Blockchain in Manufacturing: Revolutionizing Operations and Supply Chains
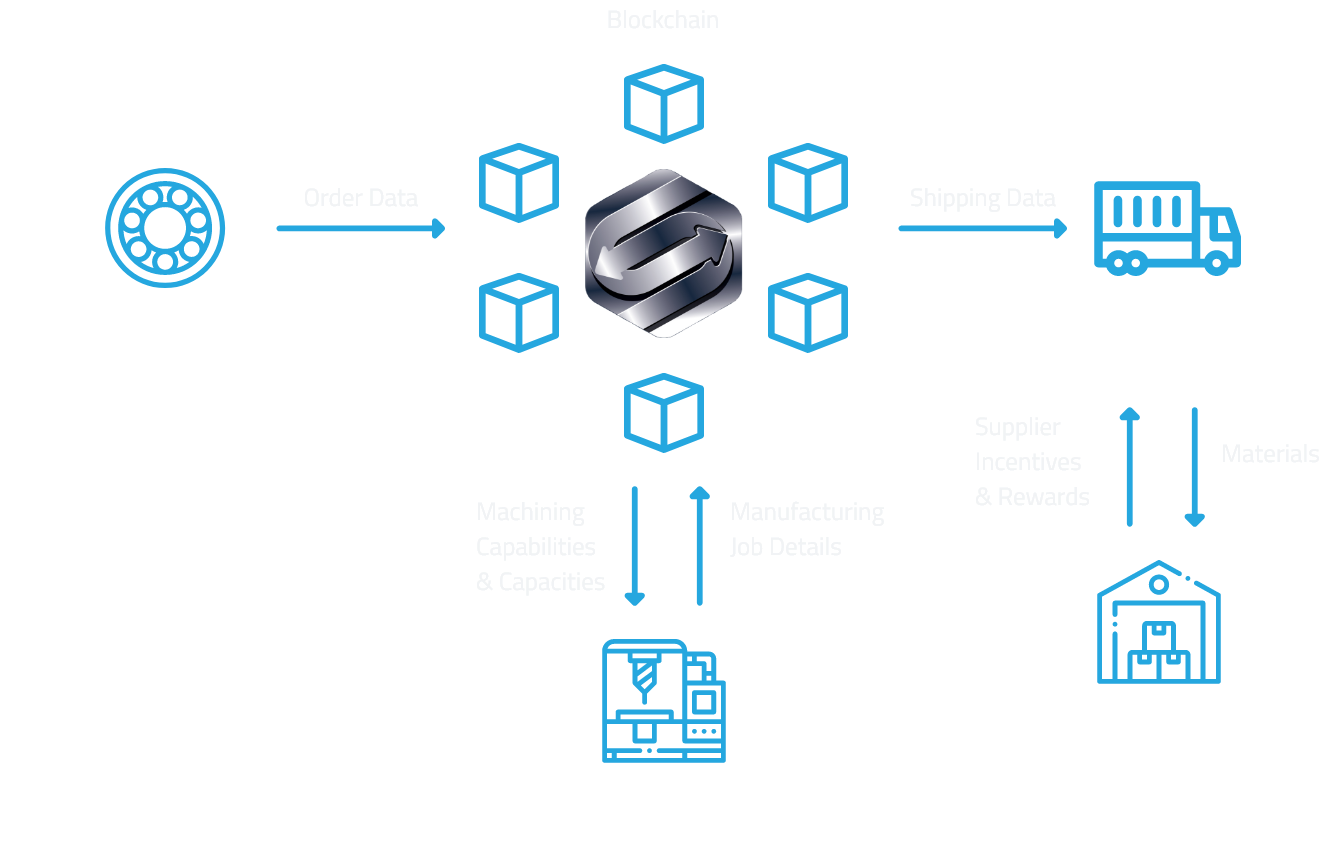
The advent of blockchain technology has brought about unprecedented advancements in various industries, transforming the way businesses operate and interact. Within the manufacturing sector, blockchain has emerged as a game-changer, streamlining operations, enhancing transparency, and revolutionizing supply chains.

Streamlining Operations
Blockchain’s inherent attributes, such as immutability, traceability, and consensus mechanisms, provide a robust framework for manufacturers to manage operations efficiently. By recording transactions and data on a distributed ledger, blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries, simplifying processes, reducing errors, and increasing productivity.
Inventory Management: Blockchain-based inventory systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels across multiple locations, enabling manufacturers to optimize stock levels and reduce waste.
Production Planning: With blockchain, manufacturers can track production processes in real-time, monitor progress, and make informed decisions to improve efficiency and minimize disruptions.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain plays a transformative role in supply chains by enhancing transparency, accountability, and collaboration among stakeholders.
Provenance and Traceability: Blockchain empowers manufacturers to trace the origins of raw materials and finished products throughout the supply chain, ensuring provenance and guaranteeing the authenticity and quality of goods.
Improved Supplier Relationships: A shared and immutable ledger facilitates seamless communication and collaboration between manufacturers and suppliers, fostering stronger partnerships and reducing disputes.
Reduced Fraud and Counterfeiting: Blockchain’s secure and tamper-resistant nature makes it an effective deterrent against fraud and counterfeiting, protecting both manufacturers and consumers.
Data Security and Privacy
Blockchain’s decentralized and encrypted nature provides robust security measures, safeguarding sensitive data and protecting against breaches and unauthorized access.
Enhanced Visibility and Trust: By providing a single, immutable source of truth, blockchain increases visibility and accountability across the entire manufacturing ecosystem.
In summary, the integration of blockchain technology within manufacturing opens up vast opportunities for streamlining operations and transforming supply chains. It empowers manufacturers to improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance transparency, and ensure the integrity of their products and processes. As the technology continues to evolve, its impact on manufacturing is poised to grow even more profound, reshaping the industry in the years to come.## Blockchain In Manufacturing: Streamlining Operations And Supply Chains
Executive Summary
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the manufacturing industry by streamlining operations, improving efficiency, and enhancing supply chain management. This article will explore the various applications of blockchain in manufacturing, focusing on the top five benefits that it can bring to the industry:
- Improved supply chain management: Increased transparency, improved traceability, reduced fraud, automated payments, and enhanced collaboration.
- Streamlined operations: Reduced paperwork, improved inventory management, just-in-time production, efficient quality control, and reduced downtime.
- Enhanced security: Secure data storage, prevention of data breaches, data immutability, increased transparency, and improved compliance.
- New business models: Pay-per-use models, fractional ownership of assets, decentralized manufacturing networks, and tokenization of physical assets.
- Increased efficiency: Automated processes, reduced need for intermediaries, optimized resource allocation, improved collaboration, and data-driven decision-making.
Improved Supply Chain Management
Blockchain can significantly enhance supply chain management by providing a shared, immutable ledger that records all transactions and activities. This leads to several benefits:
- Increased transparency: All participants in the supply chain have access to the same real-time data, eliminating information silos and improving visibility.
- Improved traceability: The ability to track each item throughout the supply chain ensures accurate and timely information about the product’s origin, movement, and current location.
- Reduced fraud: Transactions are cryptographically secured, making it nearly impossible to alter or tamper with records, reducing opportunities for fraud.
- Automated payments: Smart contracts can automate payments based on predefined conditions, reducing delays and ensuring timely execution.
- Enhanced collaboration: Blockchain provides a platform for collaboration between different stakeholders in the supply chain, enabling efficient sharing of information and coordination of activities.
Streamlined Operations
Blockchain can help manufacturers streamline operations by automating processes, reducing paperwork, and improving efficiency:
- Reduced paperwork: Digitalization of documents and processes eliminates the need for physical paperwork, saving time and reducing errors.
- Improved inventory management: Real-time data sharing enables manufacturers to track inventory levels more effectively, reducing the risk of overstocking and shortages.
- Just-in-time production: Blockchain facilitates just-in-time production by providing real-time visibility into supply chain operations, enabling manufacturers to adjust production schedules based on demand.
- Efficient quality control: Product quality can be tracked throughout the production process, ensuring compliance with standards and reducing the risk of defects.
- Reduced downtime: Blockchain-enabled predictive maintenance can identify potential equipment failures before they occur, minimizing unplanned downtime and maximizing productivity.
Enhanced Security
Blockchain’s inherent security features make it an ideal solution for protecting sensitive data in the manufacturing industry:
- Secure data storage: Data is encrypted and stored across a distributed network of computers, making it extremely difficult to hack or tamper with.
- Prevention of data breaches: The immutability of blockchain ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
- Data immutability: Transactions are recorded on a distributed ledger and cannot be modified, ensuring the accuracy and integrity of data.
- Increased transparency: The transparent and auditable nature of blockchain provides assurance to all stakeholders that data is accurate and reliable.
- Improved compliance: Blockchain can help manufacturers comply with industry regulations and standards, as it provides a tamper-proof record of all transactions and activities.
New Business Models
Blockchain opens up possibilities for new business models in manufacturing:
- Pay-per-use models: Blockchain enables manufacturers to offer pay-per-use models for equipment, reducing upfront investment costs for customers.
- Fractional ownership of assets: Blockchain allows for the fractional ownership of assets, such as heavy machinery, enabling companies to share ownership and usage.
- Decentralized manufacturing networks: Blockchain can create decentralized manufacturing networks, connecting manufacturers with customers directly, reducing intermediaries and improving efficiency.
- Tokenization of physical assets: Physical assets can be tokenized on the blockchain, making them easier to trade and facilitating new financial opportunities.
Increased Efficiency
Blockchain can improve efficiency in manufacturing by automating processes, reducing the need for intermediaries, and optimizing resource allocation:
- Automated processes: Blockchain can automate many repetitive and time-consuming tasks, such as data reconciliation, document verification, and quality control.
- Reduced need for intermediaries: Blockchain enables peer-to-peer transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries and simplifying processes.
- Optimized resource allocation: Blockchain provides real-time data visibility, enabling manufacturers to make informed decisions about resource allocation, minimizing waste and maximizing utilization.
- Improved collaboration: Blockchain facilitates collaboration among different departments and stakeholders, improving information sharing and streamlining processes.
- Data-driven decision-making: The data stored on the blockchain can be analyzed to derive insights and make better data-driven decisions.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology offers transformative potential for the manufacturing industry, enabling a wide range of improvements in operations, supply chain management, security, and business models. By embracing blockchain, manufacturers can enhance transparency, improve efficiency, reduce costs, and gain a competitive edge in the market. As blockchain technology matures and adoption grows, it is expected to play an increasingly significant role in shaping the future of manufacturing.
Keyword Tags
- Blockchain in manufacturing
- Supply chain management
- Streamlined operations
- Enhanced security
- New business models
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the benefits of blockchain in manufacturing? Improved supply chain management, streamlined operations, enhanced security, new business models, and increased efficiency.
- How can blockchain improve supply chain management? By increasing transparency, improving traceability, reducing fraud, automating payments, and enhancing collaboration.
- What are the security benefits of blockchain in manufacturing? Secure data storage, prevention of data breaches, data immutability, increased transparency, and improved compliance.
- What are some new business models enabled by blockchain in manufacturing? Pay-per-use models, fractional ownership of assets, decentralized manufacturing networks, and tokenization of physical assets.
- How can blockchain improve efficiency in manufacturing? By automating processes, reducing the need for intermediaries, optimizing resource allocation, improving collaboration, and data-driven decision-making.
