and process improvements.
- Conduct value engineering studies to reduce costs without compromising product quality or performance.
- Develop strategies for supply chain optimization and cost reduction initiatives.
- Evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of reverse engineering and ensure a positive return on investment.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering is a valuable tool that can provide large enterprises with a wealth of insights into their competitors’ products, processes, and strategies. By systematically deconstructing and analyzing these elements, enterprises can gain a deeper understanding of their competitive landscape and identify opportunities for improvement and innovation. However, successful reverse engineering requires a structured approach, expertise in the relevant industry, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By leveraging reverse engineering strategically, large enterprises can empower themselves to make informed decisions, enhance their offerings, and gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic business environment.
Keyword Tags
- Reverse Engineering
- Large Enterprises
- Product Design Analysis
- Process Optimization
- Competitive Intelligence
