Reverse Engineering for Electronic Devices

Reverse Engineering is the process of understanding and analyzing how a device works by disassembling it and studying its internal components. In the context of electronic devices, reverse engineering can involve analyzing integrated circuits (ICs), printed circuit boards (PCBs), and other components to determine their function and design.
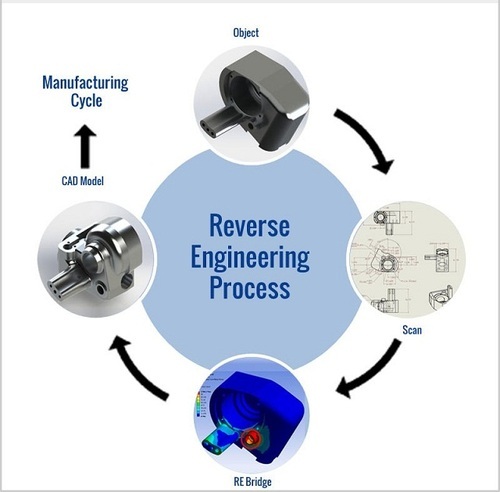
The purpose of reverse engineering can be varied. It can be used for repair purposes, to understand the operation of a device for duplication, to identify design flaws or security vulnerabilities, or to improve upon existing designs.

Reverse Engineering Process
The general process of reverse engineering involves the following steps:
-
Disassembly: The device is carefully dismantled to expose its internal components.
-
Identification: Each component is identified and its purpose determined. This can involve studying the part numbers, datasheets, and schematic diagrams if available.
-
Analysis: The interconnections between the components are examined to determine how the device functions. This can involve using tools such as oscilloscopes, logic analyzers, and debuggers.
-
Reconstruction: A detailed schematic diagram or block diagram of the device is created. This diagram should document the functionality of each component and its connections to other components.
-
Documentation: The findings of the reverse engineering process are documented in a report or technical document. This documentation can include the schematic diagram, a description of the device’s functionality, and any insights or recommendations.
Applications of Reverse Engineering
Reverse Engineering has a wide range of applications, including:
-
Device Repair: By understanding how a device works, it is possible to diagnose and repair faults.
-
Product Development: By analyzing the design of existing devices, engineers can identify strengths and weaknesses, and gain inspiration for new product designs.
-
Security Analysis: Reverse Engineering can be used to identify security vulnerabilities in electronic devices and develop countermeasures.
-
Forensic Analysis: Reverse Engineering can be used to analyze evidence in legal cases, such as determining the cause of device failures or identifying malware.## Reverse Engineering for Electronic Devices
Executive Summary
Reverse engineering is the process of understanding a system or device by examining its structure, function, and operation. This process can be used to identify potential areas for improvement, create compatible parts, or gain insight into the competitive landscape. Reverse engineering is a valuable skill for engineers, researchers, and anyone interested in understanding how electronic devices work.
Introduction
Electronic devices are becoming increasingly complex, and understanding their inner workings can be a daunting task. However, reverse engineering can provide a way to gain insight into these devices and unlock their potential. By understanding the principles of reverse engineering, you can gain the skills necessary to decipher the complexities of electronic systems and open up new possibilities for innovation.
FAQs
What are the benefits of reverse engineering?
- Identify potential areas for improvement
- Create compatible parts
- Gain insight into the competitive landscape
- Understand how complex systems work
- Develop new technologies
What are the challenges of reverse engineering?
- Acquiring the necessary knowledge and skills
- Obtaining access to the target device
- Disassembling the device without damaging it
- Interpreting the results of your analysis
What are some of the applications of reverse engineering?
- Product development
- Troubleshooting
- Competitive analysis
- Security assessment
- Forensic investigation
Top 5 Subtopics
1. Teardown Analysis
Teardown analysis involves disassembling a device to examine its physical components. This can provide insights into the device’s design, materials, and manufacturing process.
- Key pieces:
- Circuit boards
- Integrated circuits
- Capacitors
- Resistors
- Connectors
2. Circuit Analysis
Circuit analysis involves studying the electrical connections and components of a device. This can help to understand how the device functions and identify potential areas for improvement.
- Key pieces:
- Schematic diagrams
- Simulation software
- Oscilloscopes
- Multimeters
3. Firmware Analysis
Firmware analysis involves examining the software code that controls a device. This can provide insights into the device’s functionality, security features, and potential vulnerabilities.
- Key pieces:
- Decompilers
- Disassemblers
- Emulators
- Debugging tools
4. Hardware Emulation
Hardware emulation involves creating a virtual model of a device. This can allow engineers to test and debug software without the need for physical hardware.
- Key pieces:
- Emulation software
- Simulation tools
- Virtual machines
- FPGA boards
5. Intellectual Property Protection
Reverse engineering can provide insights into a device’s design and functionality, which can be valuable for protecting intellectual property.
- Key pieces:
- Patents
- Trade secrets
- Copyrights
- Non-disclosure agreements
Conclusion
Reverse engineering is a powerful tool that can be used to gain insight into the inner workings of electronic devices. By understanding the principles of reverse engineering, you can unlock the potential of these devices and open up new possibilities for innovation. Whether you are an engineer, researcher, or simply curious about how things work, reverse engineering can provide a valuable path to knowledge and innovation.
Keyword Tags
- Reverse engineering
- Electronic devices
- Teardown analysis
- Circuit analysis
- Firmware analysis
