Enhancing Accessibility With Ai: Technology For The Disabled
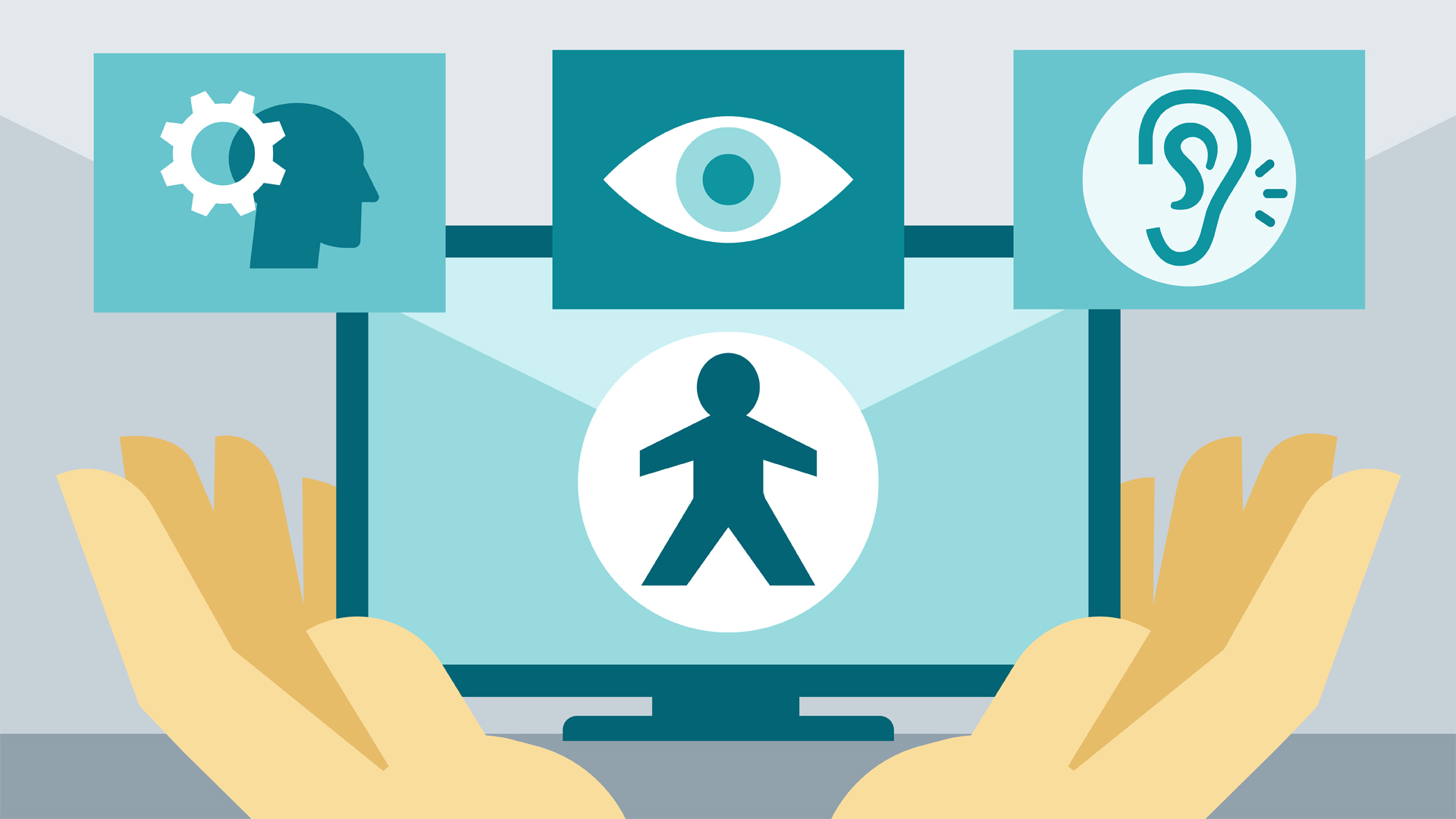

Executive Summary

In an era of technological advancements, it is imperative to harness the power of innovation to address the challenges faced by individuals with disabilities. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative tool that holds immense potential to enhance accessibility, empower disabled people, and create a more inclusive society. This article explores the multifaceted role of AI in improving accessibility, delving into specific subtopics, real-world examples, and future opportunities. By leveraging the capabilities of AI, we can empower individuals with disabilities, enabling them to fully participate in and contribute to society.
Introduction
Accessibility is a crucial aspect of modern society, ensuring that everyone, regardless of their abilities or disabilities, has equal access to opportunities, services, and information. For individuals with disabilities, accessibility challenges can often hinder their participation in various aspects of life. However, advancements in AI offer a beacon of hope, presenting innovative solutions that can revolutionize accessibility and empower disabled people.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the role of AI in enhancing accessibility?
AI plays a vital role in enhancing accessibility by providing assistive technologies that empower individuals with disabilities to overcome barriers and interact with the world more effectively.
2. How can AI assist people with visual impairments?
AI-powered assistive technologies can assist people with visual impairments by providing image recognition, text-to-speech, and object detection capabilities, enabling them to navigate their environment and access information more independently.
3. What are the benefits of AI for individuals with hearing impairments?
AI can assist individuals with hearing impairments by providing real-time captioning, speech recognition, and sign language interpretation, facilitating communication and social interaction.
Key Subtopics in AI for Accessibility
1. Image Recognition
- Object Recognition: AI algorithms can identify and label objects in images, assisting individuals with visual impairments in navigating their surroundings and recognizing objects.
- Text Recognition: AI-powered applications can extract text from images, making written information accessible to people with dyslexia or low vision.
- Landmark Recognition: AI systems can identify and locate landmarks, providing navigational assistance to individuals with visual impairments.
2. Speech Recognition
- Real-Time Captioning: AI algorithms can generate real-time captions for videos, lectures, and conversations, improving accessibility for people with hearing impairments.
- Voice Control: AI-enabled voice assistants allow individuals with physical impairments to control their devices, access information, and communicate without using their hands.
- Language Translation: AI systems can translate spoken and written language in real-time, facilitating communication between people from different linguistic backgrounds.
3. Navigation Assistance
- Route Planning: AI algorithms can provide optimized and accessible routes for individuals with mobility impairments, considering factors such as terrain, obstacles, and transportation options.
- Wayfinding: AI-powered apps can provide turn-by-turn directions and indoor navigation assistance, enabling individuals with visual impairments to explore unfamiliar environments more confidently.
- Obstacle Detection: AI systems can detect and alert individuals with visual impairments to potential obstacles in their path, ensuring safer and more independent mobility.
4. Assistive Communication
- Text-to-Speech: AI-enabled applications can convert text into spoken words, providing access to written content for individuals with dyslexia, low vision, or reading difficulties.
- Speech-to-Text: AI algorithms can transcribe spoken words into text, facilitating communication for individuals with speech impairments or hearing loss.
- Sign Language Interpretation: AI systems can recognize and interpret sign language gestures, bridging communication barriers for individuals who are deaf or hard of hearing.
5. Universal Design
- Adaptive Interfaces: AI-driven adaptive interfaces adjust to the individual needs of users with disabilities, providing customized access to applications and websites.
- Multimodal Interaction: AI enables multimodal interaction, allowing individuals with different input preferences (e.g., voice, touch, gestures) to engage with technology more effectively.
- Cognitive Accessibility: AI algorithms can identify and address cognitive accessibility barriers, making content and interfaces more accessible for individuals with cognitive disabilities.
Conclusion
AI has the potential to revolutionize accessibility for individuals with disabilities, breaking down barriers, empowering them to reach their full potential, and creating a more inclusive society. By embracing the transformative power of AI, we can harness innovation to improve the lives of disabled people, ensuring their active participation and contribution to all aspects of life.
Keyword Tags:
- Accessibility for Disabled
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Accessibility
- Assistive Technologies for Visual Impairment
- Speech Recognition for Hearing Impairment
- Universal Design for Disability
