Decentralized Content Delivery Networks (dCDNs)

Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) play a crucial role in delivering content to users with speed and efficiency. However, traditional CDNs are centralized, which can lead to single points of failure, censorship, and performance bottlenecks.
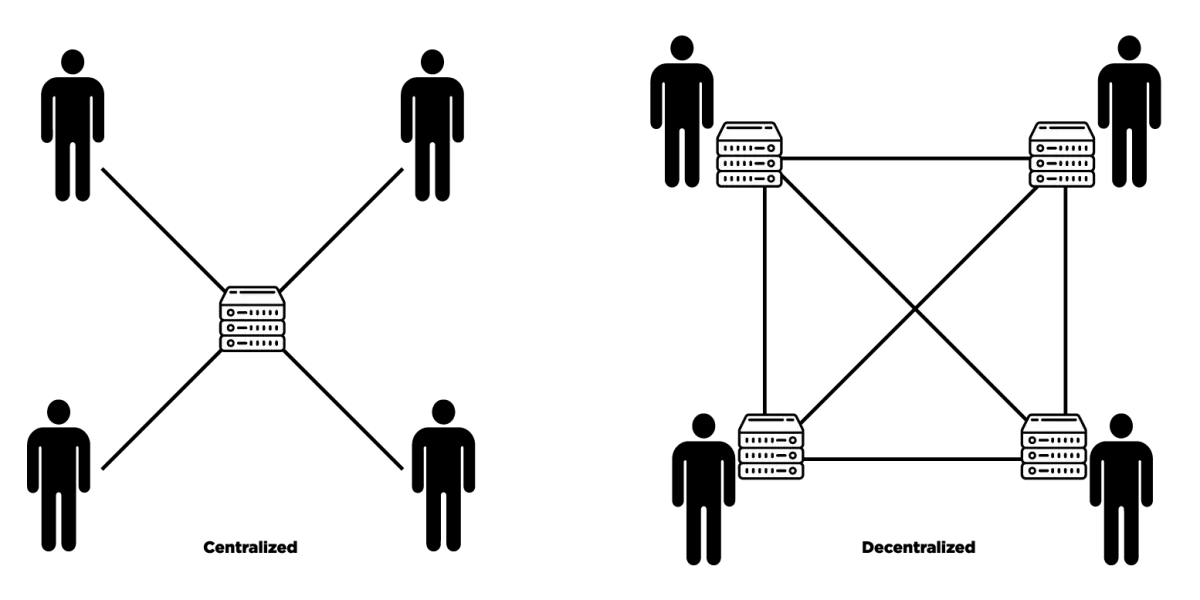
Decentralized CDNs (dCDNs) address these limitations by leveraging blockchain technology to create a distributed and censorship-resistant content delivery system.

Blockchain’s Role in dCDNs
Blockchain serves as the underlying infrastructure for dCDNs, providing:
- Decentralization: Content is stored and distributed across a network of nodes, eliminating the need for a central authority.
- Immutability: Once content is uploaded to the blockchain, it becomes immutable and cannot be altered or removed.
- Security: Blockchain’s cryptographic algorithms protect content from unauthorized access and malicious attacks.
- Transparency: All transactions and network activities are recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Advantages of dCDNs
dCDNs offer several advantages over traditional CDNs, including:
- Improved performance: Distributed storage and peer-to-peer delivery reduce latency and improve content availability.
- Increased security: Decentralization eliminates single points of failure and protects content from censorship or attacks.
- Lower costs: Decentralization reduces the need for expensive infrastructure and maintenance.
- Enhanced privacy: Users have more control over their data and content.
- Support for new technologies: dCDNs can integrate with emerging technologies, such as Web3 and the Metaverse.
Challenges and Future Trends
While dCDNs hold great potential, they also face challenges:
- Scalability: Handling large amounts of data at high speeds remains a technical hurdle.
- Interoperability: Integrating dCDNs with existing content delivery systems is complex.
- Adoption: Widespread adoption requires standardization and collaboration among industry players.
Despite these challenges, dCDNs are an active area of research and development. Future trends include:
- Increased adoption: More content providers and users will embrace dCDNs as their advantages become more evident.
- Improved scalability: Technological advancements will address scalability issues and enable dCDNs to handle massive data loads.
- Integration with other technologies: dCDNs will become part of a broader decentralized content distribution ecosystem, including Web3 and the Metaverse.
Conclusion
Decentralized CDNs are revolutionizing content delivery by leveraging blockchain technology. They offer improved performance, security, and cost-effectiveness while promoting decentralization, transparency, and user sovereignty. As dCDNs evolve and mature, they have the potential to transform the way we access and share digital content.## Decentralized CDNs: Blockchain’s Role In Content Delivery
Executive Summary
Blockchain technology is poised to revolutionize the content delivery network (CDN) landscape. By leveraging the decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain, CDNs can enhance security, improve performance, and reduce costs. This article explores the transformative role of blockchain in CDN architecture, examining its key benefits, applications, and challenges.
Introduction
Content delivery networks (CDNs) play a crucial role in ensuring the seamless and efficient delivery of online content to end-users. Traditional CDNs rely on centralized infrastructure, which can introduce vulnerabilities and performance bottlenecks. Blockchain technology offers a decentralized alternative, enabling CDNs to overcome these limitations.
FAQs
1. What are the main benefits of decentralized CDNs?
- Improved security: Blockchain’s decentralized architecture reduces the risk of data breaches and malicious attacks.
- Enhanced performance: Peer-to-peer content distribution and caching optimize delivery speed and reduce latency.
- Reduced costs: By eliminating intermediaries, decentralized CDNs significantly lower infrastructure and maintenance expenses.
2. How does blockchain technology work in a CDN?
Blockchain creates a secure and immutable ledger that records all content delivery transactions. This ensures transparency, accountability, and the integrity of the network.
3. What are some potential challenges of decentralized CDNs?
- Scaling limitations: While blockchain provides decentralization, it can face scalability challenges with large-scale content delivery.
- Interoperability issues: Different blockchain platforms may have different protocols, which can hinder interoperability between decentralized CDNs.
Key Subtopics
1. Security Enhancements
- Decentralized Infrastructure: Eliminates single points of failure, reducing vulnerability to attacks.
- Encryption and Data Integrity: Uses cryptographic techniques to secure content and prevent unauthorized access.
- Immutable Ledger: Records all content transactions on an immutable blockchain, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Peer-to-Peer Validation: Distributes content validation across multiple nodes, enhancing reliability and preventing tampering.
2. Improved Performance
- Peer-to-Peer Distribution: Enables content to be shared directly between users, reducing latency and optimizing delivery speed.
- Local Caching: Caches content closer to end-users, reducing network congestion and improving responsiveness.
- Load Balancing: Distributes content delivery across multiple nodes, ensuring optimal bandwidth utilization and reducing bottlenecks.
- Adaptive Bitrate Streaming: Delivers content at different bitrates based on user bandwidth, optimizing viewing experience.
3. Cost Reduction
- Elimination of Intermediaries: Peer-to-peer content delivery removes middlemen, significantly reducing infrastructure and operating costs.
- Pay-as-you-Go Model: Decentralized CDNs often adopt a pay-as-you-go model, eliminating fixed costs and enabling flexible scaling.
- Reduced Bandwidth Costs: Efficient content distribution and caching minimize bandwidth consumption, reducing costs for both content providers and users.
- Open Source Development: Many decentralized CDN projects are open source, leveraging community contributions to reduce development and maintenance costs.
4. Content Management
- Metadata Management: Facilitates the storage and retrieval of content metadata, including content type, size, and location.
- Content Rights Management: Enforces digital rights management (DRM) and content protection mechanisms, ensuring compliance and protecting intellectual property.
- Content Provenance: Records the origin and history of content, providing transparency and accountability in content distribution.
- Content Expiration: Automates the removal of expired or outdated content, ensuring up-to-date information delivery.
5. Edge Computing
- Content Processing: Enables edge nodes to perform content processing tasks, such as video transcoding and image resizing, closer to end-users.
- Real-Time Analytics: Provides real-time performance monitoring and analytics, optimizing content delivery strategies based on user behavior.
- Local Data Storage: Stores frequently accessed content on edge nodes, reducing latency and improving availability.
- Enhanced Security: Utilizes edge nodes as additional security layers, detecting and mitigating cyber threats at the network edge.
Conclusion
Decentralized CDNs powered by blockchain technology are poised to transform the content delivery landscape. By offering enhanced security, improved performance, and reduced costs, they present a compelling alternative to traditional CDN architectures. As blockchain continues to evolve, we can expect further innovation and adoption of decentralized CDNs, revolutionizing the way content is delivered online.
Keyword Tags
- Blockchain
- Content Delivery Networks
- Decentralized Infrastructure
- Improved Performance
- Reduced Costs
