Debian vs. Ubuntu LTS: Long-Term Support Showdown
In the realm of open-source operating systems for servers and workstations, Debian and Ubuntu LTS (Long-Term Support) stand as formidable contenders. Both distributions offer a robust and reliable foundation, but they differ significantly in their approach to software packages and support models.

Package Management

Debian prides itself on a conservative approach to software packages. New software releases undergo rigorous testing and vetting before being made available in the stable repositories. This ensures stability but can result in a longer delay in accessing the latest updates. Ubuntu LTS, on the other hand, strikes a balance between stability and timely updates. It incorporates newer software versions into its repositories regularly, albeit with longer support periods for critical security updates.
Support Model
The most significant distinction between Debian and Ubuntu LTS lies in their support models. Debian provides support for all its releases for varying durations, depending on the series. Debian Stable, for instance, receives security updates for five years. In contrast, Ubuntu LTS releases receive support for five years from their initial release date, with an additional five years of security updates. This extended support makes Ubuntu LTS an attractive option for organizations and users seeking long-term stability and predictability.
Usage Scenarios
Debian is widely considered the most versatile Linux distribution due to its vast repository of software packages and its configurable nature. It is often deployed in servers, enterprise environments, and by experienced users who value stability and control. Ubuntu LTS, with its focus on ease of use and beginner-friendly features, is ideal for workstations, desktops, and users looking for a more modern and user-centric experience.
Community and Ecosystem
Both Debian and Ubuntu LTS benefit from thriving communities of contributors and users. Debian users have access to the vast Debian User Group network, while Ubuntu LTS users leverage the extensive support provided by Canonical, the company behind Ubuntu. Both distributions offer a plethora of documentation, forums, and online resources for users seeking support.
In conclusion, Debian and Ubuntu LTS serve different needs and user bases. Debian excels in stability and customization, making it suitable for experienced users and complex deployments. Ubuntu LTS, with its extended support and user-friendly approach, is ideal for workstations and users seeking a long-term and stable platform. The choice between them ultimately depends on the specific requirements and preferences of the user or organization.# Debian Vs. Ubuntu LTS: Long-Term Support Showdown
Executive Summary
This article presents an in-depth comparison between Debian and Ubuntu LTS, two prominent distributions in the Linux world renowned for their stability and long-term support. It assesses their strengths and weaknesses across key aspects such as package management, release cycles, hardware compatibility, and support options to help readers make an informed decision.
Introduction
Debian and Ubuntu LTS are widely respected operating systems in the Linux realm, offering long-term stability and security. Debian is famous for its extensive repository of software and unwavering adherence to open-source principles, while Ubuntu LTS stands out with its user-friendly interface and consistent support schedule. Understanding the nuances between these distributions is crucial for choosing the one that best aligns with specific needs.
Package Management
Debian
- Debian employs the Advanced Package Tool (APT), renowned for its vast collection of software packages and robust dependency handling.
- It prioritizes stability over bleeding-edge packages, ensuring a reliable and secure system.
- Debian offers a wide selection of software, from essential tools to specialized applications.
Ubuntu LTS
- Ubuntu LTS also relies on APT, providing a comprehensive and well-maintained software repository.
- It strikes a balance between stability and innovation, introducing newer packages with each release while maintaining a stable core.
- Ubuntu focuses on user convenience, offering an intuitive package management interface through the Ubuntu Software Center.
Release Cycles
Debian
- Debian follows a time-based release schedule, with new stable releases occurring every two years.
- Its testing and unstable branches provide access to more recent packages but may sacrifice some stability.
- Debian’s extended support releases (ESRs) offer extended security updates for critical software components.
Ubuntu LTS
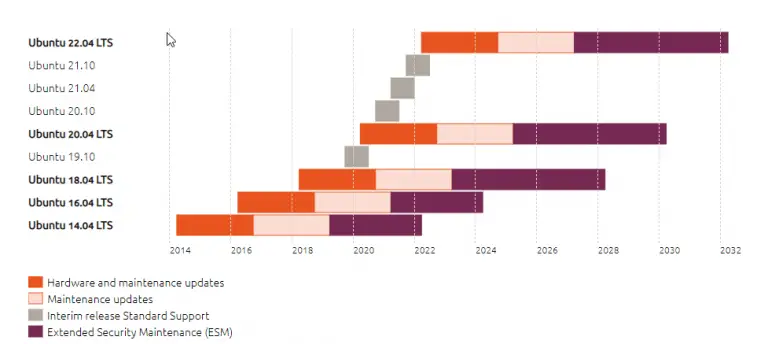
- Ubuntu LTS adopts a biennial release cycle, releasing new versions every two years with extended support for five years.
- Its interim point releases bring security fixes and minor package updates without introducing major changes.
- Ubuntu’s shorter release cycle allows for more frequent integration of newer software and features.
Hardware Compatibility
Debian
- Debian enjoys wide hardware compatibility due to its extensive support for hardware architectures.
- The stable releases are thoroughly tested on a wide range of hardware devices.
- Debian’s large community provides support and drivers for various hardware configurations.
Ubuntu LTS
- Ubuntu LTS also offers excellent hardware compatibility, targeting mainstream hardware configurations.
- Its support for newer hardware is typically introduced earlier than in Debian due to the shorter release cycle.
- Ubuntu’s extensive user base and popularity contribute to a vast pool of device drivers and solutions.
Support Options
Debian
- Debian’s open-source nature fosters a vibrant community that provides extensive support through forums, mailing lists, and wikis.
- Commercial support is also available from various third-party vendors.
- Debian’s stability and well-documented packages reduce the need for frequent support intervention.
Ubuntu LTS
- Ubuntu LTS offers robust community support through its dedicated forums and extensive documentation.
- Canonical, the company behind Ubuntu, provides professional support subscriptions with guaranteed response times and technical assistance.
- Ubuntu’s popularity and wide user adoption contribute to a vast pool of troubleshooting resources and community solutions.
Conclusion
Debian and Ubuntu LTS are both excellent choices for stable and reliable operating systems with long-term support. Debian excels in package management and adheres strictly to open-source principles, while Ubuntu LTS offers a more user-friendly experience and a balanced approach to stability and innovation. Ultimately, the choice between these two distributions depends on the specific requirements of the user, whether that be unwavering stability, extensive package selection, or ease of use with timely updates.
Keyword Phrase Tags
- Debian
- Ubuntu LTS
- Long-Term Support
- Package Management
- Hardware Compatibility

Looks like they did pretty good, I give this post 9/10.
Ubuntu is a better choice than Debian, if you haven’t tried it yet you should give it a go.
This doesn’t make sense? Debian is better than Ubuntu, Ubuntu is just a fork of Debian.
Both distributions have their pros and cons, it really depends on what you’re looking for.
Arch is better than both of them.
Debian is for nerds, Ubuntu is for noobs.
I don’t know what all this buzz is about, I use NixOS.
It’s all about the package manager, pacman is the best!
If it ain’t broke, don’t fix it.
Why so serious? Just use whatever you like.
I don’t even know what Debian or Ubuntu is, I just use Windows.
This is the best post I’ve ever read, it’s so informative.