Cryptographic Foundations of Blockchain Technology

Blockchain technology serves as the underlying framework for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. It is renowned for its inherent security and immutability, which are underpinned by robust cryptographic algorithms. These algorithms play a pivotal role in safeguarding blockchain networks and ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data stored on them.

Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key cryptography, is a cornerstone of blockchain security. It utilizes a pair of mathematically linked keys: a public key, which is shared publicly, and a private key, which is kept secret. Data encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the corresponding private key, providing a secure mechanism for user authentication, data confidentiality, and digital signatures.
Hash Functions
Hash functions are essential for ensuring data integrity in blockchains. They map arbitrary-length data to a fixed-length string known as a hash. Any alterations to the input data will result in a different hash value, making it computationally infeasible to tamper with data without detection. Hashing algorithms are used to create unique identifiers for transactions and blocks, ensuring that malicious actors cannot modify or fabricate data stored on the blockchain.
Digital Signatures
Digital signatures employ asymmetric encryption to verify the authenticity and integrity of data. A user signs a message by encrypting it with their private key. Anyone can verify the signature using the user’s public key, ensuring that the sender is indeed the owner of the private key and that the message has not been altered in transit. Digital signatures are vital for securing transactions and ensuring that only authorized parties can initiate changes to the blockchain.
Consensus Mechanisms
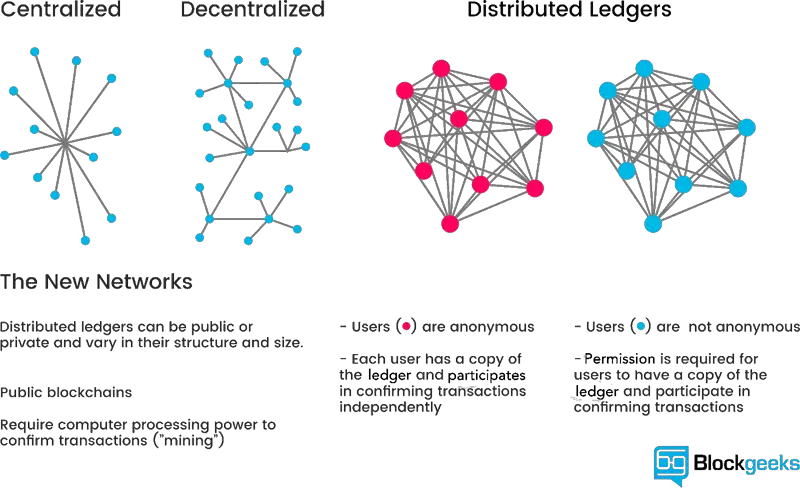
Blockchain networks rely on consensus mechanisms to reach agreement on the state of the network and the validity of transactions. Cryptographic algorithms are employed to create tamper-proof records of transactions, ensuring that all participants in the network have a consistent view of the blockchain’s history. Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) are two prominent consensus algorithms that underpin the security and integrity of blockchain networks.
Conclusion
The cryptographic foundations of blockchain technology are indispensable for safeguarding the security and immutability of blockchain networks. Asymmetric encryption, hash functions, digital signatures, and consensus mechanisms work in tandem to protect data, facilitate secure communication, prevent tampering, and ensure the integrity of the blockchain. These cryptographic algorithms form the backbone of blockchain technology, enabling the creation of secure, transparent, and verifiable distributed systems.
