Reverse Engineering Case Studies
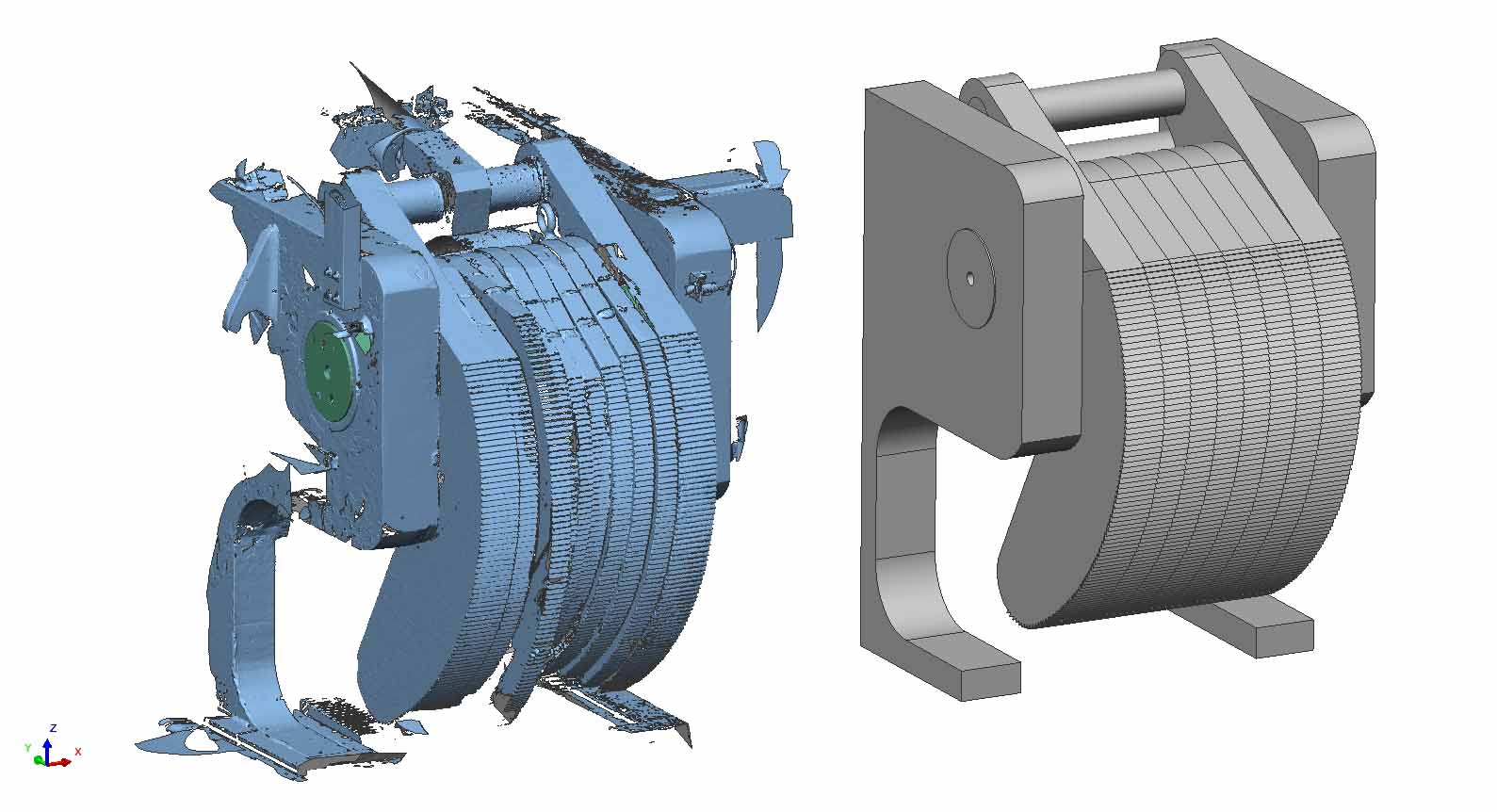
Reverse engineering, the process of analyzing and recreating a product or system by examining its components and understanding its functionality, has become an increasingly important tool in various industries. By understanding the inner workings of existing products, companies can gain valuable insights, identify areas for improvement, and innovate more effectively.
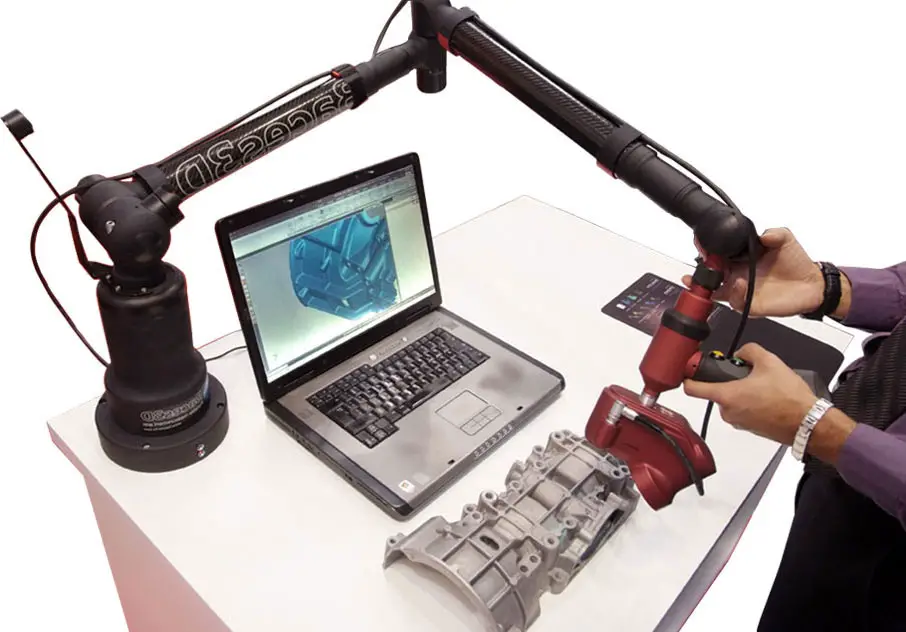

Numerous case studies highlight the successful application of reverse engineering in diverse fields.

Automotive Industry:
- Toyota’s Reverse Engineering of the Porsche 914: Toyota engineers reverse-engineered the Porsche 914 to gain insights into its advanced engineering and design. The knowledge acquired from this analysis helped Toyota develop its own sports car, the Toyota 2024GT, which rivaled the Porsche in performance and features.
- Tesla’s Open-Source Concept: Tesla has adopted an open-source approach to its electric vehicle designs, inviting other manufacturers to reverse-engineer its products. This strategy has spurred innovation and accelerated the development of electric vehicles.
Aerospace Industry:
- NASA’s Reverse Engineering of the Space Shuttle: NASA used reverse engineering to repair and restore the Space Shuttle after the Columbia disaster. By analyzing the wreckage and understanding its design, NASA was able to identify and rectify the flaws that caused the tragedy.
Medical Device Industry:
- Stryker’s Reverse Engineering of Knee Implants: Stryker utilized reverse engineering to analyze the design and performance of competing knee implants. The insights gained from this process enabled them to develop implants with improved functionality and reduce risk.
Consumer Electronics Industry:
- Apple’s Reverse Engineering of the iPod: Steve Jobs led the iconic iPod project by reverse-engineering existing MP3 players to understand their strengths and weaknesses. Apple combined these insights with innovative ideas to develop the iPod, which revolutionized the way people listened to music.
These case studies demonstrate the transformative potential of reverse engineering, offering businesses and researchers a systematic approach to gain knowledge, unlock innovation, and improve products. By utilizing advanced technologies and methodologies, organizations can leverage this technique to maximize their competitive advantage.## Reverse Engineering Case Studies
Executive Summary
Reverse engineering can be a powerful tool for businesses seeking to gain a competitive advantage. By studying the products, processes, and strategies of their competitors, companies can identify areas for improvement and develop innovative solutions. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to reverse engineering case studies, including key subtopics, benefits, and best practices.
Introduction
In today’s competitive business landscape, innovation is crucial for success. Reverse engineering is an effective technique that enables companies to understand and improve their competitors’ products and processes. By carefully analyzing a competitor’s offerings, businesses can gain valuable insights into their strengths, weaknesses, and potential growth opportunities.
FAQs
Q1: What is the purpose of reverse engineering?
Reverse engineering aims to understand a competitor’s product or process by analyzing its physical components, software, or underlying mechanisms.
Q2: How can reverse engineering benefit businesses?
- Identify areas for improvement in their own products and services
- Gain insights into competitors’ market strategies
- Enhance understanding of industry trends and technologies
Q3: What are the ethical considerations of reverse engineering?
Reverse engineering is generally considered ethical if it is used for non-commercial purposes and does not violate intellectual property rights.
Key Subtopics
Product Design and Engineering
- Analyze physical components: Identify materials, dimensions, and functionality of competitor products.
- Study manufacturing processes: Determine methods used to produce the product, including tools, machinery, and quality control techniques.
- Assess software and algorithms: Reverse code and uncover the underlying algorithms that drive competitor products.
Business Strategy and Marketing
- Identify competitive advantages: Determine the unique features, value proposition, and target market of competitor products.
- Analyze marketing campaigns: Study competitor marketing strategies, including advertising, social media, and content marketing.
- Evaluate pricing models: Understand competitor pricing strategies and identify potential areas for differentiation.
Supply Chain and Operations
- Map supplier relationships: Identify key suppliers and determine the nature of these relationships.
- Analyze production capabilities: Assess competitor production capacity, efficiency, and lead times.
- Study distribution channels: Determine the channels used by competitors to distribute their products, including logistics, warehousing, and retail partnerships.
Technology and Innovation
- Identify cutting-edge technologies: Recognize advanced technologies used by competitors and their potential impact on the industry.
- Analyze research and development strategies: Study competitor R&D investments and determine their areas of focus.
- Forecast future innovations: Utilize reverse engineering insights to anticipate future market trends and technological breakthroughs.
Best Practices
- Ensure confidentiality and protect intellectual property.
- Use multiple analytical techniques to triangulate findings.
- Focus on key areas of interest and prioritize analysis.
- Document findings thoroughly and share insights across the organization.
- Monitor competitors continuously and adapt reverse engineering strategies as needed.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering is a valuable tool that can provide businesses with a wealth of insights into their competitors’ products, strategies, and operations. By conducting thorough reverse engineering case studies, companies can identify areas for improvement, gain a competitive advantage, and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving business landscape.
