CDNs: Accelerating the Delivery of Educational Content Globally
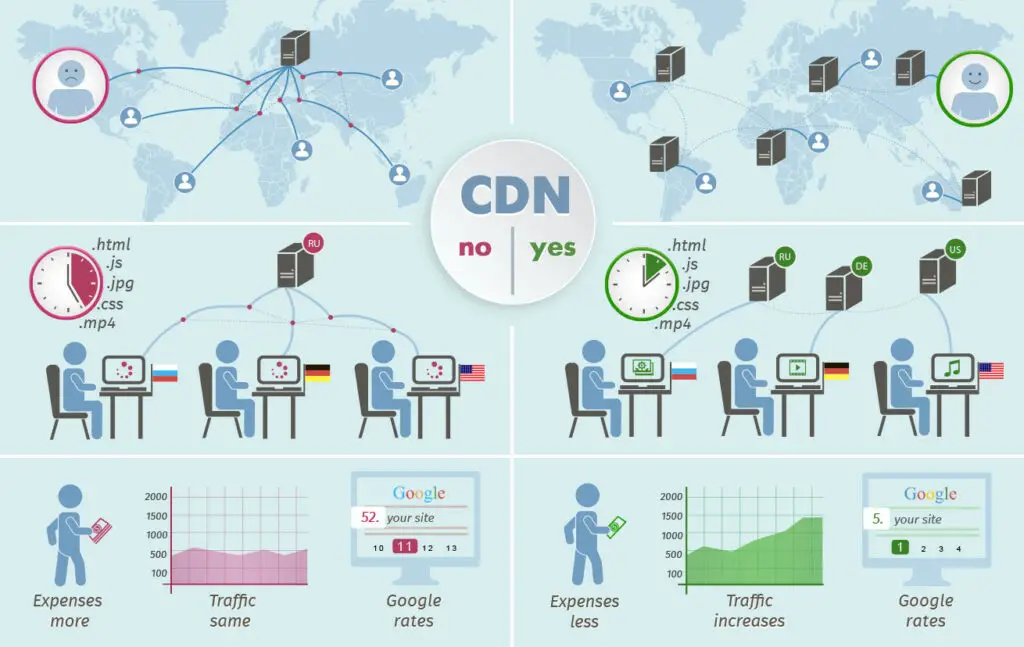
Introduction
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) have emerged as crucial enablers for the delivery of educational content globally. By caching content at edge locations closer to users, CDNs reduce latency, improve bandwidth utilization, and ensure the smooth and reliable distribution of educational materials.
Benefits of CDNs for Education
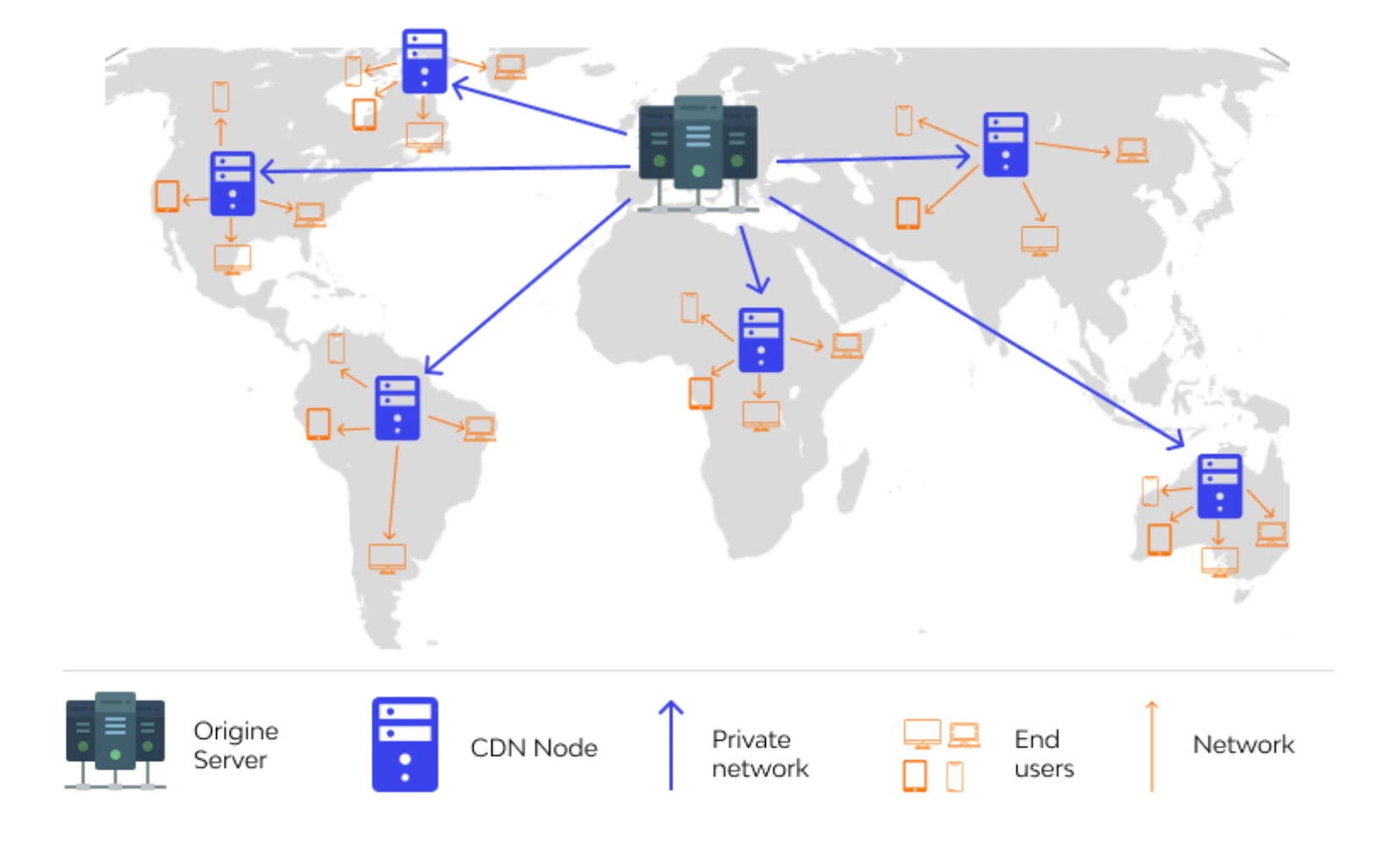
Reduced Latency: CDNs place content closer to end-users, significantly reducing the time it takes for users to access educational resources. This is crucial for online learning environments where interruptions can disrupt the learning process.

Improved Bandwidth Efficiency: CDNs optimize bandwidth usage by caching popular content and delivering it from edge locations. This results in less congestion on the network and reduced costs for educational institutions and content providers.
Global Availability: CDNs have a global presence, ensuring that educational content is accessible to students and educators regardless of their location. This promotes equity and inclusivity in education.
Enhanced Security: CDNs provide robust security features, including encryption, DDoS protection, and firewall filtering. This ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of educational content.
Applications in Education
Online Learning Platforms: CDNs empower online learning platforms to deliver video lectures, assignments, and other course materials seamlessly to students around the world.
Virtual Classrooms: CDNs facilitate real-time video conferencing and collaboration among students and instructors, creating immersive virtual learning experiences.
Educational Content Repositories: CDNs enable educational institutions and content providers to share open educational resources (OERs) and other learning materials globally, fostering knowledge sharing and collaboration.
Challenges and Solutions
Content Management: Ensuring that educational content is up-to-date and relevant requires effective content management strategies. CDNs offer tools for easy content updates and versioning.
Data Privacy and Compliance: CDNs must adhere to data privacy regulations and comply with institutional policies. CDNs provide mechanisms for data encryption, anonymization, and compliance reporting.
Cost Optimization: While CDNs offer significant benefits, their cost implications must be carefully considered. CDNs implement flexible pricing models and optimization techniques to ensure cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
CDNs are indispensable for the delivery of educational content globally, empowering educators and students to access resources seamlessly, regardless of their location or bandwidth constraints. By reducing latency, improving bandwidth efficiency, ensuring global availability, and enhancing security, CDNs contribute to the creation of equitable, accessible, and engaging educational experiences. As the demand for online and blended learning continues to grow, CDNs will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of education.## Cdns: Accelerating The Delivery Of Educational Content Globally
Executive Summary:
In an era defined by rapid technological advancements, Canadian educational institutions are poised to leverage their expertise and resources to become global leaders in the delivery of educational content. This comprehensive analysis explores the key subtopics that will shape the future of education in Canada, highlighting the opportunities and challenges associated with each. By embracing innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to equity, Canada can establish itself as a trailblazer in the global educational landscape.
Introduction:
The delivery of educational content has undergone a profound transformation in recent years, driven by the widespread adoption of digital technologies. Canadian educational institutions have a long-standing reputation for academic excellence, and they are now well-positioned to capitalize on this digital revolution to expand their reach beyond traditional geographical boundaries. By embracing emerging technologies and fostering strategic partnerships, Canada can accelerate the delivery of high-quality educational content to students worldwide.
FAQs:
- Why is it important for Canadian educational institutions to expand their global reach?
- Increased revenue streams and diversification of income sources
- Enhanced reputation and visibility on a global scale
- Contribution to Canada’s knowledge economy and international competitiveness
- What are the key challenges that Canadian educational institutions face in delivering educational content globally?
- Differences in educational systems and regulations across countries
- Cultural and linguistic barriers
- Ensuring quality control and maintaining academic standards
- How can Canadian educational institutions overcome these challenges and achieve success in delivering educational content globally?
- Establishing strategic partnerships with international organizations
- Adapting content to meet the needs of diverse learners
- Utilizing technology to enhance accessibility and engagement
Key Subtopics:
1. Online Learning Platforms
Online learning platforms have emerged as a powerful tool for delivering educational content globally, providing students with the flexibility and convenience of studying from anywhere in the world. Canadian educational institutions have the opportunity to leverage their expertise in online learning to create innovative and engaging courses that cater to the needs of international learners.
- Accessibility and Flexibility: Online platforms allow students to access educational content at their own pace and on their own time, regardless of geographical location.
- Global Reach: Online learning can extend the reach of Canadian educational institutions beyond traditional borders, making their courses available to students worldwide.
- Personalized Learning: Online platforms can be tailored to meet the individual learning needs of students, offering customized learning paths and interactive experiences.
- Scalability: Online platforms enable institutions to scale their educational offerings to meet the growing demand for global education.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Online learning can be more cost-effective than traditional face-to-face instruction, reducing the financial barriers for students.
2. Content Localization
Content localization involves adapting educational content to meet the cultural, linguistic, and educational requirements of diverse audiences. Canadian educational institutions must recognize the importance of localizing their content to ensure that it is accessible and relevant to learners from different backgrounds.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Content should be adapted to reflect the cultural nuances and values of the target audience.
- Language Translation: High-quality language translation is essential to ensure that the content is comprehensible and engaging for learners who are not native English speakers.
- Curriculum Alignment: Content should be aligned with the educational standards and curriculum requirements of the target country.
- Educational Context: Consideration must be given to the educational context of the target audience, including the level of education and prior knowledge.
- Local Expertise: Collaborating with local experts can provide valuable insights into the specific needs and preferences of the target audience.
3. Strategic Partnerships
Strategic partnerships with international organizations, such as universities, colleges, and government agencies, are crucial for Canadian educational institutions to successfully deliver educational content globally. These partnerships facilitate collaboration, resource sharing, and access to new markets.
- Joint Programs and Collaborations: Partnerships can lead to the development of joint degree programs, research projects, and other collaborative initiatives.
- Student and Faculty Exchange: Partnerships facilitate the exchange of students and faculty, promoting cross-cultural learning and research collaboration.
- Market Expansion: Partnerships can provide access to new markets and distribution channels, expanding the reach of Canadian educational content globally.
- Cultural Exchange: Partnerships promote cultural exchange and understanding, fostering global citizenship and diversity.
- Capacity Building: Partnerships can contribute to the capacity building of international partners, strengthening the global education ecosystem.
4. Technological Advancements
Rapid advancements in technology have revolutionized the way educational content is created, delivered, and accessed. Canadian educational institutions must embrace these technological advancements to enhance the quality and accessibility of their global offerings.
- Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality: These technologies can create immersive educational experiences that engage learners and make abstract concepts more tangible.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-powered tools can personalize learning experiences, provide real-time feedback, and automate administrative tasks.
- Adaptive Learning Platforms: These platforms adjust the learning content and pace to meet the individual needs and progress of learners.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can be used to secure and verify educational credentials, ensuring their authenticity and portability.
- Cloud-Based Technologies: Cloud-based platforms provide scalable and cost-effective infrastructure for delivering educational content globally.
5. Equity and Inclusivity
Ensuring equity and inclusivity in the delivery of educational content globally is essential for Canadian educational institutions to fulfill their mission of providing access to quality education for all. By addressing barriers to participation and creating inclusive learning environments, institutions can empower learners from diverse backgrounds to succeed.
- Access for Underrepresented Groups: Institutions must actively work to remove barriers to participation for underrepresented groups, such as students from low-income backgrounds, students with disabilities, and Indigenous students.
- Culturally Responsive Pedagogy: Content and teaching methods should be culturally responsive, recognizing and valuing the diverse experiences and perspectives of learners.
- Universal Design for Learning: Educational materials and platforms should be designed to be accessible and inclusive for learners with different abilities and learning styles.
- Equity-Focused Partnerships: Institutions should partner with organizations working to promote equity and inclusion in education.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regular monitoring and evaluation are essential to ensure that equity and inclusivity initiatives are effective and responsive to the needs of learners.
Conclusion:
As Canadian educational institutions embrace the opportunities and address the challenges associated with delivering educational content globally, they have the potential to establish themselves as leaders in the global education landscape. By adopting innovative technologies, forming strategic partnerships, localizing content, and prioritizing equity and inclusivity, Canadian institutions can expand their reach, enhance the quality of their offerings, and make a significant contribution to global education. The future of education is bright for Canada, and with continued dedication and innovation, Canadian educational institutions will continue to play a vital role in shaping the educational landscape for generations to come.
Keyword Tags:
- Global Education
- Online Learning Platforms
- Content Localization
- Strategic Partnerships
- Equity and Inclusivity
