Reverse Engineering for Consumer Products

Reverse engineering involves disassembling a product and analyzing its structure, function, and components to understand its design and manufacturing process. It plays a crucial role in consumer goods industries, offering various benefits:
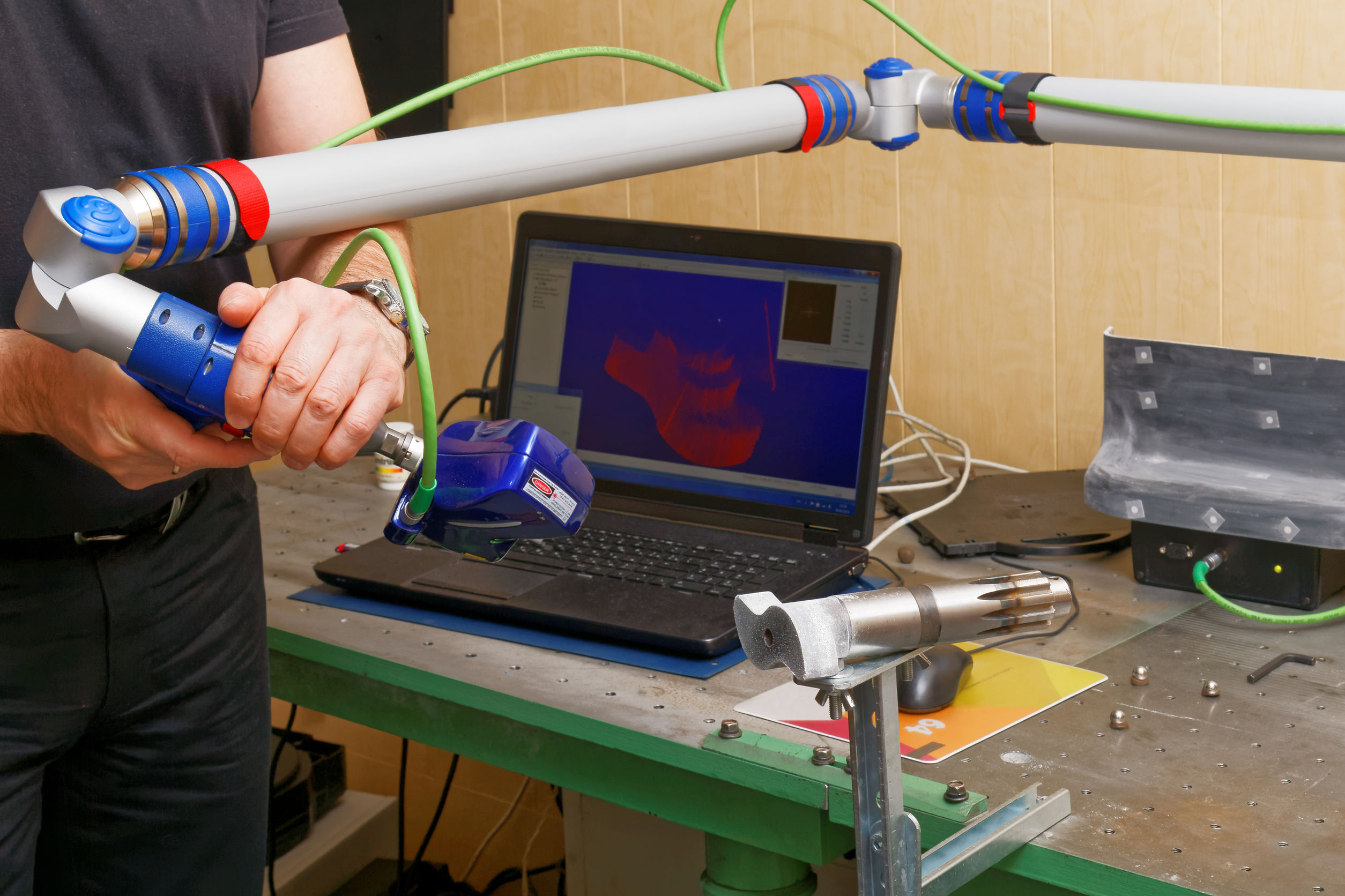
1. Competitor Analysis:
By examining competitor products, companies can identify innovative features, design aesthetics, and cost-saving techniques, allowing them to improve their products or develop new ones.
2. Quality Control and Improvement:
Reverse engineering helps manufacturers identify potential design flaws, material weaknesses, or manufacturing defects. This information can be used to improve product durability, safety, and efficiency.
3. Product Customization:
By identifying the key components and design principles of a product, companies can customize it to meet specific customer needs or market trends.
4. Component Sourcing:
Reverse engineering allows manufacturers to identify and source equivalent or better-quality components from different suppliers, reducing costs and increasing supply chain flexibility.
5. Patent Analysis:
Examining the designs and components of existing products can help companies understand the competitive landscape and avoid potential patent infringements.
Process of Reverse Engineering:

1. Disassembly:
The product is disassembled into its individual components.
2. Documentation:
Detailed documentation, including photographs, measurements, and assembly instructions, is created.
3. Analysis:
The components are examined to understand their function, materials, and manufacturing processes.
4. Reassembly:
The product is reassembled to verify its functionality and accuracy.
5. Documentation and Evaluation:
The results of the reverse engineering process are documented and evaluated to identify improvement opportunities or potential risks.
Reverse engineering is an essential tool for manufacturers of consumer products as it helps improve product design, reduce costs, and gain insights into industry trends. By understanding the structure and function of existing products, companies can stay competitive and meet the evolving needs of customers.Reverse Engineering for Consumer Products
Executive Summary
Reverse engineering products represents a powerful strategy to investigate competitor products, understand their construction, identify areas for improvement, and accelerate product development. By dissecting components, evaluating materials, and analyzing designs, companies can gain valuable insights that can propel them ahead in the competitive marketplace.
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, staying abreast of competitors’ advancements is crucial for business success. Reverse engineering provides an invaluable tool for manufacturers to unlock the secrets of competitor products, enabling them to pinpoint strengths, vulnerabilities, and potential areas for innovation.
FAQs
- What is the purpose of reverse engineering?
- To analyze competitors’ products, identify design flaws, and uncover potential improvements.
- What are the benefits of reverse engineering?
- Reduced product development time and costs, improved product quality, and enhanced competitive advantage.
- What industries benefit most from reverse engineering?
- Manufacturing, technology, automotive, and consumer goods.
Key Subtopics
Product Disassembly and Inspection
- Purpose: To break down a product into its constituent parts, identify their materials and construction.
- Important Pieces:
- Bill of materials (BOM): A comprehensive list of all components used in the product.
- Component analysis: Detailed examination of each component’s dimensions, tolerances, and materials.
- Assembly process reconstruction: Reconstructing the assembly process based on observed component interactions.
- Material testing: Evaluating the properties and performance of materials used in the product.
Design and Functionality Analysis
- Purpose: To understand the product’s design principles, functionality, and user experience.
- Important Pieces:
- Function mapping: Identifying the relationships between components and their intended functions.
- Performance evaluation: Benchmarking the product’s performance against competitors or industry standards.
- User interface analysis: Studying the product’s user interface and interactions to identify potential improvements.
- Ergonomics assessment: Evaluating the product’s fit, comfort, and ease of use.
Manufacturing Processes and Cost Analysis
- Purpose: To determine the manufacturing processes used, identify potential cost-saving areas, and assess supply chain logistics.
- Important Pieces:
- Process mapping: Creating a diagram showing the sequence of manufacturing steps.
- Cost breakdown: Estimating the costs associated with materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead.
- Supply chain analysis: Identifying suppliers, lead times, and potential risks.
- Value stream mapping: Identifying and eliminating waste in the manufacturing process.
Intellectual Property Clearance
- Purpose: To ensure that the reverse-engineered product does not infringe on any existing patents or trademarks.
- Important Pieces:
- Patent search: Conducting a thorough search for relevant patents to avoid infringement.
- Trademark protection: Registering any new designs, trademarks, or branding elements created through the reverse engineering process.
- Legal consultation: Seeking legal advice to ensure compliance with intellectual property laws.
Competitive Advantage and Innovation
- Purpose: To identify opportunities to improve upon competitor products, develop new features or applications, and gain a competitive advantage.
- Important Pieces:
- SWOT analysis: Assessing the product’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Benchmarking: Comparing the product to similar offerings in the market.
- Innovation pipeline: Identifying potential areas for product enhancements or new product development.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering for consumer products offers a potent tool for businesses to gain a deeper understanding of competitor products, pinpoint areas for improvement, and fuel product innovation. By carefully dissecting and analyzing competitor products, manufacturers can identify potential advantages and disadvantages, reduce product development timelines, and secure a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Keyword Tags
- Reverse engineering
- Product development
- Competitor analysis
- Innovation
- Competitive advantage
