Content Delivery Network (CDN) Geographic Distribution: Ensuring Global Content Accessibility
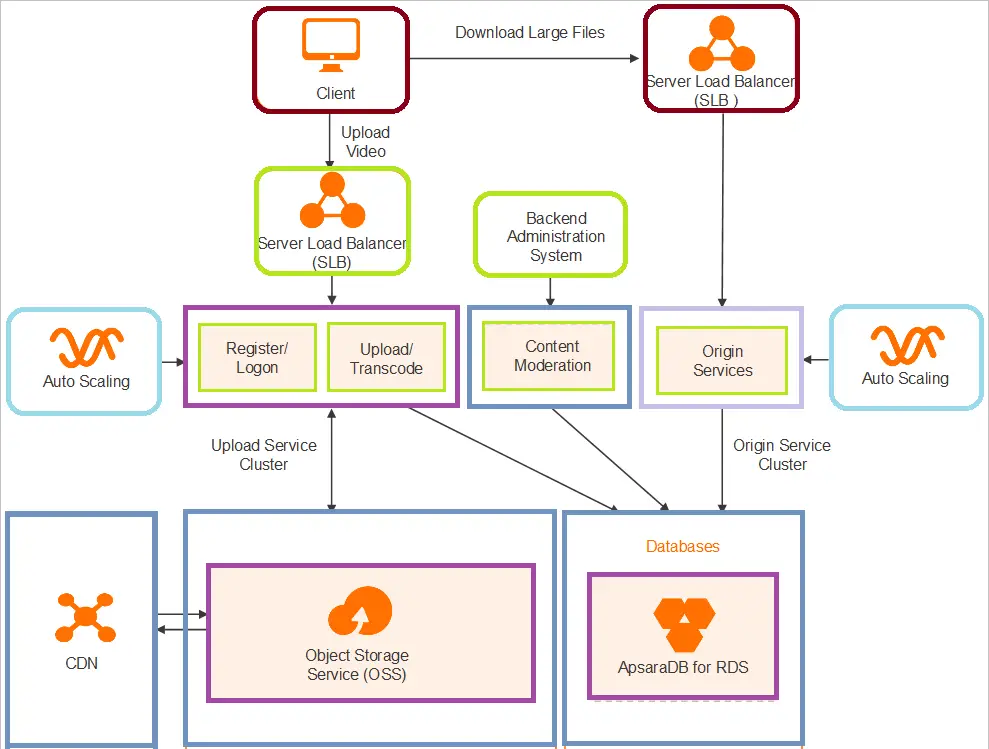
What is a CDN?
A CDN is a network of servers distributed globally that cache and deliver content closer to end-users, reducing latency and improving content delivery performance.
Importance of Geographic Distribution
Global CDN distribution ensures that content is accessible to users worldwide with minimal delay. Factors to consider include:
- Proximity to Users: Placing servers close to user locations optimizes network latency and reduces download times.
- Coverage Area: A CDN should have a wide global reach to serve users in different geographic regions.
- Resiliency: Distributing servers across multiple locations enhances availability and reliability, preventing outages in case of regional disruptions.
Benefits of Geographic Distribution
- Reduced Latency: Faster content delivery speeds up page loading, video streaming, and interactive applications.
- Improved User Experience: Users have access to content with minimal buffering or interruptions, enhancing satisfaction and engagement.
- Enhanced Scalability: A distributed CDN can handle high traffic volumes without compromising performance.
- Reduced Costs: By caching content closer to users, CDNs can reduce bandwidth usage and save on infrastructure expenses.
Strategies for Geographic Distribution
- Identify Regions with High Traffic: Analyze user demographics and traffic patterns to determine where to place servers.
- Consider Latency and Bandwidth: Choose locations with low latency and sufficient network capacity to support expected traffic.
- Establish Hierarchical Networks: Deploy multiple layers of servers with different coverage areas, such as edge servers, regional servers, and central servers.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly monitor CDN performance and make adjustments as needed to maintain optimal geographic distribution and coverage.
Factors to Consider in Server Selection
- Server Hardware: Ensure servers have sufficient processing power, memory, and storage to handle traffic demands.
- Network Infrastructure: Choose providers with high-quality network infrastructure, reliable connectivity, and redundant connections.
- Security Features: Implement security measures such as firewalls, DDoS mitigation, and intrusion detection systems to protect content and user privacy.
Conclusion
Geographic distribution is a key aspect of CDN architecture. By distributing servers strategically across the globe, CDNs can ensure that content is delivered to users with minimal delay and maximum reliability, improving the overall user experience and supporting global content accessibility.## Cdn Geographic Distribution: Ensuring Global Content Accessibility
Executive Summary
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) play a pivotal role in enhancing the online experience for users across the globe. Effective Geographic Distribution is a crucial aspect of CDN strategy, enabling businesses to deliver content swiftly, reliably, and securely to audiences worldwide. This comprehensive guide delves into the significance of CDN Geographic Distribution and explores best practices for implementing it, empowering businesses to optimize their global content delivery.
Introduction
In the digital age, businesses need to embrace a global outlook to expand their reach and cater to a diverse customer base. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) have emerged as indispensable tools for ensuring seamless and efficient content delivery on a global scale. Geographic Distribution, a key aspect of CDN strategy, involves strategically placing CDN servers in various locations worldwide to minimize latency and improve content accessibility for users. By leveraging CDN Geographic Distribution, businesses can enhance the user experience, improve website performance, and gain a competitive edge in the global market.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the primary benefit of CDN Geographic Distribution?
CDN Geographic Distribution significantly improves content delivery speed and responsiveness for users from different regions, ensuring a seamless and uninterrupted online experience.
2. How does CDN Geographic Distribution enhance website performance?
By placing CDN servers closer to users’ physical locations, Geographic Distribution reduces latency and optimizes content transfer, leading to faster page loading times and improved overall website performance.
3. What are the business advantages of CDN Geographic Distribution?
Geographic Distribution enables businesses to reach a wider audience, expand their market presence, and improve customer satisfaction by providing fast and reliable content delivery.
Top 5 Subtopics
1. Node Selection
- Strategic Placement: Carefully select server locations based on the target audience’s geographic distribution and internet infrastructure.
- Multi-Regional Presence: Establish a presence in multiple regions to ensure content availability even during regional outages.
- Load Balancing: Implement load balancing algorithms to distribute traffic evenly across nodes, preventing bottlenecks and ensuring optimal performance.
2. Content Caching
- Content Replication: Store frequently accessed content on multiple servers to reduce latency and improve availability.
- Local Content Delivery: Deliver content from servers closest to users, minimizing the distance data must travel and optimizing delivery speed.
- Intelligent Caching: Utilize caching algorithms that analyze user behavior and adapt content storage strategies to enhance performance.
3. Traffic Routing
- Dynamic DNS: Use Dynamic Domain Name System (DNS) to redirect traffic to the closest CDN node based on the user’s location.
- Geolocation Data: Leverage geolocation data to determine the user’s physical location and route traffic accordingly.
- Real-Time Traffic Analysis: Monitor traffic patterns and adjust routing strategies in real-time to optimize delivery.
4. Network Optimization
- High-Capacity Network: Ensure the CDN network has ample bandwidth and connectivity to support the projected traffic volume.
- Redundant Interconnections: Establish redundant network connections to prevent single points of failure and maintain connectivity.
- IP Anycast: Utilize IP Anycast technology to route traffic to the closest node regardless of its physical location.
5. Monitoring and Analytics
- Performance Monitoring: Track and analyze CDN performance metrics, such as latency, uptime, and request success rate.
- Real-Time Alerts: Set up alerts to notify stakeholders of performance issues or potential outages.
- Data-Driven Insights: Use analytics data to identify optimization opportunities and improve CDN configuration.
Conclusion
CDN Geographic Distribution is an indispensable strategy for businesses seeking to deliver content seamlessly and reliably to a global audience. By carefully considering the top subtopics and implementing best practices, businesses can ensure that their content is accessible, fast, and secure for users worldwide. Embracing CDN Geographic Distribution empowers businesses to enhance user experience, improve website performance, and gain a competitive edge in the global digital landscape.
Relevant Keyword Tags
- CDN Geographic Distribution
- Content Delivery Networks
- Global Content Accessibility
- Website Performance Optimization
- User Experience Improvement
