Leveraging Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) for Effective Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity

Introduction
In an increasingly digital world, businesses face constant threats to their operations due to natural disasters, cyberattacks, and infrastructure failures. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) play a crucial role in ensuring business continuity by providing reliable access to critical data and applications during disruptive events.
Key Benefits of CDNs for Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity

- High Availability: CDNs distribute content across geographically diverse locations, ensuring availability even if one or more data centers experience an outage.
- Reduced Latency: CDNs cache content close to end-users, reducing latency and improving user experience.
- Security: CDNs provide advanced security features such as DDoS protection and encryption, safeguarding data from malicious attacks.
- Scalability: CDNs can handle sudden traffic surges during emergencies, preventing service disruptions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: CDNs offer a cost-effective way to enhance disaster recovery and business continuity measures.
Implementing CDNs for Disaster Recovery
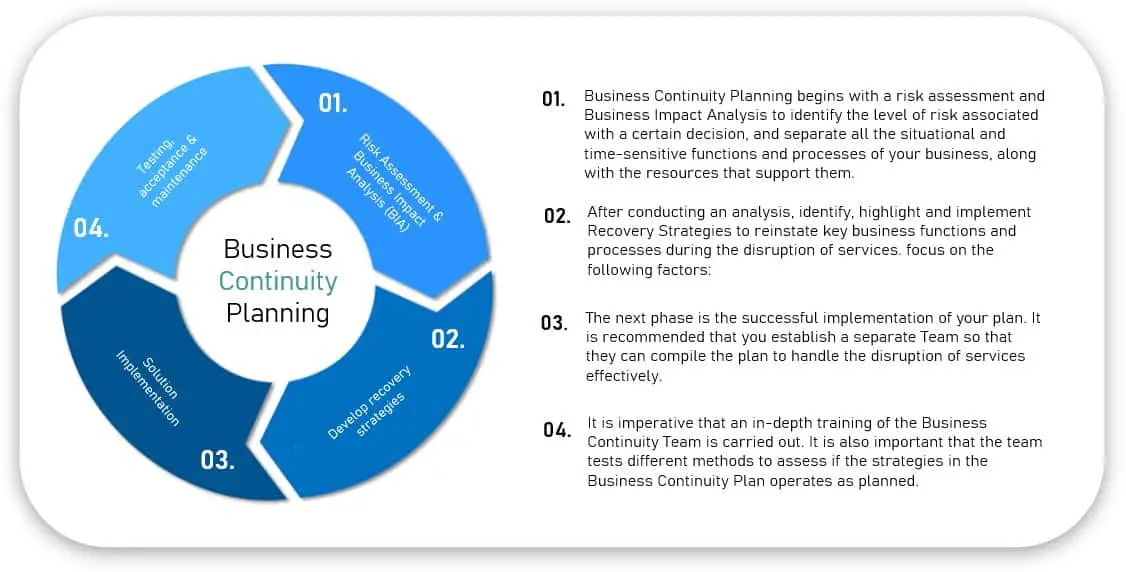
- Identify Critical Content: Determine which data, applications, and websites are essential for business operations.
- Establish Geographic Redundancy: Distribute content across multiple CDN locations to ensure availability in case of regional outages.
- Configure Replication and Failover: Set up automatic replication and failover mechanisms to ensure seamless transition to backup servers during emergencies.
- Monitor and Manage: Implement monitoring systems to track CDN performance and respond promptly to any issues.
Best Practices for Business Continuity
- Test and Verify: Regularly test the disaster recovery plan to ensure its effectiveness.
- Plan for Communication: Establish clear communication channels for employees and customers during emergencies.
- Document Procedures: Document all disaster recovery procedures to facilitate a smooth transition in case of an event.
- Train Employees: Train employees on disaster recovery procedures and their roles during an emergency.
Case Study
- During a major hurricane, a global e-commerce company experienced a network outage at its primary data center. However, thanks to its CDN, customers were still able to access the website and make purchases, minimizing business impact.
Conclusion
CDNs are an essential component of a comprehensive disaster recovery and business continuity strategy. By providing high availability, low latency, security, and scalability, CDNs help organizations maintain critical operations during disruptive events. Implementing CDNs and following best practices can ensure that businesses remain resilient and continue to serve their customers even in the face of adversity.## Leveraging CDNs for Effective Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Executive Summary
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) play a pivotal role in ensuring business continuity and disaster recovery by providing reliable, high-performance content delivery even in the face of unforeseen events. By leveraging CDNs, organizations can mitigate risks, safeguard critical data, and maintain seamless operations amidst disruptions. This article delves into the benefits, implementation, and best practices of CDNs for effective disaster recovery and business continuity.
Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, businesses rely heavily on online infrastructure and data to operate efficiently. However, unexpected events such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, or infrastructure failures can disrupt these systems, leading to costly downtime and potential data loss. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) have emerged as a key solution to address these challenges, ensuring uninterrupted access to critical data and services during disruptions.
FAQs
1. What are the primary benefits of using CDNs for disaster recovery?
- Enhanced data protection: CDNs facilitate secure data replication across multiple geographically dispersed servers, reducing the risk of data loss due to localized outages or hardware failures.
- Improved website availability: CDNs employ sophisticated routing algorithms to deliver content from the nearest and most available server, ensuring high uptime and reduced latency, even during peak traffic or outages.
2. How can CDNs help in business continuity planning?
- Backup infrastructure: CDNs provide a reliable backup infrastructure for critical business applications and data, enabling organizations to continue operations seamlessly if primary systems become unavailable.
- Traffic management: CDNs can intelligently redirect traffic to alternative servers during disruptions, mitigating the impact of outages and ensuring continuity of services.
3. What are the key considerations when selecting a CDN provider?
- Network reach: The CDN’s network should cover the target geographical regions and have a proven track record of reliability and performance.
- Security: The CDN must offer robust security features, including encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry standards such as PCI DSS and ISO 27001.
Subtopics
Global Network Infrastructure
- Geographically dispersed servers: CDNs maintain a global network of servers located in multiple regions, ensuring redundancy and reduced latency for users worldwide.
- Multiple points of presence (PoPs): PoPs are strategically placed within regions to provide local connectivity and reduce network hops, improving content delivery efficiency.
- Load balancing: CDNs employ load balancing techniques to distribute traffic across multiple servers, preventing overloading and ensuring optimal performance.
Caching and Content Delivery
- High-speed caching: CDNs cache frequently accessed content on edge servers, dramatically reducing load times and improving user experience.
- Content delivery optimization: CDNs use techniques such as compression, image optimization, and intelligent routing to deliver content in an optimized format, reducing bandwidth consumption and improving load times.
- Content compression: CDNs compress content using advanced algorithms to reduce file sizes, minimizing bandwidth utilization and speeding up delivery.
Security and Reliability
- Encrypted data transfer: CDNs implement robust encryption protocols to protect data in transit and at rest, ensuring data privacy and compliance.
- Redundant infrastructure: CDNs maintain multiple levels of redundancy within their network, mitigating the impact of hardware failures or localized outages.
- Load balancing: Load balancing mechanisms prevent overloading on individual servers, ensuring high availability and consistent performance.
Performance Monitoring and Analytics
- Real-time monitoring: CDNs provide sophisticated monitoring tools that allow administrators to track network performance, content delivery metrics, and user experience in real time.
- Comprehensive analytics: CDNs offer detailed analytics on traffic patterns, content performance, and user engagement, enabling data-driven optimization and decision-making.
- Reporting and alerts: CDNs generate customizable reports and alerts, providing organizations with timely insights into network health and content delivery performance.
Cost Considerations and Value Proposition
- Scalability and flexibility: CDNs offer flexible pricing models that allow organizations to scale bandwidth and storage capacity as needed, providing cost-effective disaster recovery and business continuity.
- Reduced downtime costs: CDNs minimize downtime and data loss, reducing the financial impact of disruptions and protecting brand reputation.
- Improved user experience: By ensuring fast and reliable content delivery, CDNs improve user satisfaction, enhance engagement, and drive business growth.
Conclusion
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are essential for effective disaster recovery and business continuity. They provide a resilient and highly available infrastructure for data storage, content delivery, and traffic management. By leveraging CDNs, organizations can mitigate risks, safeguard critical data, and maintain seamless operations even in the face of unexpected disruptions. With careful planning and selection of a reliable CDN provider, businesses can ensure they are fully prepared to withstand challenges and emerge stronger from adversity.
Keywords
- Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Disaster Recovery
- Business Continuity
- High Availability
- Content Delivery Optimization
