Reverse Engineering for Analog Products

Reverse engineering for analog products involves analyzing and reconstructing an existing analog circuit or system to extract its design, functionality, and specifications. The process typically encompasses several stages:
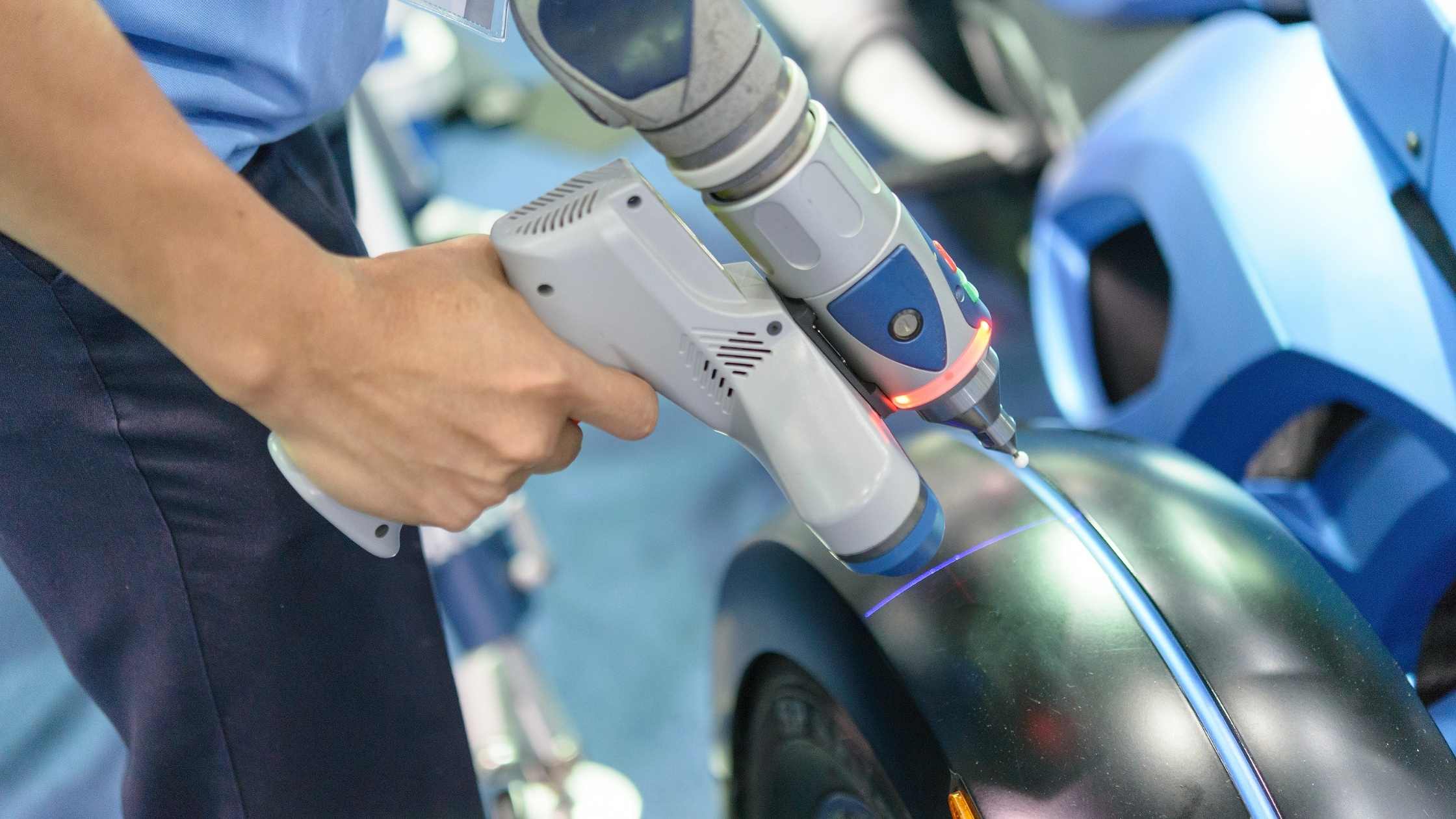

1. Physical Analysis:
- Disassembly of the product to access its internal components.
- Examination of the components, including their types, values, and interconnections.
- Documentation of the physical layout, including the component placement and traces.
2. Circuit Analysis:
- Creation of a schematic diagram based on the observed physical connections.
- Analysis of the circuit’s topology, component functions, and signal flow.
- Identification of key parameters, such as gain, bandwidth, and frequency response.
3. Simulation and Modeling:
- Simulation of the circuit using SPICE or other software tools to verify its functionality.
- Development of mathematical models to represent the circuit’s behavior and key characteristics.
4. Functional Testing:
- Testing of the circuit using various input signals and conditions.
- Measurement of performance parameters, such as noise, distortion, and bandwidth.
- Comparison of measured results with expected specifications.
5. Component Identification and Sourcing:
- Identification and sourcing of discontinued or obsolete components used in the circuit.
- Cross-referencing of component values and manufacturers to find suitable replacements.
6. Design Reconstruction:
- Re-creation of the original design using the acquired knowledge and analysis results.
- Development of alternative or improved designs based on the understanding gained.
- Documentation of the redesigned circuit, including schematics, component specifications, and performance characteristics.
Benefits of Reverse Engineering for Analog Products:
- Gaining insights into the design and functionality of complex analog systems.
- Troubleshooting and repairing existing products by identifying faulty components and design flaws.
- Creating drop-in replacements or clones of legacy products.
- Verifying the performance and reliability of analog circuits.
- Developing new designs or enhancements based on established designs.
- Reducing development time and costs by leveraging existing knowledge and components.## Reverse Engineering For Analog Products
Executive Summary
Reverse engineering analog products involves studying and analyzing existing products to understand their design, functionality, and implementation. It is a valuable technique for gaining insights, identifying design flaws, and developing new and improved products. This article provides a comprehensive overview of reverse engineering for analog products, discussing key subtopics, applications, and best practices.
Introduction
Reverse engineering has become an integral part of product development, especially in the analog domain. By dissecting and analyzing existing products, engineers can extract valuable information that can inform design decisions, optimize performance, and identify potential areas for improvement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the benefits of reverse engineering analog products?
- Gain insights into design principles and functionality
- Identify potential design flaws and areas for improvement
- Develop new and innovative products
- Reduce development time and costs
2. What types of analog products can be reverse engineered?
- Audio amplifiers
- Power supplies
- Operational amplifiers
- Sensors
- Mixed-signal devices
3. What are the key steps involved in reverse engineering analog products?
- Acquisition and disassembly of the target product
- Functional analysis and testing
- Schematic capture and simulation
- Design analysis and optimization
Subtopics
1. Functional Analysis
- Characterization of input/output relationships
- Identification of key components and their roles
- Determination of signal paths and feedback mechanisms
2. Schematic Capture
- Reconstruction of the circuit diagram based on reverse engineered components
- Validation of the schematic using simulation tools
- Identification of critical components and potential failure points
3. Design Analysis
- Assessment of component values and tolerances
- Analysis of circuit stability and performance
- Identification of design flaws or areas for optimization
4. Simulation and Testing
- Validation of the reverse engineered design through simulation
- Fabrication and testing of prototype circuits
- Refinement of the design based on test results
5. Applications of Reverse Engineering
- Product improvement and innovation
- Failure analysis and troubleshooting
- Counterfeit detection and prevention
- Patent infringement analysis
Conclusion
Reverse engineering analog products is a powerful technique that can provide valuable insights and advantages in the design and development process. By understanding the principles and steps involved, engineers can harness the potential of reverse engineering to develop innovative products, improve existing designs, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Keyword Tags
- Analog product reverse engineering
- Reverse engineering techniques
- Functional analysis
- Schematic capture
- Design optimization
