Reverse Engineering for Data
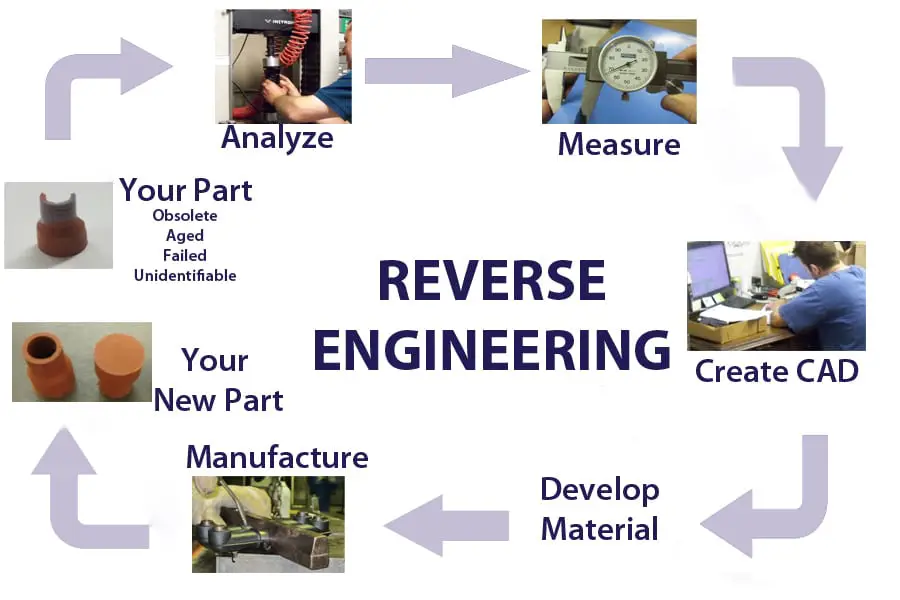
Executive Summary
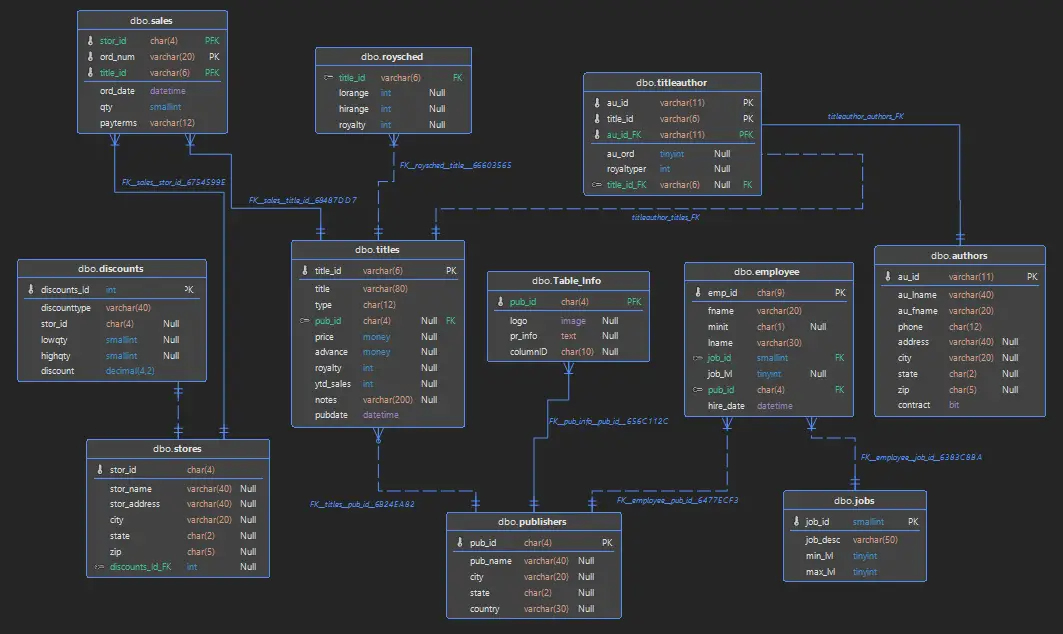
Reverse engineering data, the process of analyzing existing data to gain insights and uncover patterns, is a valuable technique for improving data management and decision-making. By understanding the underlying structure, relationships, and dependencies within data, organizations can optimize data collection, analysis, and storage practices. This comprehensive guide explores the key concepts and applications of reverse engineering for data, empowering businesses to leverage their data assets effectively.

Introduction:
Reverse engineering data is an essential process for organizations seeking to maximize the value of their data. It involves examining existing data sources to identify patterns, extract understanding, and improve data management practices. This article delves into the depths of reverse engineering for data, providing a comprehensive analysis of its techniques, applications, and benefits.
FAQs:
- What is the purpose of reverse engineering data?
- To understand the structure, relationships, and dependencies within data.
- What are the benefits of reverse engineering data?
- Improved data management, enhanced data analysis, and optimized data storage.
- How can organizations implement reverse engineering for data?
- Use specialized software tools or engage with data engineering professionals.
Top 5 Subtopics:
1. Data Profiling
Data profiling is the initial stage of reverse engineering, involving the analysis of data characteristics such as data types, value distributions, and missing values. Important considerations include:
- Data structure and format: Analyze the organization and layout of the data.
- Data completeness: Assess the extent of missing or incomplete data.
- Data quality: Evaluate the accuracy, consistency, and validity of the data.
2. Data Mapping
Data mapping involves creating visual representations of data relationships and dependencies. Key aspects to consider:
- Data lineage: Trace the flow of data from its source to its destination.
- Data relationships: Identify the connections and associations between different data elements.
- Data transformation: Analyze the processes that convert raw data into usable information.
3. Data Optimization
Data optimization aims to improve data efficiency and effectiveness. Important considerations include:
- Data compression: Reduce the size of data without compromising its integrity.
*Data normalization: Ensure data consistency and eliminate redundancies. - Data indexing: Enhance data retrieval speed and performance.
4. Data Integration
Data integration combines data from multiple sources into a unified dataset. Key considerations include:
- Data compatibility: Ensure that data from different sources can be merged seamlessly.
- Data cleansing: Identify and correct errors and inconsistencies in the data.
- Data standardization: Transform data into a consistent format for analysis and comparison.
5. Data Analytics
Data analytics involves applying analytical techniques to extract insights from data. Important considerations include:
- Data visualization: Create graphical representations of data for easier interpretation.
- Data mining: Discover hidden patterns and relationships within data.
- Data forecasting: Predict future trends and outcomes based on historical data.
Conclusion:
Reverse engineering data is a powerful technique for organizations seeking to maximize the value of their data assets. By understanding the underlying structure, relationships, and dependencies within data, businesses can optimize data collection, analysis, and storage practices, leading to improved data management, enhanced decision-making, and increased business efficiency. Implementing reverse engineering for data requires a combination of technological tools and skilled professionals to ensure successful execution and realization of its benefits.
Keywords:
- Reverse engineering
- Data analysis
- Data management
- Data optimization
- Data integration
