Digital Identity Issues: Managing User Identities Across Platforms
In today’s digital world, users interact with a multitude of platforms ranging from social media to e-commerce and productivity tools. Each platform requires users to create and manage their own digital identity, including personal information, credentials, and privacy settings. This fragmentation of digital identities across platforms presents several challenges:
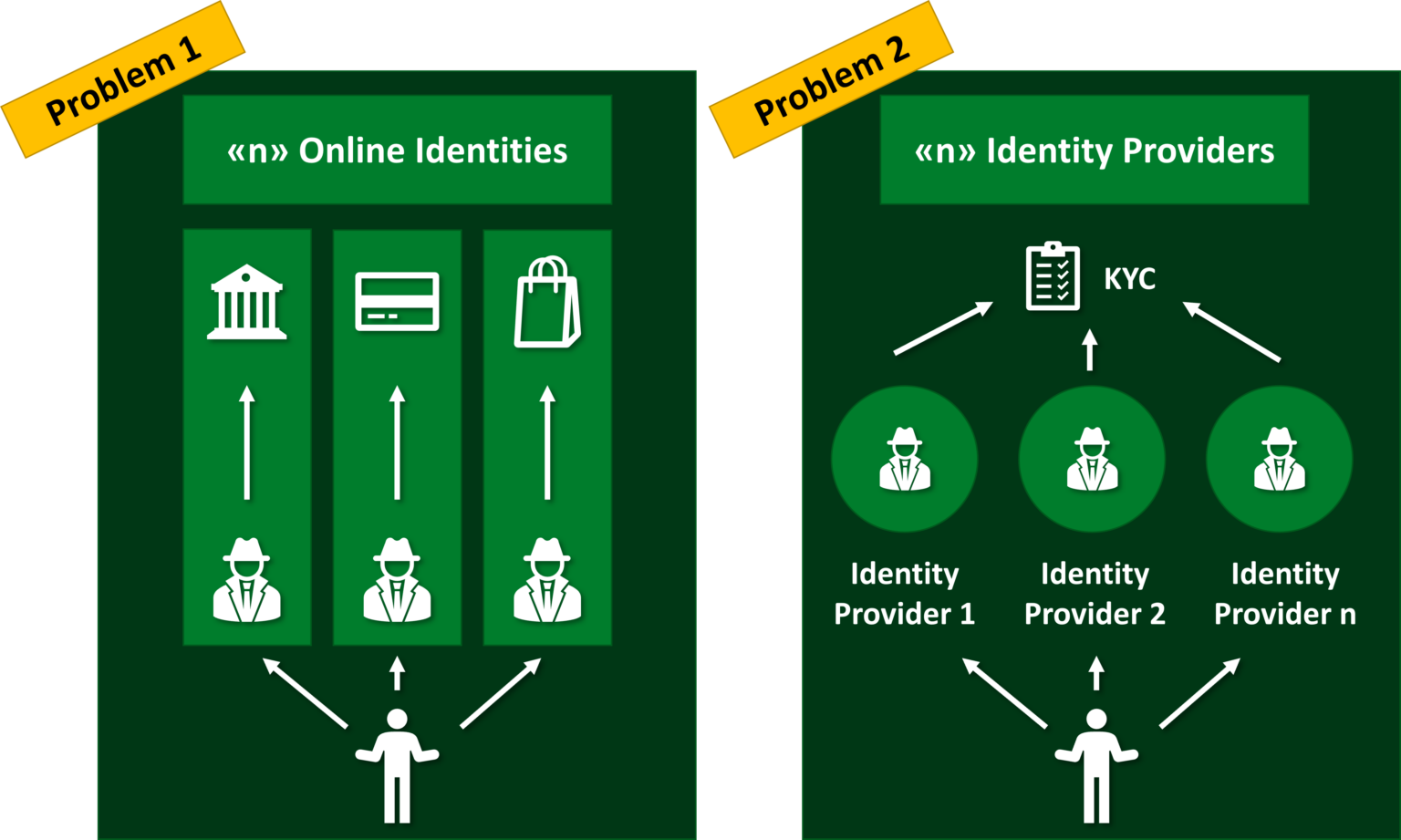
- Security risks: Each platform has its own authentication and security measures, which can vary in effectiveness. Users may have to remember multiple passwords, leading to weakened security practices. Moreover, compromised credentials on one platform could potentially be used to access sensitive information on others.
- User experience: Managing multiple digital identities can be cumbersome and time-consuming. Users may have to switch between platforms and reset passwords frequently. This can hinder productivity and create frustration for users.
- Privacy concerns: Platforms often collect and use personal information to tailor experiences and deliver targeted advertising. Users need to manage privacy settings across multiple platforms to prevent unwanted data sharing or security breaches.
To address these challenges, centralized digital identity solutions have emerged. These solutions allow users to create a single digital identity that can be used across multiple platforms. By authenticating users once and retrieving their identity information from a centralized repository, these solutions offer the following benefits:
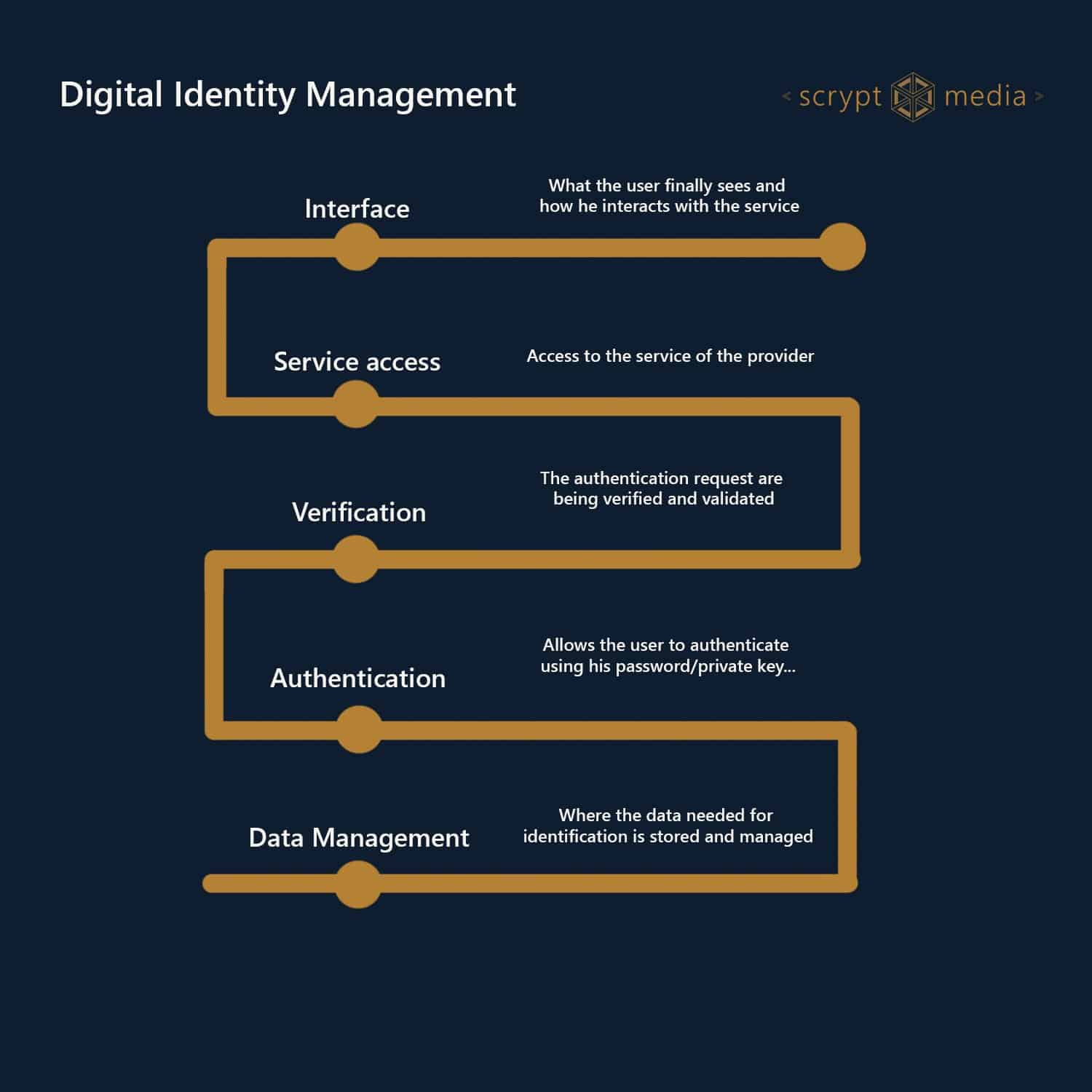
- Enhanced security: Centralized digital identity providers typically employ robust security measures, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud.
- Streamlined user experience: Users can access multiple platforms seamlessly without the need to remember multiple passwords or reset credentials.
- Improved privacy: Users have more control over their personal information, as they can set privacy preferences once for all platforms accessing their digital identity.
However, centralized digital identity solutions also raise concerns about data privacy and control. Users must trust the centralized authority with their sensitive information, which could potentially be used for surveillance or profiling purposes. It is important to carefully consider the trade-offs between convenience and control when implementing centralized digital identity solutions.## Digital Identity Issues: Managing User Identities Across Platforms
Executive Summary
The proliferation of digital platforms and services has led to an explosion in the number of user identities that individuals must manage. This can be a challenge, as users often need to remember multiple usernames, passwords, and other credentials. It can also be a security risk, as users who reuse passwords across multiple platforms are more likely to be victims of account takeover and other cyberattacks.
This article will discuss the key issues related to digital identity management and provide some tips for users on how to manage their identities more effectively.
Introduction
Digital identity is a representation of an individual’s identity in the digital world. It consists of the various attributes that identify a person online, such as their name, email address, social media profiles, and IP address.
Digital identity management is the process of creating, managing, and using digital identities. This process can be complex, as it involves balancing the need for security with the need for convenience.
FAQs
- What is the difference between a digital identity and a physical identity?
A digital identity is a representation of an individual’s identity in the digital world, while a physical identity is a representation of an individual’s identity in the physical world. Digital identities are often more fluid and less permanent than physical identities, as they can be easily changed or deleted.
- Why is digital identity management important?
Digital identity management is important because it allows individuals to control their online presence and protect their personal information. It also helps to ensure that individuals are able to access the online services they need in a secure and convenient manner.
- What are some of the challenges of digital identity management?
One of the key challenges of digital identity management is the need to balance security with convenience. Individuals need to be able to create and manage their digital identities in a way that is both secure and convenient. Another challenge is the need to manage multiple digital identities across different platforms and devices.
Top 5 Subtopics
1. Password Management
Password management is one of the most important aspects of digital identity management. Individuals need to create strong passwords that are difficult to guess and unique for each account they create. They also need to store their passwords securely and avoid reusing them across multiple platforms.
- Use a password manager. A password manager is a software program that can generate and store strong passwords for you. Password managers can also help you to organize your passwords and share them securely with others.
- Use two-factor authentication. Two-factor authentication is a security measure that requires you to enter two different pieces of information when you log in to an account. This makes it much more difficult for attackers to gain access to your account, even if they have your password.
- Use a strong password policy. A strong password policy requires users to create passwords that are at least 12 characters long and include a mix of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
2. Social Media Management
Social media is a powerful tool for staying connected with friends and family and sharing information. However, it is important to manage your social media accounts carefully to protect your privacy and security.
- Be mindful of what you share. Do not share personal information, such as your address or phone number, on social media. Also, be careful about what photos and videos you share, as they could be used to identify you or track your location.
- Use privacy settings. Social media platforms offer a variety of privacy settings that you can use to control who can see your posts and who can contact you. Make sure to review your privacy settings regularly and adjust them as needed.
- Be careful about who you connect with. Do not accept friend requests from people you do not know. Also, be careful about clicking on links in messages from people you do not know.
3. Data Privacy
Data privacy is the practice of protecting personal information from unauthorized access or disclosure. Individuals need to be aware of the data that they share online and take steps to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Read privacy policies. Before you create an account on a new website or service, read the privacy policy to understand how your personal information will be used and shared.
- Be careful about what you share. Do not share personal information, such as your address or phone number, on public websites or forums. Also, be careful about what photos and videos you share, as they could be used to identify you or track your location.
- Use privacy-enhancing tools. There are a number of privacy-enhancing tools that you can use to protect your personal information online. These tools include ad blockers, tracking blockers, and virtual private networks (VPNs).
4. Identity Theft
Identity theft is a crime that occurs when someone uses your personal information to impersonate you. Identity thieves can use your personal information to open new accounts, make purchases, or even file taxes in your name.
- Protect your personal information. Keep your personal information, such as your Social Security number and credit card numbers, confidential. Do not share this information with anyone unless you are absolutely sure that they are trustworthy.
- Monitor your credit reports. Regularly review your credit reports for any unauthorized activity. If you see any suspicious activity, report it to the credit bureaus immediately.
- File a police report. If you are a victim of identity theft, file a police report. This will help to document the crime and protect your rights.
5. Digital Legacy
Your digital legacy is the collection of digital content that you leave behind after you die. This content can include your social media profiles, email accounts, and online photos. It is important to plan for your digital legacy so that your wishes are respected after you die.
- Create a digital will. A digital will is a legal document that allows you to specify what happens to your digital content after you die. You can use a digital will to designate a digital executor who will be responsible for managing your digital content after you die.
- Store your digital content in a secure location. Store your digital content in a secure location, such as a password-protected hard drive or a cloud storage service. This will help to protect your content from unauthorized access after you die.
- Let your family know about your digital content. Let your family know where your digital content is stored and who your digital executor is. This will help to ensure that your wishes are respected after you die.
Conclusion
Digital identity management is a complex and challenging issue. However, by following the tips in this article, you can take steps to protect your privacy and security and manage your digital identities more effectively.
Keyword Tags
- Digital Identity
- Identity Management
- Password Management
- Social Media Management
- Data Privacy


