Implementing Ethical AI in Government Services

Executive Summary

Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionize government services, but it also raises important ethical concerns around bias, accountability, and transparency. This report provides a comprehensive guide to implementing ethical AI in government services, outlining key principles, best practices, and challenges. By addressing ethical considerations from the outset, governments can harness the benefits of AI while safeguarding public trust and ensuring equitable access to services.
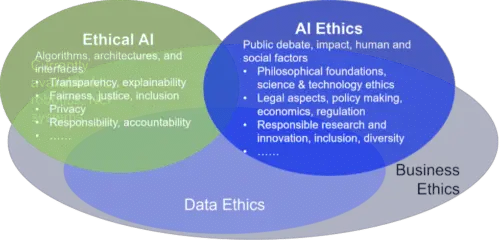
Introduction
The integration of AI in government services offers numerous advantages, including improved efficiency, personalized experiences, and enhanced decision-making. However, the development and deployment of AI systems must be guided by ethical principles to avoid potential risks and unintended consequences. This article explores the key subtopics of ethical AI in government services, providing a roadmap for responsible implementation and best practices for addressing ethical challenges.
FAQs
Q: What are the ethical concerns surrounding AI in government services?
A: Key ethical concerns include bias, accountability, transparency, and privacy.
Q: How can governments address bias in AI systems?
A: Strategies include collecting diverse data, employing fairness algorithms, and conducting regular audits.
Q: What are the benefits of transparent AI in government?
A: Transparency promotes trust, accountability, and allows citizens to understand how AI systems make decisions.
Subtopics
Bias Mitigation
- Data Collection: Ensuring diverse data sources and representations to minimize bias in AI models.
- Fairness Algorithms: Employing algorithms and techniques to identify and mitigate potential biases, such as adjusting for demographic disparities.
- Auditing and Monitoring: Regularly reviewing AI systems for accuracy, fairness, and bias.
- User Feedback: Incorporating user feedback loops to detect and address biases that may arise in practice.
Accountability and Transparency
- Attribution: Clearly defining the roles and responsibilities of individuals involved in the development and deployment of AI systems.
- Auditability: Providing transparency into AI decision-making processes through documentation, logging, and explainable AI techniques.
- Citizen Oversight: Establishing mechanisms for citizens to participate in the oversight and governance of AI systems.
Privacy and Data Protection
- Data Security: Implementing robust data security measures to protect sensitive personal information collected and processed by AI systems.
- Consent and Data Retention: Obtaining informed consent for the collection and use of data, and adhering to appropriate data retention policies.
- Data Anonymization: Minimizing the risk of re-identification by anonymizing or de-identifying data used for AI training and analysis.
Human-Centered AI
- Equity and Accessibility: Ensuring AI systems are designed to benefit all citizens, including underserved communities.
- Job Displacement: Mitigating the potential for AI to displace human workers by investing in reskilling and upskilling programs.
- Value Alignment: Ensuring AI systems are aligned with human values and priorities, considering ethical implications at every stage of development.
Governance and Regulation
- Ethics Committees: Establishing independent ethics committees to review and guide AI development and deployment.
- Ethical Frameworks: Developing comprehensive ethical frameworks to provide guidance on the responsible use of AI in government.
- Public Consultation: Engaging citizens and stakeholders in the ethical considerations and decision-making processes surrounding AI implementation.
Conclusion
Implementing ethical AI in government services requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses bias mitigation, accountability, privacy, human-centric design, and governance. By embracing these principles, governments can harness the transformative power of AI while ensuring public trust, promoting transparency, and safeguarding the rights and well-being of citizens. As AI continues to evolve, it is crucial for governments to remain vigilant in monitoring ethical implications and adapting their strategies accordingly.
Keyword Tags
- Ethical AI
- Government Services
- Data Privacy
- Accountability
- Bias Mitigation
