Reverse Engineering: A Legal Perspective
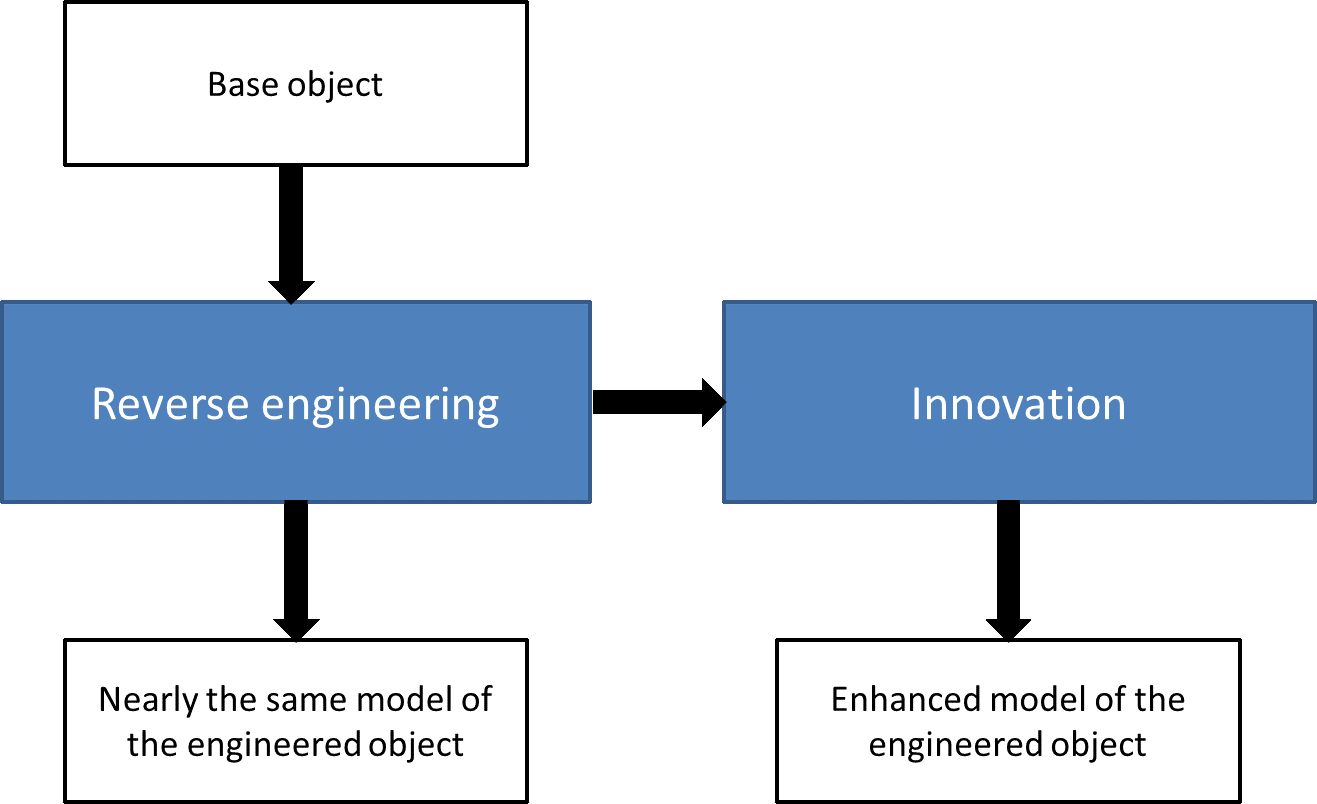
Reverse engineering, the process of analyzing a product or system to determine its design, function, and operation, is a powerful tool in the technology industry. However, it also raises a number of legal issues, particularly with regard to intellectual property rights.

Copyright Law
Copyright law protects original works of authorship, such as software code, circuit designs, and industrial designs. Reverse engineering can be considered a violation of copyright law if it involves reproducing or distributing copyrighted material without authorization.
Patent Law
Patent law protects inventions and grants exclusive rights to their owners. Reverse engineering can be considered a patent infringement if it involves using or selling a patented invention without permission.
Exceptions to Reverse Engineering
There are a number of exceptions to the general prohibition on reverse engineering. These include:
- Fair use: Reverse engineering may be considered fair use if it is done for the purpose of research, criticism, or education.
- Clean room design: Reverse engineering can be done in a “clean room” environment, where the engineers do not have access to the original product or its design.
- Independent development: Reverse engineering is permissible if the engineer develops the product independently, without copying the original design.
Legal Considerations
When considering reverse engineering, it is important to take into account the following legal considerations:
- Identify the applicable laws: Determine which laws govern reverse engineering in the relevant jurisdiction.
- Obtain permission: Seek permission from the copyright or patent holder before reverse engineering a product or system.
- Document the process: Keep a detailed record of the reverse engineering process, including the source of the original product and the methods used.
- Consider the implications: Understand the potential legal consequences of reverse engineering, such as copyright infringement, patent infringement, or trade secret misappropriation.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering is a valuable tool in the technology industry, but it is important to be aware of the legal implications before engaging in this process. By following the correct legal procedures and obtaining the necessary permissions, businesses can reverse engineer products and systems safely and legally.## Reverse Engineering: A Legal Perspective
Executive Summary
Reverse engineering, the process of analyzing a product or system to understand its design and functionality, has significant implications for the legal landscape. This detailed analysis explores the complex legal framework surrounding reverse engineering, examining its definitions, boundaries, and potential consequences.
Introduction
Reverse engineering has become an essential tool for technological advancement and innovation. However, its potential for intellectual property infringement and the unauthorized use of proprietary information have raised legal concerns. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the legal aspects of reverse engineering, guiding readers through its nuances and implications.
Key Subtopics
1. Definition of Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering refers to the systematic examination of a product or device to uncover its underlying design, construction, and functioning. It typically involves disassembling the product, analyzing its components and materials, and reconstructing its functionality.
2. Boundaries of Legal Reverse Engineering
Certain activities may fall within the boundaries of legal reverse engineering, including:
- Interoperability: Understanding a product’s functionality to create compatible products.
- Maintenance and Repair: Performing repairs or modifications without infringing copyrights or patents.
- Research and Education: Analyzing products for educational or research purposes.
3. Intellectual Property Concerns
Reverse engineering can raise concerns related to intellectual property rights, such as:
- Copyright Infringement: Copying or reproducing protected expression within a product’s design.
- Patent Infringement: Using patented inventions or processes without authorization.
- Trade Secret Misappropriation: Acquiring confidential information through unauthorized means.
4. Legal Defenses and Exceptions
Defenses against reverse engineering claims may include:
- Fair Use: Limited use of copyrighted material for criticism, commentary, or research purposes.
- Experimental Use: Using reverse engineering to develop new technologies or products.
- Repair Doctrine: Legally permissible reverse engineering for repair or maintenance purposes.
5. Legal Consequences
Unauthorized or illegal reverse engineering can lead to legal consequences, such as:
- Injunctions: Court orders prohibiting further reverse engineering activities.
- Damages: Compensation for economic losses caused by infringement.
- Criminal Penalties: In certain cases, intentional infringement may result in criminal prosecution.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering presents a complex intersection between technological progress and intellectual property protection. While it can facilitate innovation, it must be conducted within legal boundaries. By understanding the legal framework surrounding reverse engineering, businesses, researchers, and individuals can leverage its benefits while mitigating potential risks.
Keyword Tags
- Reverse Engineering
- Legal Framework
- Intellectual Property
- Innovation
- Patent Infringement
FAQ
1. Can I reverse engineer a purchased product for personal use?
Yes, within certain limits. Reverse engineering for maintenance, repair, or non-commercial purposes is generally permissible.
2. What are the consequences of infringing a patent through reverse engineering?
Unauthorized use of patented inventions can lead to legal action, including damages and injunctions.
3. Is it legal to reverse engineer a copyrighted work?
Limited fair use of copyrighted material may be allowed for criticism, commentary, or research purposes.
4. Can unauthorized trade secrets be acquired through reverse engineering?
Unlawful acquisition of trade secrets through reverse engineering may result in misappropriation claims.
5. How can I protect my product from unauthorized reverse engineering?
Consider using patents, trade secrets, and other intellectual property protections to safeguard your intellectual assets.

