Leveraging CDNs for Efficient Content Replication and Synchronization
Introduction:
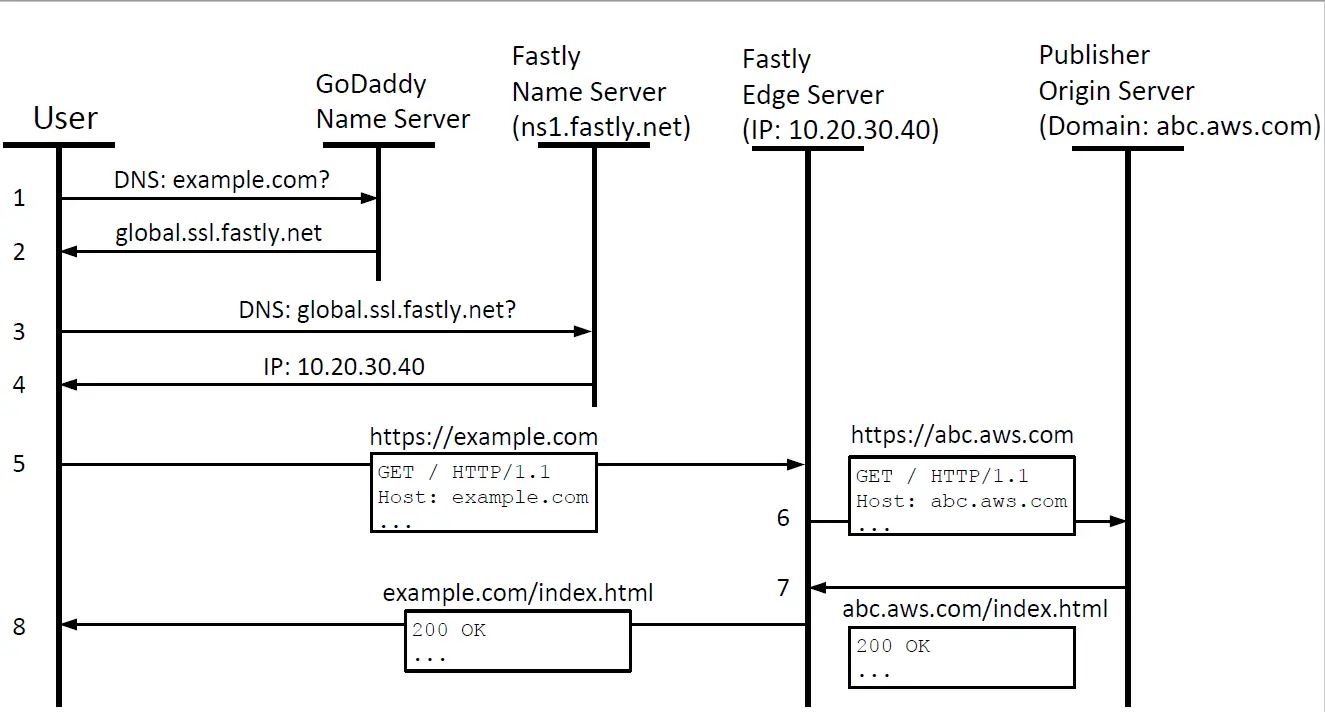
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are geographically distributed networks of servers that store and deliver content to users, improving website performance and reducing latency. They play a crucial role in content replication and synchronization, ensuring that content is available consistently across all edge locations.
Content Replication:
CDNs replicate content across multiple edge locations to bring it closer to end users. By caching content on edge servers, requests can be served from the nearest location, reducing network latency and improving download speeds. This approach reduces the load on central servers and improves overall website performance.
Synchronization:
CDNs ensure that content remains synchronized across all edge locations. When content is updated on the origin server, it is automatically pushed to all edge locations. This ensures that users receive the latest version of the content, regardless of their location. Synchronization mechanisms include cache invalidation and push/pull techniques.
Benefits of Using CDNs for Content Replication and Synchronization:
- Reduced Latency: Serving content from the nearest edge location significantly reduces latency and improves user experience.
- Increased Availability: CDNs provide a reliable and redundant infrastructure, ensuring that content is always available even in the event of outages.
- Improved Performance: By caching content closer to end users, CDNs reduce bandwidth consumption and improve overall website performance.
- Reduced Costs: CDNs can help reduce infrastructure costs by eliminating the need to host and manage content on multiple servers.
- Scalability: CDNs can easily scale to meet changing traffic demands, ensuring that content is delivered efficiently during peak usage periods.
Considerations:

- Edge Network Expansion: The more edge locations a CDN has, the better the coverage and latency reduction.
- Cache Management: Effective cache management strategies are crucial to avoid caching outdated content and ensure synchronization.
- Security: CDNs must implement robust security measures to protect content from unauthorized access and attacks.
- Cost Optimization: Carefully evaluate the costs and benefits of using a CDN to determine the most cost-effective solution.
Conclusion:
CDNs are an essential tool for efficient content replication and synchronization. By leveraging CDNs, businesses can improve website performance, reduce latency, increase availability, and optimize their infrastructure. With careful consideration of the factors discussed, organizations can effectively implement CDNs to enhance the user experience and achieve their content delivery goals.## Leveraging CDNs for Efficient Content Replication and Synchronization
Executive Summary
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are an essential tool for businesses looking to improve the performance and availability of their digital content. By leveraging CDNs, businesses can replicate and synchronize their content across multiple geographically distributed servers, ensuring that users have fast and reliable access to the content they need.
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital world, users expect instant access to high-quality content. To meet this demand, businesses must find ways to deliver their content quickly and efficiently. CDNs provide a cost-effective and efficient solution by caching content on servers that are located close to users. This reduces latency and improves the user experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a CDN?
A CDN is a geographically distributed network of servers that caches and delivers content to users based on their location.
2. Why should I use a CDN?
By using a CDN, you can improve the performance, availability, and scalability of your content delivery.
3. How do I choose the right CDN for my business?
When choosing a CDN, consider factors such as performance, reliability, security, and cost.
Top 5 Subtopics
1. Content Caching
- Caching frequently requested content on servers located close to users.
- Reduces latency and improves load times.
- Can be implemented using various caching strategies, such as browser caching, CDN caching, and edge caching.
2. Load Balancing
- Distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers to prevent overloading.
- Ensures that users have consistent access to content even during peak traffic periods.
- Can be implemented using various load balancing algorithms, such as round-robin, weighted round-robin, and least connections.
3. Geolocation Routing
- Directing users to the nearest CDN server based on their location.
- Reduces latency and improves the user experience by providing localized content.
- Can be implemented using techniques such as IP address analysis and geographic databases.
4. Content Compression
- Reducing the size of content before sending it over the network.
- Reduces bandwidth usage and improves load times.
- Can be implemented using various compression algorithms, such as Gzip, Brotli, and Zopfli.
5. Security
- Protecting content from unauthorized access, tampering, and malicious attacks.
- Can be implemented using various security measures, such as HTTPS, SSL/TLS encryption, and intrusion detection systems.
Conclusion
CDNs are a powerful tool for businesses looking to improve the performance, availability, and security of their digital content. By leveraging CDNs, businesses can ensure that their users have fast and reliable access to the content they need, regardless of their location.
Keyword Tags
- Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Content Replication
- Content Synchronization
- Content Caching
- Geolocation Routing
