Reverse Engineering: A Global Perspective
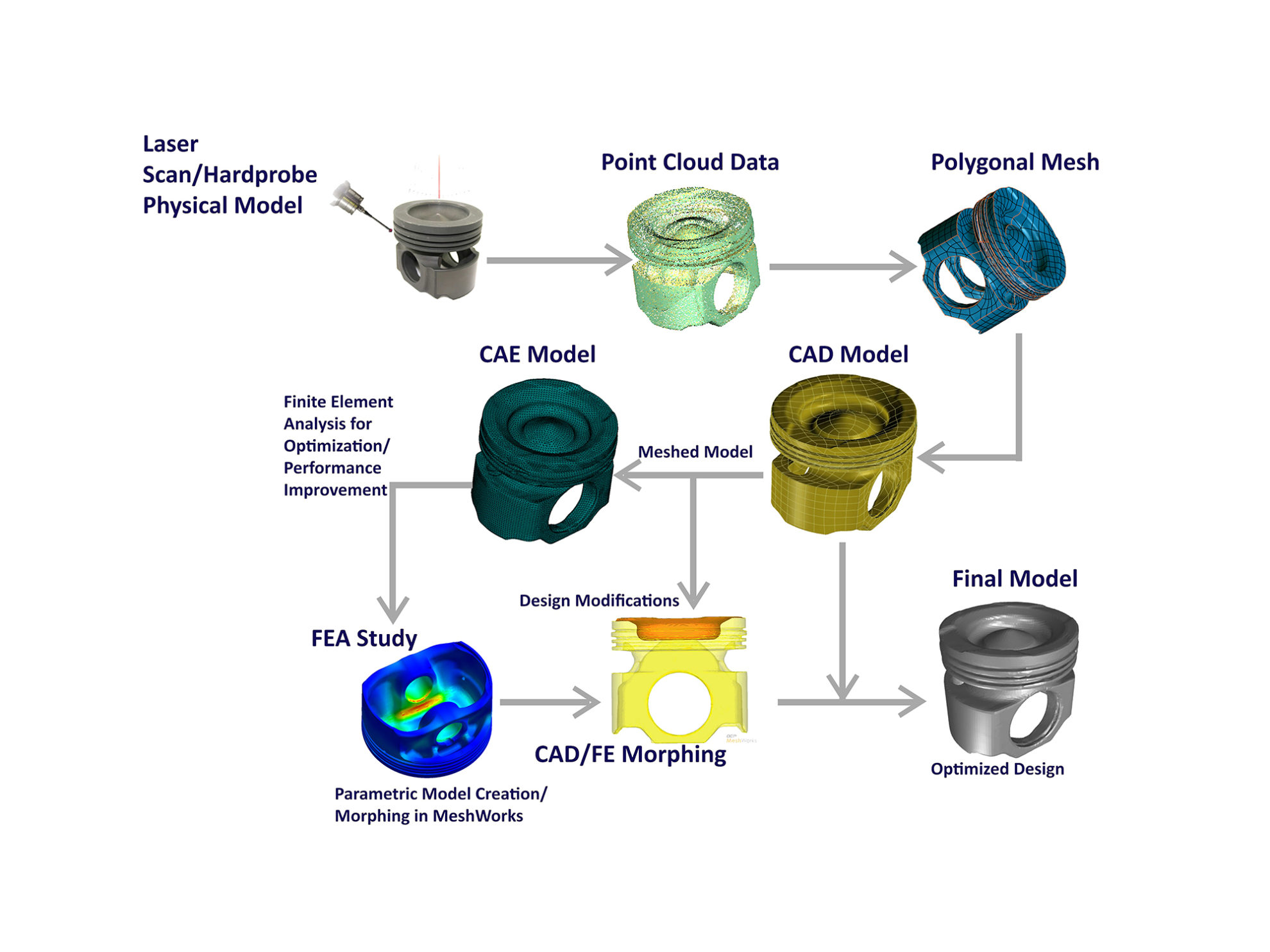
Reverse engineering is the process of analyzing a system or product to create a representation that outlines its design and function. It involves breaking down a product to its component parts and then studying those parts to understand how they work together. This process can be used for a variety of purposes, such as:
- To understand how a product is made
- To identify potential improvements
- To develop new products
- To exploit weaknesses
How Reverse Engineering Works
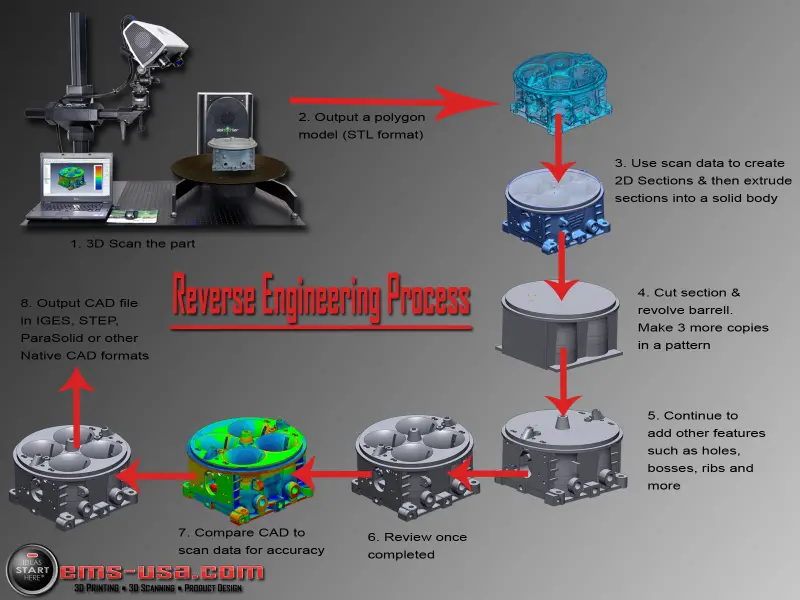
Reverse engineering typically involves the following steps:
- Inspection: The first step is to carefully inspect the product to identify its components and how they are attached to each other.
- Disassembly: The next step is to disassemble the product into its individual pieces. This must be done carefully to avoid damaging any of the parts.
- Analysis: Once the product is disassembled, it is necessary to analyze the individual pieces to understand how they work. This may involve studying their design, material properties, and function.
- Documentation: The final step is to document the results of the analysis. This may include creating drawings, diagrams, and reports.
Applications of Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering has a wide variety of applications, including:
- Manufacturing: Reverse engineering can be used to understand how products are made so that they can be replicated or improved.
- Product Design: Reverse engineering can be used to identify potential improvements to existing products or to develop new products.
- Software Engineering: Reverse engineering can be used to analyze software to identify security vulnerabilities or to port software to different platforms.
- Industrial Espionage: Reverse engineering can be used to obtain proprietary information about products or processes.
Benefits of Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering can offer a number of benefits, including:
- Improved Understanding: Reverse engineering can provide a deeper understanding of how a product works.
- Innovation: Reverse engineering can lead to new ideas and innovations.
- Cost Savings: Reverse engineering can help companies save money by understanding how products are made and how they can be improved.
- Competitive Advantage: Reverse engineering can give companies a competitive advantage by providing them with information about their competitors’ products.
Challenges of Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering can also pose some challenges, including:
- Complexity: Reverse engineering can be a complex and time-consuming process.
- Lack of Information: It may not always be possible to obtain all of the information needed to complete a reverse engineering project.
- Intellectual Property Issues: Reverse engineering can raise intellectual property issues if the product being analyzed is protected by patents or copyrights.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering is a powerful tool that can be used to understand how products work, to identify potential improvements, to develop new products, and to exploit weaknesses. However, reverse engineering can also be a complex and challenging process, and it is important to be aware of the potential risks involved before undertaking a reverse engineering project.## Reverse Engineering: A Global Perspective
Executive Summary
Reverse engineering is a valuable technique in various industries, offering benefits such as improved product development, faster troubleshooting, and reduced design time. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of reverse engineering on a global scale, covering its benefits, applications, and considerations for successful implementation.
Introduction
Reverse engineering involves analyzing an existing product or system to determine its design, manufacturing processes, and functional principles. It provides insights into competitor strategies, enables product improvement, and streamlines innovation cycles.
FAQs
- What are the main benefits of reverse engineering?
- Understanding competitor designs
- Identifying product weaknesses
- Enhancing existing products
- Developing new product ideas
- What are the different applications of reverse engineering?
- Aerospace and defense
- Automotive
- Medical devices
- Electronics
- What are key considerations for successful reverse engineering?
- Non-invasive techniques
- Access to high-quality documentation
- Expertise in engineering analysis
Subtopics:
1. Design Reconstruction
- Creating a 3D model or technical drawing of the product
- Analyzing component structures and materials
- Identifying manufacturing tolerances and assembly processes
2. Functional Analysis
- Understanding the intended purpose and operating principles of the product
- Testing and evaluating performance under various conditions
- Determining safety features and environmental specifications
3. Process Optimization
- Identifying inefficient manufacturing processes
- Proposing alternative materials or assembly techniques
- Implementing lean manufacturing principles to reduce costs
4. Quality Control and Troubleshooting
- Analyzing product defects and failures
- Identifying sources of quality issues
- Developing preventive measures to enhance product reliability
5. Competitive Analysis
- Benchmarking against competitor products
- Identifying strengths and weaknesses of competitor designs
- Developing strategies to gain market advantage
Conclusion
Reverse engineering has emerged as an essential tool for innovation and product development. By embracing this technique, businesses can gain valuable insights into competitor designs, enhance their own products, and accelerate innovation cycles. To ensure successful implementation, it is crucial to employ non-invasive techniques, secure access to high-quality documentation, and leverage expertise in engineering analysis. Reverse engineering offers immense potential for businesses seeking to gain a competitive edge in the global marketplace.
Keyword Tags
- Reverse Engineering
- Product Development
- Competitor Analysis
- Innovation
- Global Perspective
