Title: Debian Vs. Ubuntu LTS: Stability Or Support?
Executive Summary

When selecting a Linux distribution, stability and support are typically key factors. Ubuntu LTS (Long Term Support) and Debian are two prominent options, each renowned for these aspects. Comprehending their distinctions will enable you to make an informed decision based on your specific requirements and preferences.
Introduction
When considering Linux distributions, Debian and Ubuntu LTS frequently emerge as leading contenders, particularly for individuals seeking stability and long-term support. While both distributions share a common foundation, Debian’s stability has long been its trademark, while Ubuntu LTS has garnered praise for its 5-year support cycle. This detailed analysis delves into the distinctive characteristics of these distributions, providing a comparative guide to assist in selecting the optimal solution.
1. Distinctive Traits and Origins
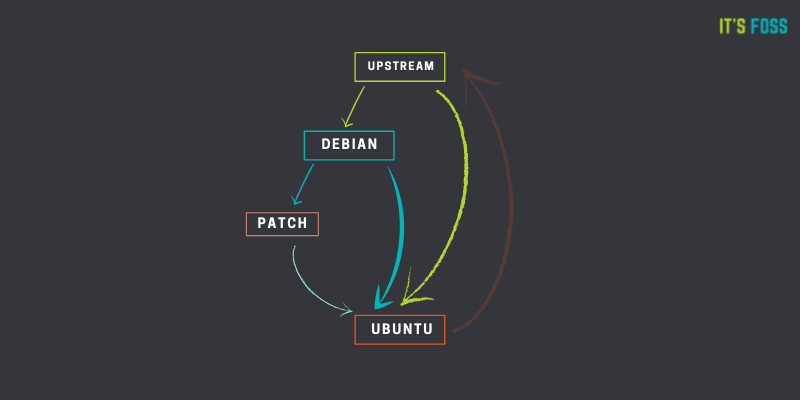
Debian’s Enduring Stable Core: Debian, a longstanding and influential distribution, is notable for its stable core, rigorous testing process, and strict adherence to open-source principles.
- Meticulous Packaging: It adheres to a stringent approach to software packaging, prioritizing stability over cutting-edge features.
- Wide Application: Debian’s extensive repository encompasses a vast array of software, applications, and utilities, catering to diverse user needs.
- Community-Driven Development: Its development is driven by a large community of contributors, ensuring long-term support and sustainability.
Ubuntu’s User-Friendly Facade: Ubuntu is known for its user-friendly design, catering to novices and experienced users alike with refined aesthetics and intuitive interfaces.
- Regular Updates and Upgrades: Ubuntu’s regular updates and upgrades guarantee access to the latest security enhancements and emerging technologies.
- Proprietary Software Inclusion: A defining feature of Ubuntu is its integration of non-free software, striking a balance between open-source values and user convenience.
- Pre-Installed Packages: For enhanced user convenience, Ubuntu comes with an assortment of pre-installed packages and applications.
2. Stability vs. Support: A Comparative Analysis
Stability: Debian’s conservative approach to change, rigorous testing process, and stable core make it the superior option for stability. It infrequently introduces drastic changes, minimizing the potential for disruptive issues.
- Minimal Releases: Debian releases new versions sparingly, prioritizing extensive testing and thorough stabilization of software packages.
- Longer Support Cycle: Debian provides extended support for its stable releases, ensuring ongoing updates and security patches for many years.
- Wide Ranging Support: The broader Linux community, not solely Debian developers, provides various forms of support, broadening accessible resources.
Support: When it comes to support, Ubuntu LTS takes the lead with its dedicated support structure and extensive documentation.
- Rapid Releases: Ubuntu’s regular releases ensure timely access to the latest technologies and security updates.
- Official Support Channels: Ubuntu users have access to official support channels, such as the Ubuntu Forums, bug tracking systems, and online documentation.
- Commercial Support Options: Enterprise-level users can purchase premium support contracts, providing direct access to experienced engineers.
3. Software Accessibility
Debian’s Extensive Repositories: Debian houses a vast repository, containing a vast array of software, applications, and tools catering to diverse user preferences and niche requirements.
- Comprehensive Selection: Developers have access to a wide selection of specialized tools for various tasks and projects.
- Longstanding Availability: Debian’s long-standing history means many applications retain compatibility with subsequent releases, promoting longevity.
- Package Maintenance and Quality: Debian maintainers diligently work to ensure the accuracy and quality of the extensive packages available.
Ubuntu’s Extensive Software Ecosystem: Ubuntu boasts a comprehensive software ecosystem, encompassing a wide range of applications, tools, and utilities.
- Beginner-Friendly Interface: Ubuntu’s user-centric approach provides a refined and intuitive graphical interface, easing access for novice users.
- Focused Software Selection: It features a curated selection of software, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance within the Ubuntu environment.
- Pre-Installed Applications: Ubuntu’s assortment of pre-installed applications, like the LibreOffice suite and Firefox web browser, elevates user convenience.
4. Community and Ecosystem
Debian’s Strong Community: Debian boasts a fervent and dedicated community, spanning the globe, contributing to the project’s development and assuring its enduring legacy.
- Open-Source Collaboration: It embodies the open-source ethos, fostering collaboration among developers worldwide, encouraging contributions and enhancements.
- Diverse Community Participation: The extensive community comprises developers, contributors, testers, and advocates, ensuring the project thrives.
- Wide User Base: Debian’s global user base contributes to its ongoing development and refinement, cultivating a robust ecosystem.
Ubuntu’s Varied Contributions: Ubuntu benefits from a large and active community, ranging from Canonical employees to open-source enthusiasts, ensuring its evolution and vitality.
- Canonical Leadership: Canonical, Ubuntu’s parent company, plays a crucial role in driving development, managing infrastructure, and providing enterprise-level support.
- Open-Source Appeal: Ubuntu’s adherence to open-source principles invites contributions from the broader developer community, stimulating innovation and growth.
- Supportive Ecosystem: An extensive ecosystem has emerged around Ubuntu, encompassing documentation, blogs, forums, and training resources, amplifying its user benefits.
5. Preferred Use Cases
Debian’s Optimal Applications:
- Stability-Critical Servers: For mission-critical servers requiring steadfast stability and resistance to frequent changes, Debian excels.
- Long-Term Embedded Systems: Debian is the preferred choice for embedded systems, offering prolonged support and minimal disruption once deployed.
- Custom Distributions: It serves as a foundation for creating custom distributions tailored to specific requirements or specialized applications.
Ubuntu’s Suitable Applications:
- Workstations and Desktops: Home users, students, and professionals seeking a user-friendly, modern, and well-supported desktop experience will find Ubuntu an ideal solution.
- Web and Cloud Hosting: With comprehensive software repositories and robust support options, Ubuntu efficiently accommodates web and cloud hosting environments.
- IoT (Internet of Things): This distribution’s extensive hardware support, robust security features, and open-source nature make it ideal for IoT deployments.
Conclusion
In the realm of Linux distributions, Debian and Ubuntu LTS occupy distinct positions. From Debian’s steadfast stability to Ubuntu’s extensive support, both cater to different needs. Weighing the contrasting stability and support characteristics is crucial in navigating this intricate choice. Those prioritizing stability and tested software will find Debian an ideal partner. Concurrently, those seeking regular updates, comprehensive support, and a user-friendly interface may favor Ubuntu LTS. Ultimately, the optimal selection hinges upon the unique requirements and preferences.
Keyword Phrase Tags:
- Debian vs Ubuntu comparison
- Stability vs support Linux
- Best Linux for servers
- Desktop Linux security
- Ubuntu for cloud computing

I’ve been using Debian for years and I’ve never had any problems. It’s a great distribution for those who value stability.
I’ve tried both Debian and Ubuntu LTS and I prefer Ubuntu LTS. I find it more user-friendly and it has a larger software repository.
Debian is a great choice for servers and other systems that need to be stable and reliable. Ubuntu LTS is a good choice for desktops and other systems that need to be kept up-to-date with security patches.
I don’t think there’s much difference between Debian and Ubuntu LTS. They’re both good distributions. It really comes down to personal preference.
I love the fact that Debian is so stable. I’ve never had a problem with it. It’s the perfect distribution for those who value stability.
I’ve used Ubuntu LTS for years and I’ve never had any problems. It’s a great distribution for those who need long-term support.
I’ve tried both Debian and Ubuntu LTS and I can’t decide which one I like better. They’re both great distributions.
Debian is a great choice for those who value stability. It’s a very conservative distribution and it does not change very often.
I’ve tried both Debian and Ubuntu LTS and I prefer Ubuntu LTS. I find it more user-friendly and it has a larger software repository.
I don’t think there’s much difference between Debian and Ubuntu LTS. They’re both good distributions. It really comes down to personal preference.
I love the fact that Debian is so stable. I’ve never had a problem with it. It’s the perfect distribution for those who value stability.
I’ve used Ubuntu LTS for years and I’ve never had any problems. It’s a great distribution for those who need long-term support.
I’ve tried both Debian and Ubuntu LTS and I can’t decide which one I like better. They’re both great distributions.