Blockchain and Privacy: Enhancing Security in a Digital Age
As the digital landscape rapidly evolves, safeguarding privacy has become paramount. Blockchain technology, renowned for its immutability and transparency, offers a promising solution for enhancing security and protecting sensitive information.
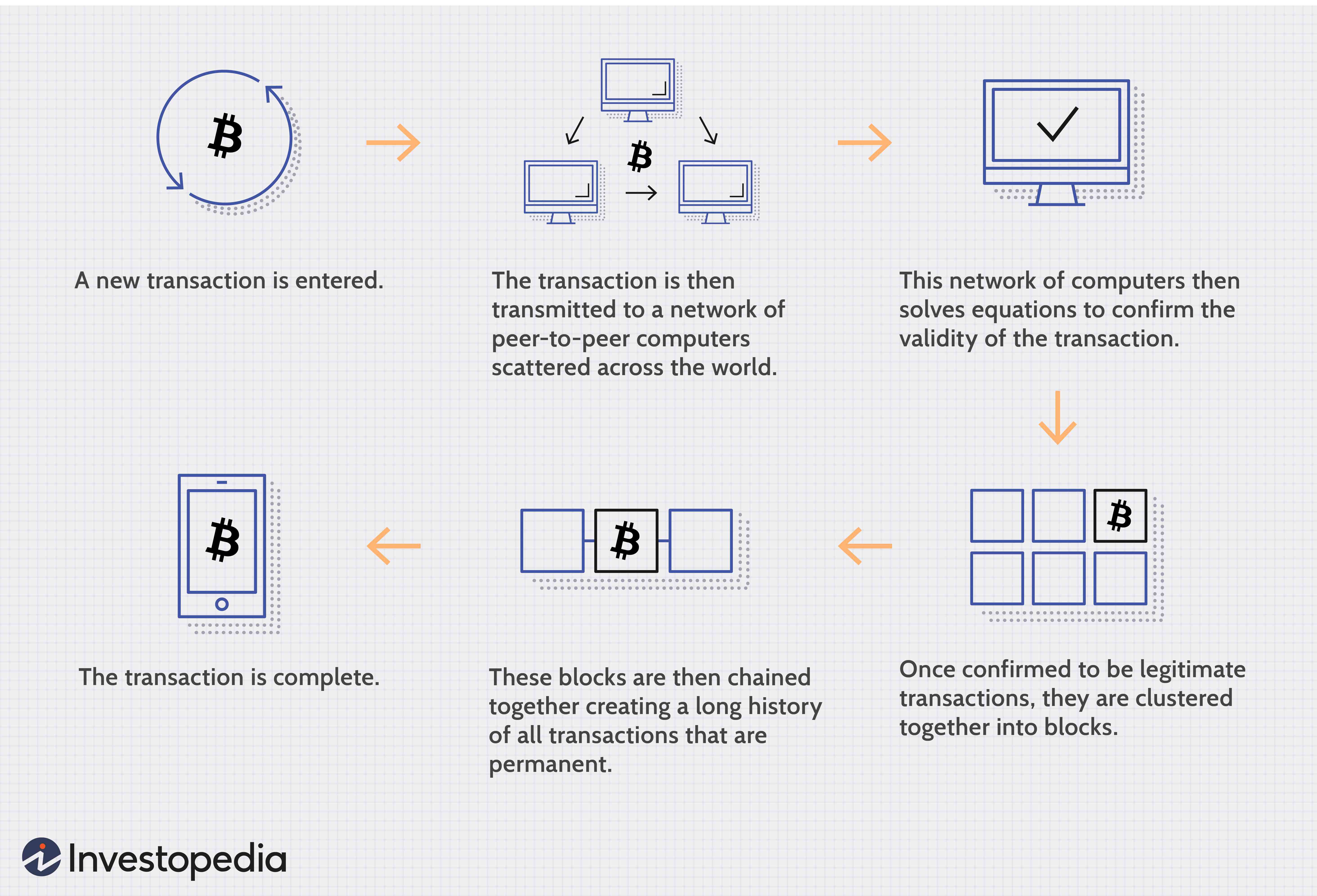
Blockchain, a distributed ledger system, securely records transactions in a chronological and tamper-proof manner. Each block in the chain contains a timestamp, transaction details, and a cryptographic hash of the previous block. This structure ensures that any attempt to alter past transactions would be easily detectable.

Privacy-Enhancing Features of Blockchain
Blockchain leverages several features to enhance privacy:
- Anonymity: Blockchain transactions can be conducted anonymously, allowing users to maintain their privacy without compromising security.
- Pseudonymity: Users can utilize pseudonyms to represent their identities, concealing their true names while enabling traceability.
- Cryptography: Blockchain employs advanced cryptographic techniques to encrypt data and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Decentralization: The distributed nature of blockchain eliminates central points of failure, reducing the risk of privacy breaches.
Applications in Privacy-Sensitive Domains
Blockchain finds applications in numerous privacy-sensitive domains:
- Healthcare: Securely storing and sharing medical records while safeguarding patient confidentiality.
- Finance: Protecting financial transactions, preventing fraud, and enhancing anti-money laundering measures.
- Supply Chain Management: Tracking the movement of goods throughout the supply chain, ensuring transparency and preventing counterfeiting.
- Voting: Facilitating secure and transparent elections, protecting against vote tampering and coercion.
- Identity Management: Creating secure and verifiable digital identities, reducing the risk of identity theft.
Challenges and Considerations
While blockchain offers significant privacy benefits, it poses certain challenges:
- Scalability: As blockchain networks grow in size, maintaining privacy while ensuring acceptable transaction speeds can be challenging.
- Cost: Implementing and maintaining blockchain solutions can be resource-intensive.
- Regulation: Balancing privacy with regulatory compliance remains an ongoing concern, requiring careful evaluation.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology presents a transformative opportunity to enhance privacy and security in the digital age. Its anonymity, pseudonymity, cryptography, and decentralization features make it a valuable tool for protecting sensitive information in various domains. However, ongoing research and development are essential to address scalability, cost, and regulatory challenges. By leveraging blockchain’s privacy-preserving capabilities, we can establish a more secure and trustworthy digital ecosystem that respects individual privacy rights.## Blockchain And Privacy: Enhancing Security In A Digital Age
Executive Summary
Blockchain technology, renowned for its immutability and decentralized nature, is rapidly transforming the digital landscape. Its potential to enhance privacy and bolster security in a world increasingly reliant on technology is a topic of growing interest. This article elucidates the symbiotic relationship between blockchain and privacy, exploring the transformative potential that blockchain holds in safeguarding our data and empowering individuals in the digital age.
Introduction
In the era of ubiquitous digitalization, safeguarding personal information has become a paramount concern. Technological advancements have led to an explosion of data collection, often without users’ explicit consent or full understanding of its potential implications. As a result, the need for robust privacy measures has never been more pressing. Blockchain technology emerges as a beacon of hope, offering a secure and transparent framework for managing and protecting sensitive data.
Key Components of Privacy in Blockchain
Data Privacy
- Encryption: Blockchain utilizes advanced cryptographic algorithms to ensure that data is encrypted and secure from unauthorized access.
- Pseudonymity: Transactions on blockchain networks are often linked to pseudonyms rather than real identities, providing anonymity while still allowing for accountability.
- Limited Data Exposure: Blockchains only record necessary information, reducing the risk of data breaches and identity theft.
Access Control
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing smart contracts govern access to data on a blockchain, ensuring that only authorized parties can view or modify information.
- Permissioned Blockchains: Access to certain blockchains can be restricted to specific individuals or entities, further enhancing data privacy.
- Decentralized Governance: Distributed ledger technology eliminates the need for centralized authorities, reducing the risk of data manipulation and misuse.
Auditability
- Immutable Ledger: Blockchain records are immutable, providing a secure and tamper-proof history of transactions and data changes.
- Transparency: Anyone can review and audit blockchain transactions, promoting transparency and accountability.
- Accountability: Blockchain allows for the tracking of data usage and access, enabling the identification of potential misuse.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize privacy in the digital age. By harnessing its decentralized, immutable, and cryptographically secure nature, blockchain can empower individuals with greater control over their personal data. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, it is expected to play an increasingly vital role in protecting our privacy and safeguarding our digital identities.
Keyword Tags
- Blockchain
- Privacy
- Data Security
- Data Privacy
- Decentralization
FAQs
- Can blockchain guarantee complete anonymity?
No, blockchain provides pseudonymity rather than complete anonymity. Transactions are linked to pseudonyms, but skilled investigators may be able to de-anonymize users. - How does blockchain prevent data hacking?
Blockchain’s distributed and encrypted nature makes it extremely difficult for hackers to access or modify data. Even if a hacker gains access to one node, the immutable record on multiple nodes ensures data integrity. - Can blockchain be used to track user behavior?
While blockchains can provide a transparent record of transactions, they do not inherently track user behavior. However, privacy-conscious blockchains with limited data exposure can mitigate this risk. - Is blockchain privacy only applicable to financial transactions?
No, blockchain privacy extends beyond financial transactions. It can be applied to any type of data that requires secure management, such as medical records, personal identification, and supply chain tracking. - What are the challenges to implementing blockchain for privacy?
Challenges include scalability limitations, the need for user education, and the development of interoperable blockchain platforms. However, research and innovation are actively addressing these challenges.
