Penetration Testing Perils: Uncovering and Fixing Security Vulnerabilities
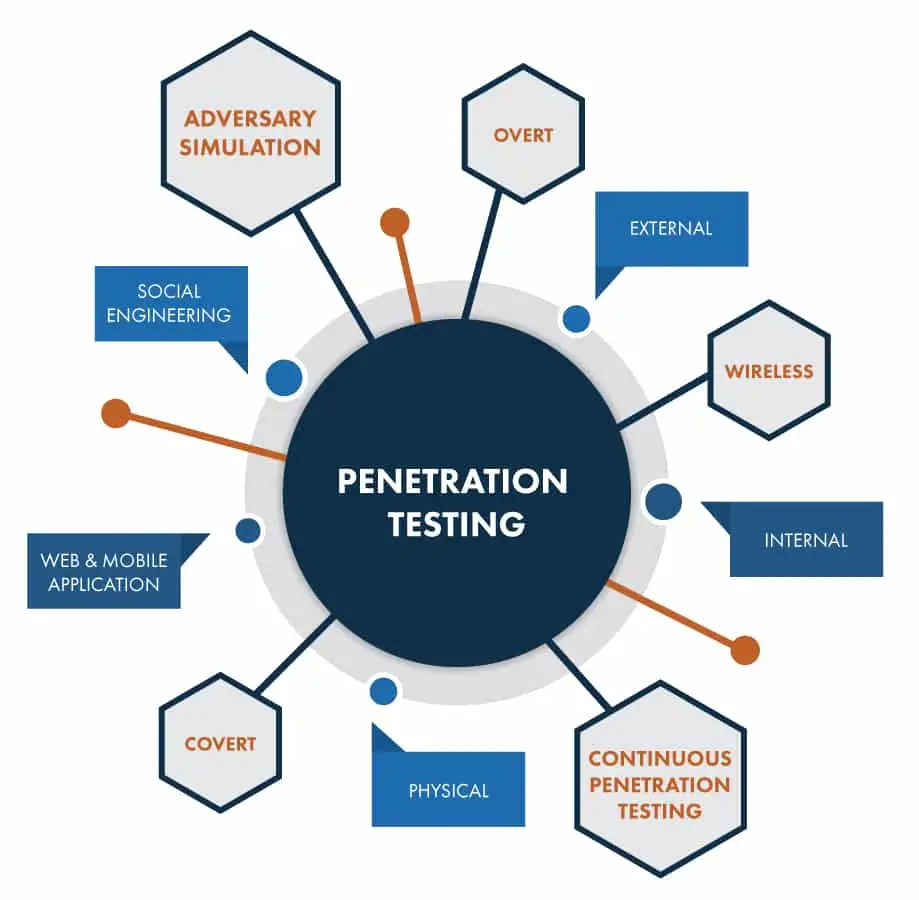
Penetration testing is a crucial security measure that organizations should regularly conduct to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities within their IT infrastructure. However, it comes with its own set of perils that can potentially compromise the security posture of an organization.
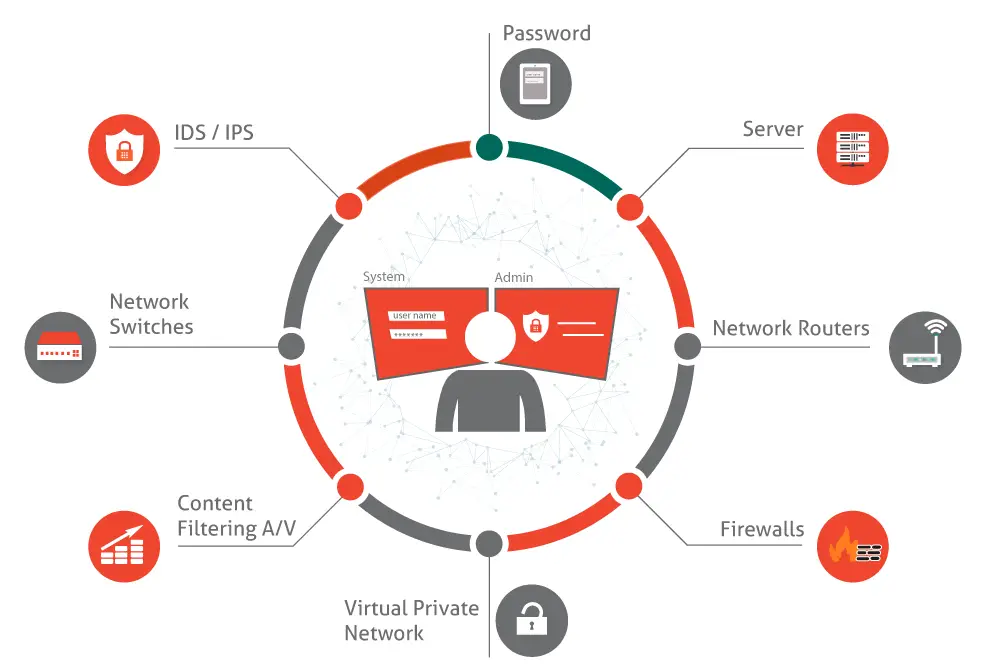
Unintended Consequences:

Penetration testing involves ethical hacking techniques to simulate real-world attacks. While these tests are designed to identify vulnerabilities, they can also inadvertently introduce additional vulnerabilities or disrupt operations if not executed properly. For instance, overzealous testing might crash critical systems, leading to downtime or data loss.
False Positives:
Penetration testing tools can produce false positives, indicating the presence of a vulnerability when none exists. This can lead to wasted resources and unnecessary remediation efforts. It is essential for organizations to verify the authenticity of reported vulnerabilities through additional testing or code review to avoid addressing non-existent issues.
Limited Scope:
Penetration tests often focus on specific targets or attack vectors, leaving other areas of the IT infrastructure untested. This limited scope can result in overlooking vulnerabilities in other components or communication channels, creating blind spots for potential attackers.
False Sense of Security:
Passing a penetration test does not guarantee complete security. It is a snapshot of a system’s security at a specific point in time. New vulnerabilities can emerge due to changes in software, hardware, or configurations, which may not be covered by the initial test. Regular testing is necessary to stay current with the evolving threat landscape.
Mitigation Strategies:
To address these perils, organizations should follow best practices:
- Plan Thoroughly: Define clear testing objectives, scope, and limitations to ensure a focused and effective test.
- Engage Skilled Testers: Utilize reputable penetration testing companies with experienced security professionals who understand the nuances of the organization’s systems.
- Verify Results Meticulously: Confirm the accuracy of reported vulnerabilities through manual code review or additional testing to avoid false positives.
- Implement Recommendations: Address identified vulnerabilities promptly and record remediation actions to prevent reemergence.
- Conduct Regular Testing: Regularly schedule penetration tests to keep pace with the constantly evolving threat landscape and maintain proactive security posture.
By adhering to these strategies, organizations can minimize the risks associated with penetration testing while effectively uncovering and resolving security vulnerabilities to strengthen their overall security posture.## Penetration Testing Perils: Uncovering and Fixing Security Vulnerabilities
Cyber intrusions can result in massive financial losses, reputational damage, and compromised sensitive data for businesses of all sizes. Penetration testing plays a crucial role in identifying vulnerabilities, evaluating risks, and hardening security defenses against potential threats. By simulating real-world attacks, penetration tests help organizations proactively strengthen their security posture.
Executive Summary
Penetration testing is an invaluable tool for organizations seeking to bolster their cybersecurity safeguards. It offers a comprehensive overview of potential risks by mimicking real-life attack scenarios. Penetration testing strengthens security measures by uncovering vulnerabilities, assessing threats, and providing remediation recommendations. By investing in regular penetration testing, organizations can remain vigilant against emerging cyber threats, ensuring the integrity of their data and systems.
Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity is paramount. As organizations strive to safeguard their assets and maintain customer trust, penetration testing emerges as an indispensable ally in the relentless battle against cyber threats. This article aims to shed light on the significance of penetration testing and its potential to enhance an organization’s security strategy.
FAQs
-
What is penetration testing?
Penetration testing involves authorized simulated cyberattacks against an organization’s systems and infrastructure to identify vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. -
Why is penetration testing important?
Penetration testing provides a proactive approach to security by exposing vulnerabilities, assessing risks, and offering remediation guidance, enabling organizations to stay ahead of potential threats. -
What are the benefits of penetration testing?
Penetration testing offers numerous benefits, including enhanced security posture, regulatory compliance, reduced risk exposure, and improved incident response capabilities.
Subtopics
Identifying Vulnerabilities
Penetration testing is critical for uncovering vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems, applications, and networks. This subtopic delves into methods for discovering these vulnerabilities:
- Vulnerability scanning: Automated tools identify common vulnerabilities based on known patterns and signatures.
- Code review: Manual inspection of code to uncover potential weaknesses that could be exploited.
- Fuzz testing: Providing unexpected or malformed inputs to detect flaws that may lead to crashes or data leakage.
Assessing Risks
Penetration testing not only identifies vulnerabilities but also evaluates the associated risks for each vulnerability. This subtopic covers factors considered in risk assessment:
- Likelihood: The probability of a vulnerability being exploited.
- Impact: The potential consequences of a vulnerability being exploited, including financial losses, data breaches, or reputational damage.
- Technical controls: Existing security measures and safeguards that may mitigate the risk associated with the vulnerability.
Remediation Recommendations
Penetration testing guides organizations towards mitigating risks effectively. This subtopic focuses on the process of recommending and implementing corrective actions:
- Patch management: Applying updates and security patches to address vulnerabilities and prevent exploitation.
- Configuration hardening: Strengthening system configurations to enhance security and reduce the attack surface.
- Mitigation strategies: Implementing technical or procedural measures to minimize the impact of vulnerabilities until permanent fixes can be applied.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Penetration testing plays a vital role in ensuring regulatory compliance for organizations subject to data protection and information security standards. This subtopic highlights key regulatory requirements:
- PCI DSS: Requires businesses processing credit card data to maintain robust security measures, including regular penetration testing.
- GDPR: Mandates organizations to implement appropriate security controls to protect personal data, including conducting regular penetration testing.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Provides a comprehensive guide for organizations to improve their cybersecurity posture, including penetration testing as a recommended practice.
Post-Penetration Testing Considerations
Penetration testing is not a one-time event but an ongoing process requiring continuous vigilance. This subtopic covers essential post-penetration testing considerations:
- Remediation tracking: Monitoring the implementation and effectiveness of recommended remediation actions.
- Vulnerability management: Maintaining an up-to-date inventory of vulnerabilities and prioritizing their mitigation based on risk.
- Incident response planning: Incorporating penetration testing findings into incident response plans to enhance preparedness and minimize impact.
Conclusion
Penetration testing remains an indispensable tool for organizations aiming to strengthen their cybersecurity defenses. By identifying vulnerabilities, assessing risks, and providing actionable remediation guidance, penetration testing empowers organizations to proactively safeguard their valuable assets against cyber threats. Embracing penetration testing as an integral part of an organization’s security strategy is a testament to the organization’s commitment to maintaining a robust security posture in an increasingly interconnected and rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Keyword Tags
- Penetration Testing
- Cybersecurity
- Vulnerability Assessment
- Risk Management
- Compliance

