Deep Learning And Ai: Pushing The Boundaries
Executive Summary
This article provides a comprehensive insight into Deep Learning and Artificial Intelligence, exploring their capabilities, applications, limitations, and ethical implications. It delves into various subtopics, including Natural Language Processing, Machine Learning, Computer Vision, Robotics, and Reinforcement Learning, explaining their key concepts and significance. Additionally, the article discusses the challenges of bias and interpretability in AI systems and offers guidance on building ethical AI solutions.

Introduction
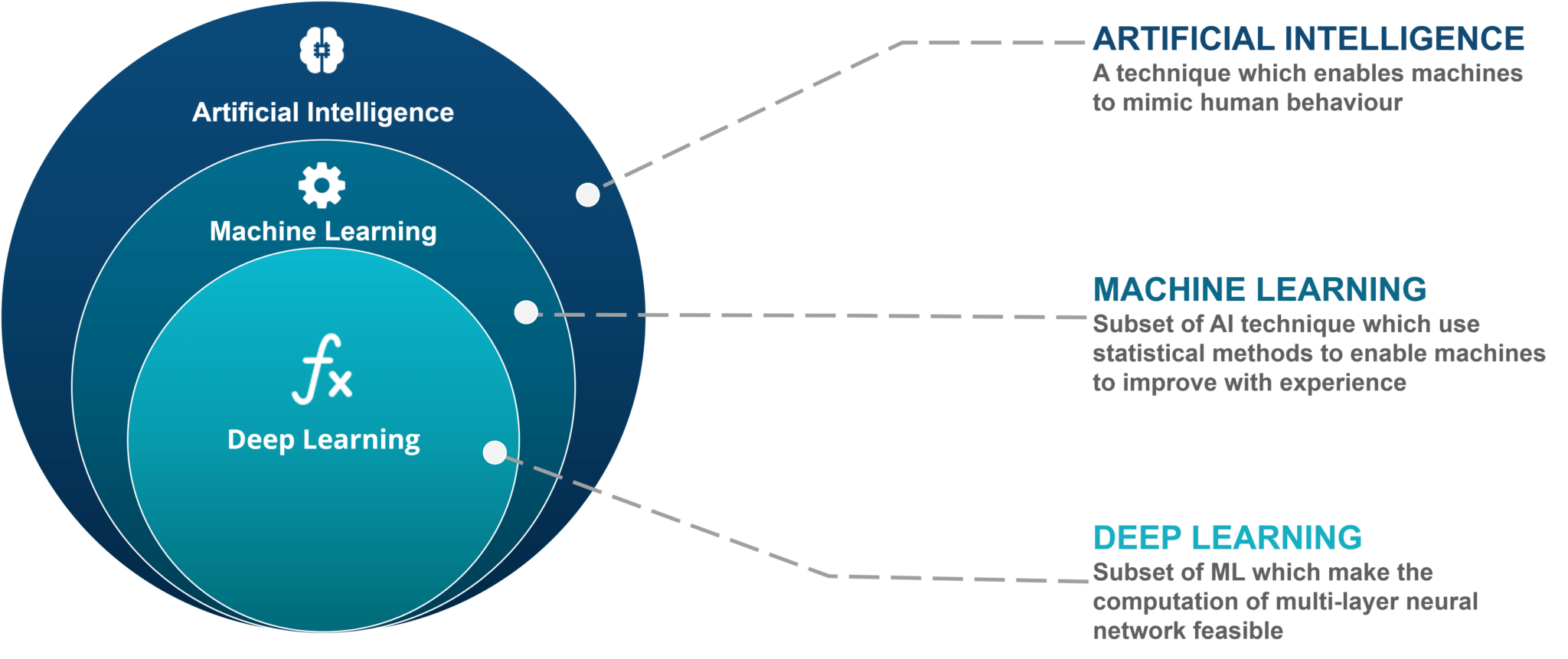
Deep Learning, a subset of Machine Learning, has revolutionized various industries with its ability to analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and make predictions. Artificial Intelligence, a broader concept encompassing Deep Learning, is driving advancements in automation, decision-making, and problem-solving. This article explores the intricacies of these technologies, their applications, and the ethical considerations surrounding their use.
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP is a field of AI that deals with the interaction between computers and human (natural) languages. It enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language in various forms, such as text, speech, and gestures.
-
Machine Translation: Translates text from one language to another, enabling global communication and access to information.
-
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Provides conversational AI experiences, answering queries, offering recommendations, and automating customer service tasks.
-
Text Summarization and Generation: Condenses large amounts of text into concise summaries, and generates text from data or instructions.
-
Sentiment Analysis: Determines the emotional tone of text data, useful for market research, social media monitoring, and customer feedback analysis.
-
Named Entity Recognition: Identifies and extracts specific entities, such as names, locations, and organizations, from text, aiding in information extraction and document summarization tasks.
2. Machine Learning (ML)
ML is a type of AI that allows computers to learn from data without explicit programming. It involves algorithms capable of identifying patterns, making predictions, and improving their performance over time.
-
Supervised Learning: Utilizes labeled data to train a model to perform specific tasks, such as image classification or text classification.
-
Unsupervised Learning: Finds patterns and structures in unlabeled data, useful for tasks like anomaly detection, dimensionality reduction, and clustering.
-
Reinforcement Learning: Agents learn through interactions with their environment, experiencing rewards and penalties for specific actions, aiming to maximize long-term rewards.
-
Deep Learning: A subset of ML using artificial neural networks with multiple layers, allowing models to learn complex representations of data, enabling tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and speech recognition.
-
Ensemble Learning: Combines outputs from multiple models to improve overall performance, accuracy, and reliability.
3. Computer Vision (CV)
Computer Vision enables computers to interpret and understand the visual world. It involves algorithms that process and analyze images and videos, extracting meaningful information.
-
Image Classification: Classifies images into predefined categories, useful for object recognition, scene understanding, and medical imaging.
-
Object Detection: Locates and identifies objects within images, enabling applications such as self-driving cars, facial recognition, and surveillance systems.
-
Image Segmentation: Divides images into distinct segments or regions based on object boundaries, aiding in medical imaging, autonomous navigation, and content moderation.
-
Facial Recognition: Analyzes facial features to identify individuals, used in security systems, biometric authentication, and video surveillance.
-
Remote Sensing: Interprets data from satellites and aerial imagery for land use classification, environmental monitoring, and disaster response.
4. Robotics and Autonomous Systems
Robotics involves developing machines capable of autonomous movement, perception, and decision-making. Autonomous systems operate without human intervention, performing tasks ranging from manufacturing to space exploration.
-
Industrial Robotics: Automates tasks in manufacturing, automotive, and logistics industries, improving efficiency, precision, and safety.
-
Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars, trucks, and drones use sensors, AI algorithms, and GPS to navigate and respond to their surroundings.
-
Personal Robotics: Robots for household and personal use, such as vacuum cleaners, lawnmowers, and even companion robots, are becoming increasingly common.
-
Medical Robotics: Assists in surgical procedures, rehabilitation, and patient care, providing greater precision and efficiency.
-
Underwater and Space Exploration: Robots explore harsh and remote environments, facilitating scientific research and enabling missions beyond human capabilities.
5. Reinforcement Learning (RL)
RL focuses on developing agents that can learn and improve their decision-making through interactions with their environment. It involves the concept of rewards and penalties for actions, leading to optimal decision-making over time.
-
Game Playing: RL agents achieve superhuman performance in complex games like chess, Go, and StarCraft, mastering strategies through self-learning.
-
Robotics and Control: RL enables robots to learn optimal control policies in dynamic and uncertain environments, improving their adaptability and autonomy.
-
Resource Allocation and Scheduling: RL optimizes decision-making in resource-constrained environments, such as network management, energy distribution, and production planning.
-
Trading and Finance: RL agents analyze market data, learn trading strategies, and make investment decisions based on historical data and real-time market conditions.
-
Healthcare and Treatment Planning: RL algorithms personalize treatment plans for patients, considering individual characteristics and medical data to optimize outcomes.
Conclusion
Deep Learning and AI are powerful tools that hold immense potential to transform industries, solve complex problems, and enhance human capabilities. However, it is crucial to address challenges such as bias, interpretability, and ethical considerations to ensure the responsible and beneficial use of AI technologies. As these technologies continue to advance, we can expect even more groundbreaking applications and discoveries in the years to come.
Keyword Phrase Tags:
- Deep Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Machine Learning
- Computer Vision
- Natural Language Processing


This was an interesting read on the uses of deep learning and AI. I was impressed by the examples you provided, such as self-driving cars. However, I wonder if you have any thoughts on the potential risks of AI, such as job displacement or privacy concerns.
Great article! I’m a software engineer and I’m very interested in deep learning and AI. I would love to learn more about how these technologies are being used in different industries. Thanks for sharing!
I’m not sure I understand how deep learning and AI work. Can you explain it to me in a way that’s easy to understand?
This article is so boring. I don’t understand why anyone would be interested in this stuff.
I think it’s really cool how deep learning and AI are being used to solve real-world problems. I’m excited to see what these technologies will be able to do in the future.
I’m concerned about the potential risks of deep learning and AI, such as job displacement and privacy concerns. I hope that researchers and policymakers will carefully consider these risks before these technologies are widely adopted.
This was a great overview of deep learning and AI. I’m glad I took the time to read it.
I think it’s amazing how far deep learning and AI have come in recent years. I can’t wait to see what these technologies will be able to do in the future.
I’m really interested in learning more about how deep learning and AI are being used in the healthcare industry. Thanks for sharing this article!
I’m not sure I understand how deep learning and AI work. Can you explain it to me in a way that’s easy to understand?
This article is so boring. I don’t understand why anyone would be interested in this stuff.