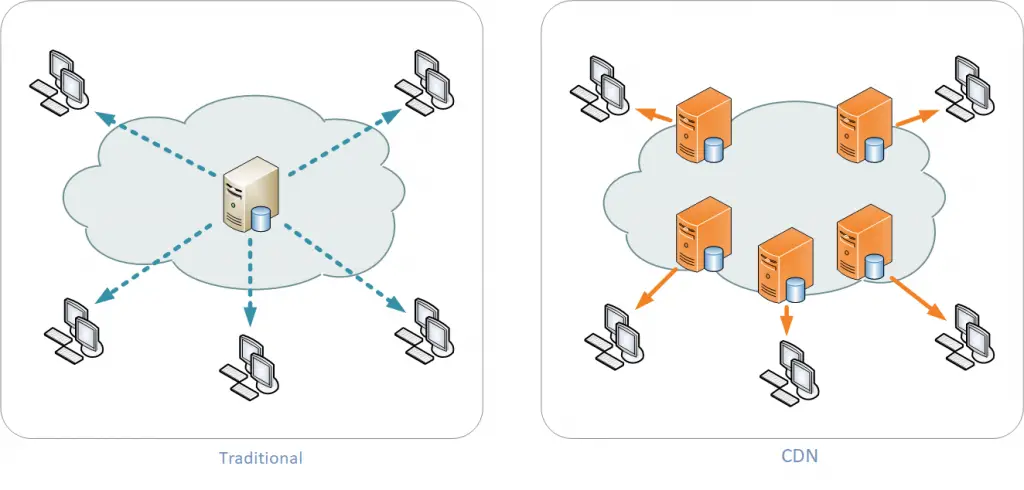
Cloud-based CDN Services vs. Traditional CDN: A Comparison
Definition:
- Cloud-based CDN: A content delivery network (CDN) that runs on cloud computing infrastructure, typically provided as a managed service.
- Traditional CDN: A CDN that operates on dedicated servers and is managed by the provider or the customer.
Key Differences:

| Feature | Cloud-based CDN | Traditional CDN |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Ownership | Cloud provider | CDN provider or customer |
| Management | Managed by the cloud provider | Managed by the provider or customer |
| Scalability | Highly scalable and flexible | Can be scalable, but requires additional hardware |
| Cost | Typically pay-as-you-go | Upfront capital investment and ongoing maintenance costs |
| Latency | Low latency due to distributed servers | Can vary based on hardware and network infrastructure |
| Performance Monitoring | Built-in monitoring and analytics | May require additional tools |
| Security | Inherits the security measures of the cloud platform | Requires separate security configurations |
| Customization | Limited customization options | More customization options available |
| Integration | Easy integration with other cloud services | May require complex integrations |
Advantages of Cloud-based CDNs:
- High scalability: Cloud-based CDNs can easily scale to handle sudden traffic spikes or large content volumes.
- Low cost: Pay-as-you-go pricing eliminates upfront capital investment and reduces ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Low latency: Distributed servers ensure fast delivery of content to users.
- Ease of management: Managed by the cloud provider, eliminating the burden of CDN operations.
- Security: Inherits the security measures of the cloud platform, providing robust data protection.
Advantages of Traditional CDNs:
- Customization: Allows for greater control and customization, such as custom caching rules and load balancing algorithms.
- Hardware control: Gives the customer direct control over hardware configurations, potentially improving performance.
- High performance: Dedicated servers can provide consistent and predictable performance, especially for demanding applications.
- Security: Isolated infrastructure can provide enhanced security and privacy.
- Legacy support: Traditional CDNs may be better suited for legacy applications that require specific hardware or software environments.
Conclusion:
Both cloud-based and traditional CDNs have their advantages. Cloud-based CDNs excel in scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of management, making them suitable for most businesses and applications. Traditional CDNs provide more customization options and hardware control, cater to demanding applications, and support legacy environments. The choice between the two depends on specific requirements, such as performance, customization, and budget considerations.