Decoding Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
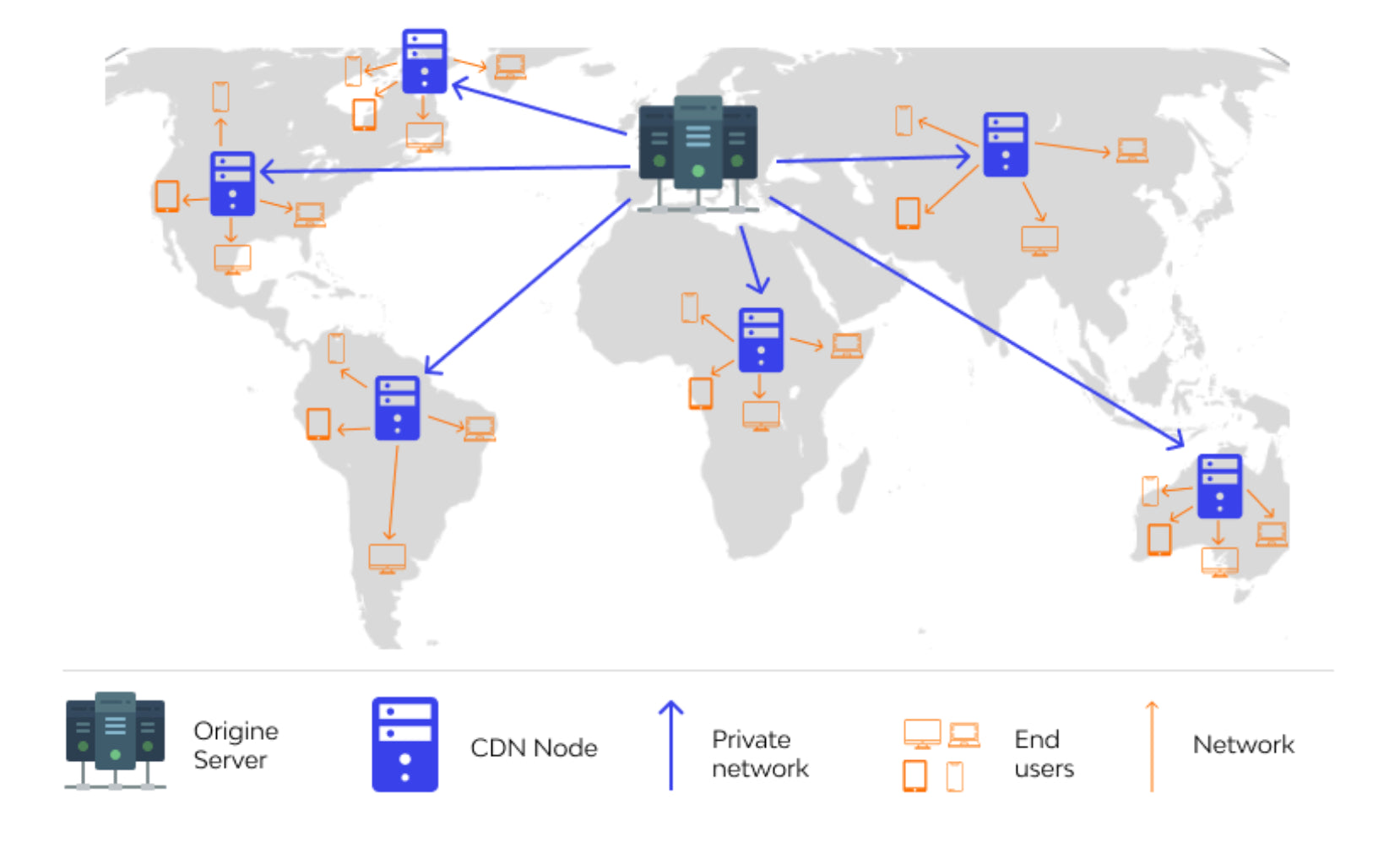
What is a CDN?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a distributed network of servers that work together to deliver web content to users around the globe as efficiently as possible. It acts as an intermediary between the origin server (where the content is hosted) and the end-user, reducing latency and improving the user experience.
How CDNs Work
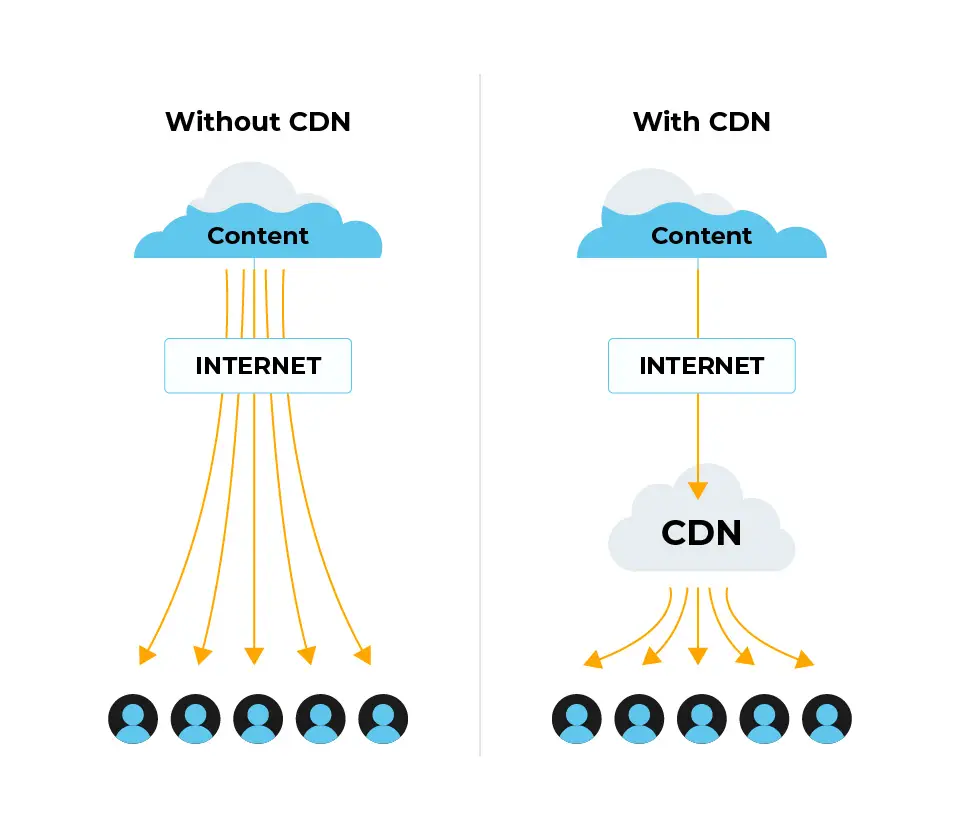
- Content Caching: CDNs store copies of frequently accessed content on their edge servers, which are located in different geographic regions. This reduces the distance between the user and the content, decreasing download times.
- Request Routing: When a user requests a web page, the CDN routes the request to the nearest edge server with the cached content. This ensures minimal latency and high-speed delivery.
- Load Balancing: CDNs distribute traffic across their edge servers to prevent any single server from becoming overloaded. This maintains optimal performance even during peak traffic times.
- Security: CDNs often provide security features such as SSL encryption, malware filtering, and DDoS protection to protect both the content and the end-user.
Benefits of Using CDNs
- Faster Content Delivery: Reduced latency improves page load times and enhances the user experience.
- Improved Performance During Peak Times: Load balancing ensures smooth performance even when web traffic surges.
- Global Reach: CDNs have edge servers strategically placed around the world, providing access to content from anywhere.
- Bandwidth Savings: By caching content, CDNs reduce the bandwidth usage on the origin server, saving costs.
- Reduced Server Load: CDNs take on the responsibility of delivering content, freeing up the origin server to focus on other tasks.
- Enhanced Security: CDNs provide additional layers of security, protecting against attacks and ensuring data integrity.
Types of CDNs
- Public CDNs: Available to all users for a fee, offering a wide range of features and global coverage.
- Private CDNs: Designed for specific businesses or organizations, providing customized solutions and increased control.
- Hybrid CDNs: Combine elements of both public and private CDNs, offering flexibility and cost optimization.
Conclusion
Content Delivery Networks are essential for delivering high-performance web content globally. By caching content on edge servers, routing requests efficiently, and providing security features, CDNs enable businesses and organizations to create a seamless and engaging user experience. As the internet continues to evolve, CDNs will undoubtedly play an increasingly vital role in ensuring fast and reliable web content delivery.## Decoding CDN: The Technology Behind Fast Web Content Delivery
Executive Summary
In today’s fast-paced digital world, users expect websites and applications to load quickly and reliably. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) play a pivotal role in ensuring the seamless delivery of digital content by efficiently distributing it from multiple locations around the globe. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of CDN technology, unraveling its benefits, architecture, and best practices to empower businesses with the knowledge necessary to optimize their web content delivery strategies.
Introduction
The internet has revolutionized the way we consume information and access services. With the rapid adoption of online platforms, businesses face the challenge of delivering high-quality content to a geographically dispersed audience while ensuring optimal performance. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) have emerged as a critical solution to this challenge, providing a robust infrastructure for the distribution of web content, images, videos, and other digital assets.
FAQs
1. What is a Content Delivery Network (CDN)?
A Content Delivery Network is a geographically distributed network of servers that work together to deliver content to users with high speed and reliability. CDNs cache content at various locations, reducing the distance between users and the content they request, resulting in faster load times.
2. How does a CDN improve website performance?
CDNs enhance website performance by reducing latency, the delay between the time a user requests content and when it becomes available. By caching content closer to users, CDNs eliminate the need for long-distance data transfers, significantly improving page load speeds and overall user experience.
3. What are the benefits of using a CDN?
CDNs offer numerous benefits, including:
- Improved website performance and user experience
- Reduced bandwidth costs
- Enhanced security and protection against DDoS attacks
- Increased scalability to handle traffic spikes and growth
- Improved SEO rankings due to faster load speeds
Subtopics
CDN Architecture
– Edge Servers: These servers are located at the edge of the CDN network, closest to the end users. They cache frequently requested content to reduce latency and improve performance.
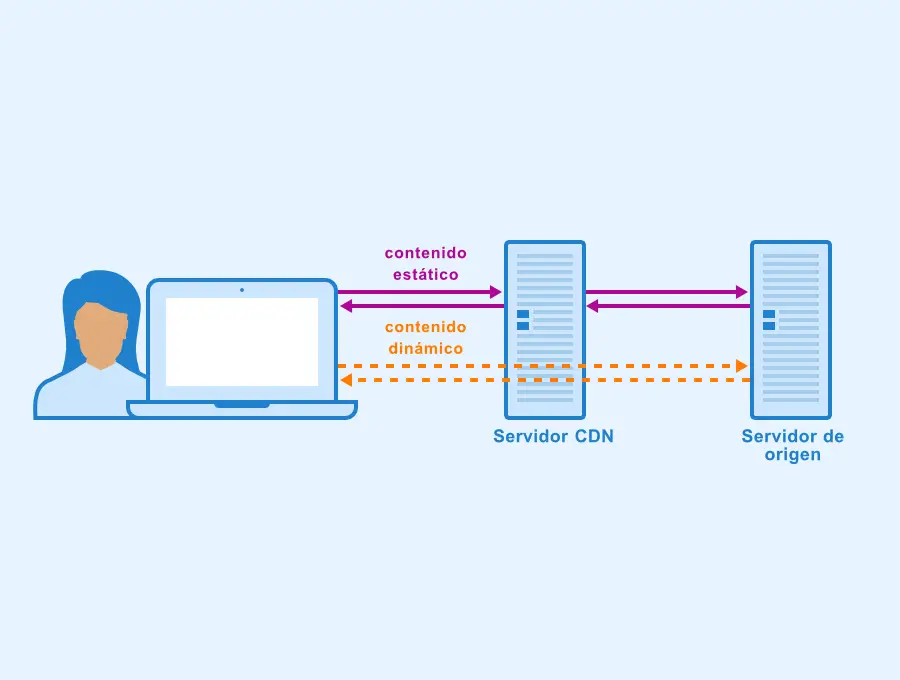
– Origin Server: This is the server that hosts the original version of the content being delivered. CDNs fetch content from the origin server and store it in their edge servers for faster delivery.
– Point of Presence (PoP): PoPs are physical locations where CDN servers are deployed to provide local content delivery to users in specific regions.
CDN Content Types
– Static Content: This includes files that remain unchanged over time, such as images, CSS, and JavaScript files. CDNs cache static content to significantly improve load times.
– Dynamic Content: This refers to content that is generated dynamically based on user requests, such as personalized web pages or search results. CDNs can also cache dynamic content, but may require additional configuration and caching strategies.
CDN Security Features
– Web Application Firewall (WAF): A WAF protects websites from malicious traffic and attacks by filtering incoming requests and blocking malicious ones.
– DDoS Mitigation: CDNs provide protection against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks by distributing traffic across multiple servers, making it difficult for attackers to overwhelm the network.
– SSL/TLS Encryption: CDNs offer SSL/TLS encryption to secure data transmissions between users and servers, protecting sensitive information from eavesdropping.
CDN Performance Optimization
– Content Compression: CDNs compress content before delivering it to reduce file sizes and improve load speeds.
– Load Balancing: CDNs distribute traffic across multiple servers to prevent overloading and maintain optimal performance even during traffic spikes.
– Monitoring and Analytics: CDNs provide detailed analytics and monitoring tools to track performance metrics and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
Content Delivery Networks have become indispensable for businesses seeking to deliver high-performing and reliable web content. By understanding the technology behind CDNs, their benefits, and best practices, businesses can optimize their web content delivery strategies to enhance user experience, drive traffic, and achieve business success. With the right CDN strategy in place, businesses can effectively cater to the growing demand for fast and seamless digital content consumption.
Keyword Tags
- CDN
- Content Delivery Network
- Web Performance Optimization
- Website Speed
- User Experience
