Azure CDN and its Impact on Microsoft’s Cloud Computing Services
Azure Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a global network of servers that delivers content to end users with high performance and low latency. It caches content at the edge of the network, closer to users, so that it can be delivered quickly and efficiently.

Azure CDN has a number of benefits for Microsoft’s cloud computing services:
- Improved performance: Azure CDN can significantly improve the performance of websites and applications by caching content at the edge of the network. This reduces the amount of time it takes for content to be delivered to end users, resulting in a better user experience.
- Reduced latency: Azure CDN can also reduce latency, or the time it takes for content to be delivered to end users. This is especially important for applications that require real-time or near-real-time performance, such as gaming and video streaming.
- Increased scalability: Azure CDN can help Microsoft’s cloud computing services scale to meet the demands of a rapidly growing user base. By caching content at the edge of the network, Azure CDN can reduce the load on Microsoft’s servers, allowing them to handle more users and traffic.
- Improved security: Azure CDN can also help improve the security of Microsoft’s cloud computing services. By caching content at the edge of the network, Azure CDN can protect Microsoft’s servers from DDoS attacks and other malicious traffic.
Overall, Azure CDN has a number of benefits for Microsoft’s cloud computing services. It can improve performance, reduce latency, increase scalability, and improve security. As a result, Azure CDN is a valuable asset for Microsoft’s cloud computing business.
Specific Examples of How Azure CDN Impacts Microsoft’s Cloud Computing Services
Here are some specific examples of how Azure CDN impacts Microsoft’s cloud computing services:
- Azure Storage: Azure CDN can be used to cache Azure Storage objects, such as images, videos, and documents. This can significantly improve the performance of applications that access Azure Storage objects.
- Azure Virtual Machines: Azure CDN can be used to cache the content of Azure Virtual Machines. This can improve the performance of applications that are hosted on Azure Virtual Machines.
- Azure App Service: Azure CDN can be used to cache the content of Azure App Service web apps. This can improve the performance of web apps and reduce the load on Azure App Service servers.
- Microsoft 365: Azure CDN can be used to cache the content of Microsoft 365 applications, such as Office Online and SharePoint Online. This can improve the performance of Microsoft 365 applications and reduce the load on Microsoft 365 servers.
Conclusion
Azure CDN is a valuable asset for Microsoft’s cloud computing business. It can improve performance, reduce latency, increase scalability, and improve security. As a result, Azure CDN is used by a number of Microsoft’s cloud computing services, including Azure Storage, Azure Virtual Machines, Azure App Service, and Microsoft 365.## Azure CDN and Its Impact on Microsoft’s Cloud Computing Services
Executive Summary
Azure CDN, Microsoft’s Content Delivery Network, is a crucial component of the company’s cloud computing services. It enables faster and more reliable delivery of content to end-users, improving the user experience and driving business growth. This article explores the key benefits, features, and use cases of Azure CDN, demonstrating its significant impact on Microsoft’s cloud computing services.
Introduction
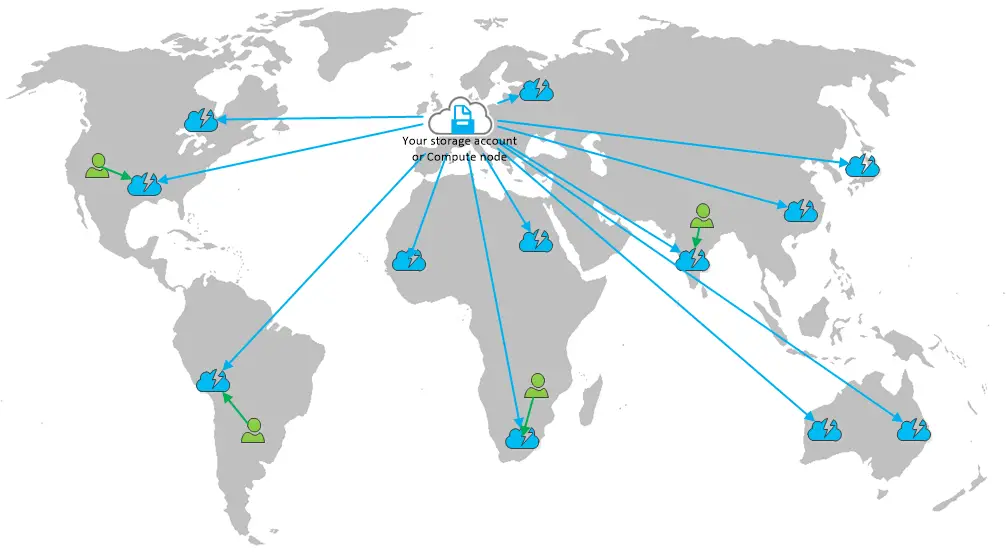
Content delivery networks (CDNs) play a vital role in modern web and cloud architectures. They cache content at strategically located edge servers, reducing latency and improving performance for users. Azure CDN, Microsoft’s CDN service, is deeply integrated with other Azure services, providing seamless content delivery across the globe.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the key benefits of using Azure CDN?
- Improved website performance and reduced latency
- Increased scalability and reliability
- Reduced bandwidth costs
- Enhanced security and compliance
Q: How does Azure CDN work?
Azure CDN caches content at edge locations close to end-users. When a user requests content, it is delivered from the nearest edge server, significantly reducing latency and improving performance.
Q: What types of content can be delivered through Azure CDN?
Azure CDN can deliver various types of content, including web pages, images, videos, audio files, and software updates. It supports popular protocols such as HTTP, HTTPS, and RTMP.
Key Subtopics
Performance Optimization
- Caching: Caches content at edge locations to reduce latency and improve performance.
- Traffic Management: Routes traffic to the most optimal edge servers based on factors such as location and network conditions.
- Compression: Compresses content to reduce file size and accelerate delivery.
- SSL Offloading: Handles SSL encryption at the CDN edge, reducing the load on origin servers.
Security and Compliance
- DDoS Protection: Protects against distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks by filtering and mitigating malicious traffic.
- Web Application Firewall (WAF): Blocks malicious traffic and protects web applications from attacks such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Data Encryption: Encrypts content at rest and in transit to ensure data privacy and compliance with regulations.
Scalability and Availability
- Global Presence: Deploys edge servers in over 100 locations worldwide, providing low-latency content delivery to a global audience.
- Load Balancing: Distributes traffic across multiple edge servers to handle high volumes of traffic during peak periods.
- Failover and Redundancy: Automatically fails over to backup servers in case of failure, ensuring continuous content delivery.
Integration and Management
- Seamless Integration: Tightly integrated with other Azure services, such as Azure Storage, Azure Virtual Machines, and Azure App Service.
- Centralized Management: Provides a central management portal for monitoring, configuring, and optimizing CDN performance.
- API and CLI Support: Enables programmatic access to CDN features through APIs and command-line tools.
Cost Optimization
- Pay-as-you-go Pricing: Offers flexible pricing options, allowing customers to pay only for the resources they use.
- Origin Offloading: Reduces bandwidth costs on origin servers by caching content on edge servers.
- Traffic Management: Optimizes traffic flow and routing to minimize data transfer costs.
Conclusion
Azure CDN is a powerful and comprehensive CDN service that significantly enhances the performance, security, and scalability of Microsoft’s cloud computing services. By caching content at strategically located edge servers, Azure CDN reduces latency, improves website performance, and ensures a seamless user experience for customers worldwide. Its integration with other Azure services and rich feature set make it an indispensable tool for businesses looking to optimize their web and cloud applications.
Keyword Tags
- Azure CDN
- Microsoft Cloud Computing
- Content Delivery Network
- Website Performance Optimization
- Security and Compliance

