Decentralizing Power: Blockchain’s Role In Empowering Communities
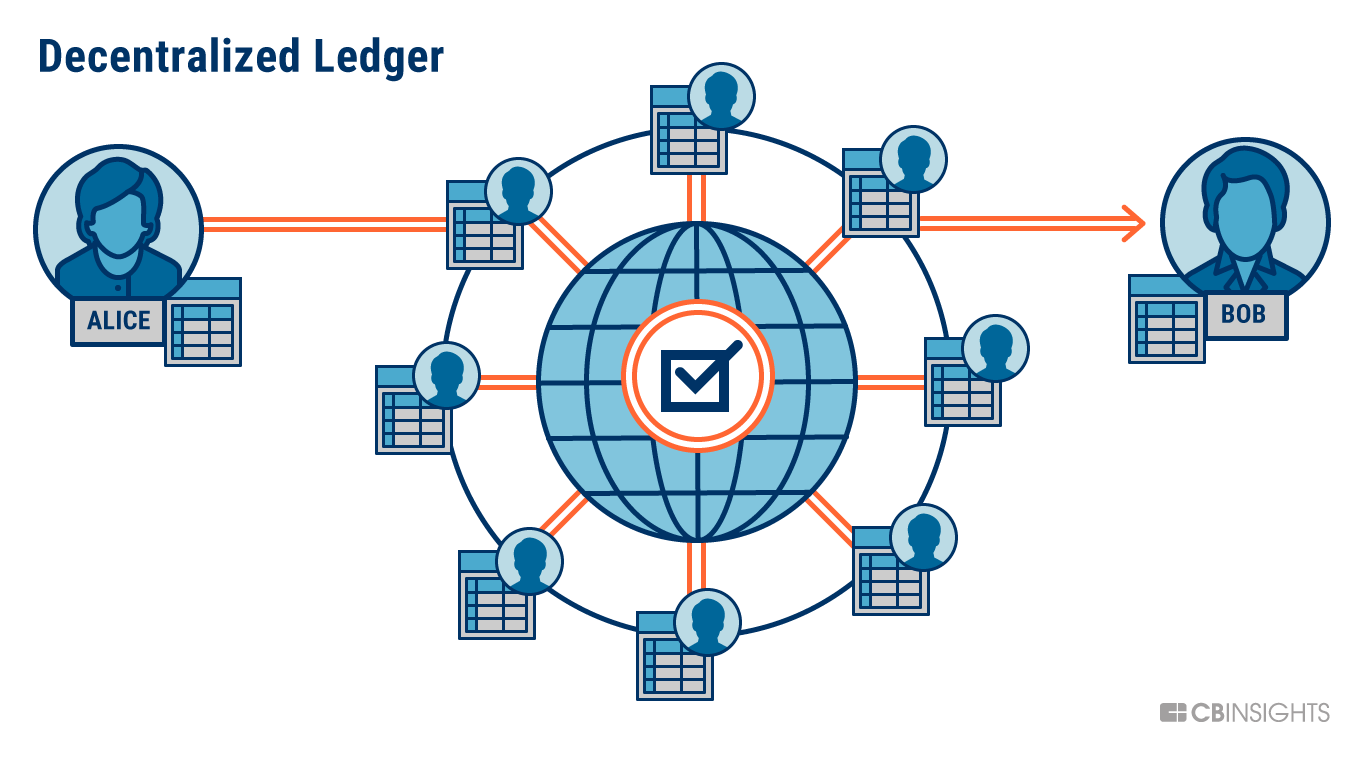
Blockchain technology, popularized by cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has the potential to revolutionize the way communities are structured and governed. By decentralizing power and enabling greater participation, blockchain can empower individuals and create more equitable and inclusive societies.

Decentralization:

Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that maintains a secure and tamper-proof record of transactions. It is not controlled by a central authority, instead, it relies on a network of computers to validate and record data. This decentralized nature removes the need for intermediaries and reduces the risk of corruption and fraud.
Participation and Empowerment:
Blockchain technology allows every individual in a network to participate in decision-making and governance. Anyone with access to the internet and a device can join the network, contribute to its governance, and vote on proposals. This democratizes the decision-making process and gives all members of a community a voice.
Transparency and Accountability:
All transactions and interactions on a blockchain are recorded and visible to all participants. This transparency promotes accountability and reduces the likelihood of power abuses. Individuals can easily track the flow of resources and hold those in authority accountable for their actions.
Empowerment of Marginalized Communities:
Blockchain technology can empower marginalized communities by providing them with access to resources and decision-making power. By eliminating intermediaries and reducing barriers to participation, blockchain can create a level playing field and enable individuals from all backgrounds to contribute to their communities.
Applications of Blockchain in Community Empowerment:
- Governance: Blockchain can be used to create decentralized governance systems that empower community members to directly participate in decision-making and policy development.
- Resource Management: Blockchain can provide secure and transparent records of resource allocation, ensuring equitable distribution and preventing corruption.
- Identity and Verification: Blockchain can establish decentralized identity systems, providing individuals with secure and verifiable control over their personal data.
- Legal and Regulatory Frameworks: Blockchain can be used to create decentralized legal and regulatory frameworks that are enforceable and transparent.
Conclusion:
Blockchain technology has the potential to decentralize power, empower communities, and create more just and equitable societies. By enabling greater participation, transparency, and accountability, blockchain can revolutionize community governance models and improve the lives of individuals from all backgrounds.## Decentralizing Power: Blockchain’s Role In Empowering Communities
Executive Summary
Blockchain technology has emerged as a powerful tool for decentralizing power and empowering communities. By enabling the creation of distributed, immutable ledgers, blockchain can foster transparency, accountability, and inclusivity in various aspects of society. This article explores the transformative potential of blockchain in five key subtopics:
- Community Finance
- Identity Management
- Supply Chain Transparency
- Voting and Governance
- Social Impact and Empowerment
Introduction
The centralized structures that govern many aspects of our lives often create power imbalances and limit community participation. Blockchain, with its decentralized nature and ability to create secure and transparent systems, offers a compelling solution to these challenges. By empowering communities to take ownership of their systems and processes, blockchain can foster a more just and equitable society.
Community Finance
- Decentralized finance (DeFi): Leverages blockchain to create accessible and inclusive financial services for communities, including lending, borrowing, and investing.
- Community currencies: Enables communities to create their own tokens or cryptocurrencies that facilitate local commerce and promote economic resilience.
- Microfinance: Provides small-scale loans and financial services to marginalized communities often excluded from traditional banking systems.
- Remittances: Simplifies and reduces the cost of sending and receiving money across borders, empowering immigrant communities and their families.
Identity Management
- Self-sovereign identity (SSI): Empowers individuals to control their own digital identities, reducing reliance on intermediaries and enhancing privacy.
- Blockchain-based digital IDs: Provides communities with a secure and verifiable means to manage and distribute digital identities, streamlining access to services and reducing fraud.
- Biometric authentication: Integrates biometric data into blockchain-based identity systems, enhancing security while minimizing the risk of identity theft.
- Decentralized reputation systems: Enables communities to establish transparent and accountable reputation mechanisms, fostering trust and accountability among members.
Supply Chain Transparency
- Provenance tracking: Blockchain enables real-time tracking of goods and materials throughout the supply chain, ensuring transparency and preventing fraud.
- Origin authentication: Verifies the origin and authenticity of products, empowering consumers to make informed choices and promote ethical sourcing.
- Fairtrade and sustainability: Blockchain can facilitate the fair distribution of profits and ensure sustainable practices throughout the supply chain.
- Reduced carbon footprint: Mitigates environmental impact by tracking and reducing carbon emissions associated with supply chains.
Voting and Governance
- Decentralized voting systems: Enables secure, transparent, and verifiable voting processes, promoting civic participation and reducing the risk of fraud.
- Community governance: Facilitates collective decision-making and community involvement in local governance initiatives, empowering citizens to shape their own communities.
- Participatory budgeting: Allows communities to allocate public resources based on their needs and priorities, fostering inclusivity and accountability.
- E-petitions and advocacy campaigns: Empowers citizens to voice their concerns and rally support for causes they care about.
Social Impact and Empowerment
- Community-owned platforms: Enables communities to establish their own platforms for communication, collaboration, and resource sharing.
- Educational initiatives: Empowers underprivileged communities by providing access to quality education, training, and vocational resources.
- Healthcare access: Facilitates access to affordable and efficient healthcare services for marginalized communities, improving their overall well-being.
- Disaster relief and humanitarian aid: Streamlines the distribution of aid and resources during emergencies, ensuring transparency and accountability in humanitarian efforts.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a transformative tool that empowers communities by decentralizing power and fostering transparency, accountability, and inclusivity. By creating distributed and immutable ledgers, blockchain can disrupt centralized systems and empower communities to take ownership of their decision-making, economic activities, and social interactions. As blockchain continues to evolve, its potential for community empowerment will only grow, leading to a more just and equitable society for all.
Keyword Tags
- Blockchain
- Decentralization
- Community Empowerment
- Identity Management
- Social Impact
