Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
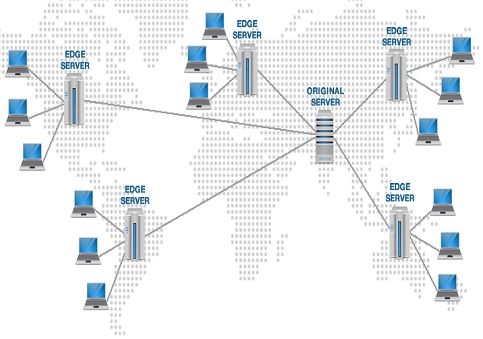
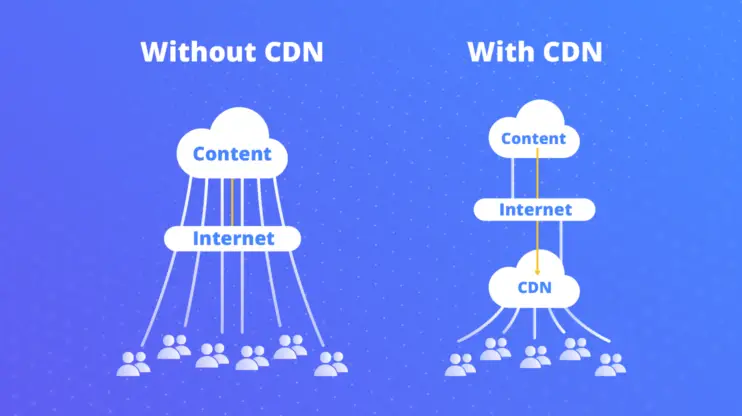
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are distributed networks of servers located in various locations around the world. They improve the delivery of content to end-users by caching and serving content closer to their geographic location.
Benefits of CDNs
- Increased reach and availability: CDNs have a global presence, enabling content to reach users in different countries and regions.
- Improved performance: By serving content from servers closer to users, CDNs reduce latency and improve page loading times.
- Reduced bandwidth costs: CDNs cache content, reducing the amount of data that needs to be transferred from the origin server, lowering bandwidth expenses.
- Improved security: CDNs provide DDoS protection and other security measures to prevent content tampering or distribution disruptions.
How CDNs Work
- Content origination: Content is uploaded to a CDN’s origin server, which is the primary source of the content.
- Caching: The CDN caches copies of the content on its network of servers located in different geographic regions.
- Content retrieval: When a user requests content from a website, the CDN determines the nearest server that has the cached version of the content.
- Content delivery: The content is streamed directly to the user’s device from the nearest CDN server, reducing latency and improving performance.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a CDN
- Network presence: Ensure the CDN has a presence in the regions where your target audience is located.
- Performance: Test the CDN’s latency and throughput to ensure it meets your performance expectations.
- Security: Choose a CDN that provides robust security measures to protect your content from unauthorized access or distribution.
- Cost: Compare the cost of different CDNs and select one that fits within your budget.
- Support: Look for a CDN provider with reliable support and technical expertise to assist you with any issues.
Conclusion
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are essential tools for enterprises seeking to achieve global reach and deliver content seamlessly to end-users worldwide. By caching content on a distributed network of servers, CDNs improve performance, reduce latency, and ensure the accessibility of content regardless of the user’s location. Businesses that leverage CDNs can enhance their online presence, improve customer satisfaction, and drive business growth.## Achieving Global Reach With Content Delivery Networks
Executive Summary
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) play a crucial role in ensuring the seamless delivery of online content to users worldwide. This article delves into the world of CDNs, exploring their key components, benefits, and best practices for effective implementation. By leveraging the power of CDNs, businesses can unlock global reach, enhance user experience, and optimize website performance.
Introduction
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, the ability to deliver online content quickly and reliably is paramount. With users dispersed across the globe, traditional web hosting solutions often struggle to provide consistent performance and availability. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) emerge as the solution to this challenge, enabling businesses to extend their reach and ensure a seamless user experience regardless of location.
FAQ
- What is a Content Delivery Network (CDN)?
A CDN is a distributed network of servers strategically positioned in data centers around the world. It stores and caches frequently accessed content, such as website files, images, and videos, closer to users. When a user requests content from a CDN-enabled website, the request is routed to the nearest server, significantly reducing latency and improving download speeds.
- Why Use a CDN?
CDNs offer a range of benefits, including:
* **Global Reach:** Expand your website's reach to users worldwide by caching content in multiple locations.
* **Improved User Experience:** Reduce page load times and enhance overall user satisfaction by delivering content faster.
* **Website Performance Optimization:** Free up your origin server by offloading static content to CDNs, improving website performance and scalability.
* **Enhanced Security:** Protect your website from malicious attacks by leveraging CDNs' security features, such as DDoS mitigation and SSL encryption.
* **Cost Savings:** Reduce bandwidth costs by caching content closer to users, potentially saving on infrastructure expenses.- How Do CDNs Work?
CDNs operate on a simple yet effective principle:
* **Caching:** CDNs store frequently accessed content on multiple servers.
* **Content Delivery:** When a user requests content, the CDN routes the request to the server closest to the user's location.
* **Optimized Delivery:** The CDN delivers the content using protocols optimized for fast and efficient transfer.Key Components of a CDN
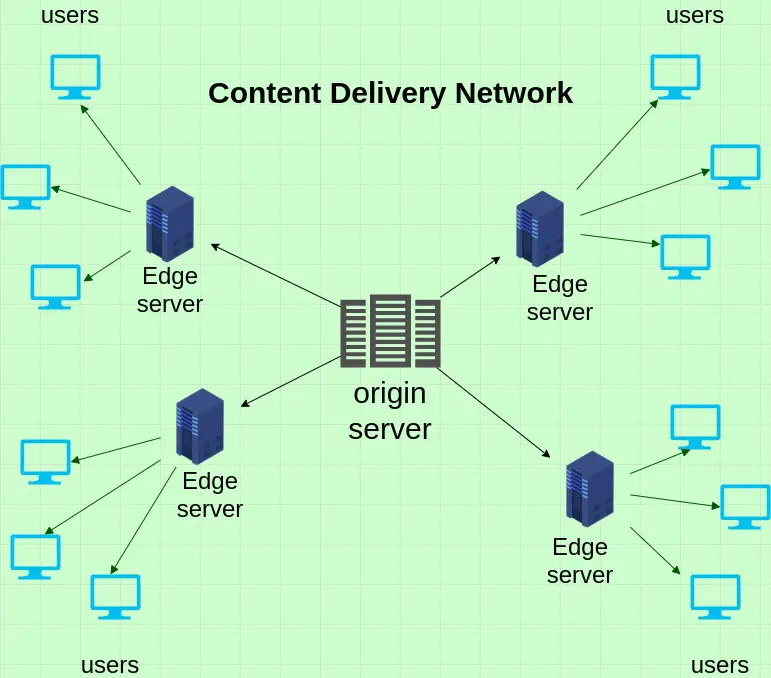
- Origin Server: The server that hosts the original content, such as your website’s files.
- PoPs (Points of Presence): Strategically located data centers around the world where CDN servers are deployed.
- Edge Servers: Servers within PoPs that store and deliver cached content to users.
- Caching Mechanisms: Algorithms and protocols used to store and manage cached content effectively.
Benefits of Using a CDN
- Reduced Latency: Deliver content faster to users by caching it closer to their location.
- Improved Page Load Times: Faster content delivery leads to quicker page load times, enhancing user experience.
- Increased Website Availability: CDNs mitigate downtime risks by distributing content across multiple locations, ensuring high availability.
- Enhanced Scalability: CDNs can handle high traffic volumes by automatically scaling their resources to meet demand.
- Improved Security: CDNs provide enhanced security features, such as DDoS protection and SSL encryption, to safeguard your website from threats.
Best Practices for CDN Implementation
- Choose the Right CDN Provider: Select a CDN provider that aligns with your performance, security, and support requirements.
- Configure Caching Rules: Optimize caching settings to ensure efficient delivery of your content.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor CDN performance metrics to identify any potential issues or areas for optimization.
- Integrate with Your Website: Ensure seamless integration between the CDN and your website to avoid any disruptions.
- Leverage CDN Features: Explore and utilize advanced CDN features, such as geo-blocking and load balancing, to enhance content delivery.
Conclusion
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are indispensable tools for businesses seeking to extend their global reach and provide an unparalleled user experience. By leveraging the power of CDNs, businesses can optimize website performance, improve security, and reduce costs while delivering content seamlessly to users worldwide. Implementing a CDN effectively can unlock significant benefits and drive business growth in today’s competitive online landscape.
Keyword Tags
- Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Content Delivery
- Website Performance
- Global Reach
- User Experience Optimization
